Abstract
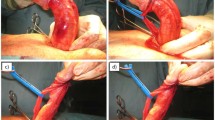
Severe Peyronie’s disease (PD) and concomitant erectile dysfunction (ED) may require plaque incision/excision and grafting (PIG) as an adjunct to penile prosthesis implantation (IPP). Currently, there is no available consensus on the best graft material to use. Our aim was to systematically review graft materials used as patches following PIG + IPP. Literature search was performed in March 2021. Only original articles in English with a series of 10 or more patients were included. Overall, a total of 17 studies were included, corresponding to a cohort of 662 patients. The mean age ranged from 45 to 65 years and most patients had curvatures >45°. Average penile lengthening ranged from 1 to 3.5 cm, average residual curvatures from 0 to 20% and decreased glans sensitivity from 0 to 20%. Eighty to 100% of patients were satisfied with cosmetic and functional results. PIG + IPP with the use of various grafts offers promising results for the treatment of patients suffering from severe PD with concomitant ED. Unfortunately, the absence of high quality and comparative studies makes it difficult to establish the optimum graft. Therefore, the level of experience of the surgical team with one or more methods should guide their choice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ralph D, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Mirone V, Perovic S, Sohn M, Usta M, et al. The Management of Peyronie’s Disease: Evidence-based 2010 Guidelines. J Sex Med. 2010;7:2359–74.
Chung E, Gillman M, Rushton D, Love C, Katz D. Prevalence of penile curvature: a population-based cross-sectional study in metropolitan and rural cities in Australia. BJU Int. 2018;122:42–9.
Schwarzer U, Sommer F, Klotz T, Braun M, Reifenrath B, Engelmann U. The prevalence of Peyronie’s disease: results of a large survey. BJU Int. 2001;88:727–30.
Sommer F, Schwarzer U, Wassmer G, Bloch W, Braun M, Klotz T, et al. Epidemiology of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:379–83.
Segundo A, Glina S. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Erectile Dysfunction Associated With Peyronie’s Disease Among Men Seeking Urological Care. Sex Med. 2020;8:230–6.
Nelson CJ, Diblasio C, Kendirci M, Hellstrom W, Guhring P, Mulhall JP. The chronology of depression and distress in men with Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1985–90. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18554257/.
Smith JF, Walsh TJ, Conti SL, Turek P, Lue T. Risk factors for emotional and relationship problems in Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2179–84.
Rosen R, Catania J, Lue T, Althof S, Henne J, Hellstrom W, et al. Impact of Peyronie’s disease on sexual and psychosocial functioning: qualitative findings in patients and controls. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1977–84. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18564146/.
Chung E, Ralph D, Kagioglu A, Garaffa G, Shamsodini A, Bivalacqua T, et al. Evidence-based management guidelines on Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2016;13:905–23.
Mulhall J, Anderson M, Parker M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: Functional and satisfaction outcomes. J Sex Med. 2005;2:132–8.
Wilson SK. Surgical techniques: modeling technique for penile curvature. J Sex Med. 2007;4:231–4.
Chung PH, Scott JF, Morey AF. High patient satisfaction of inflatable penile prosthesis insertion with synchronous penile plication for erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1593–8.
Garaffa G, Minervini A, Christopher NA, Minhas S, Ralph DJ. The management of residual curvature after penile prosthesis implantation in men with Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2011;108:1152–6.
Djordjevic ML, Kojovic V. Penile prosthesis implantation and tunica albuginea incision without grafting in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease with erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:391–4.
Garcia-Gomez B, Ralph D, Levine L, Moncada-Iribarren I, Djinovic R, Albersen M, et al. Grafts for Peyronie’s disease: a comprehensive review. Andrology. 2018;6:117–26.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097 https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
Lue TF, EL-Sakka AI. Venous patch graft for Peyronie’s disease. Part I. J Urol. 1998;160:2047–9. http://gateway.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=crossref&AN=00005392-199812010-00029.
EL-Sakka AI, Rashwan HM, Lue TF Venous patch graft for Peyronie’s disease. Part II. J Urol. 1998;2050–3. http://gateway.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=crossref&AN=00005392-199812010-00030.
Montorsi F, Salonia A, Maga T, Bua L, Guazzoni G, Barbieri L, et al. Evidence based assessment of long-term results of plaque incision and vein grafting for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2000;163:1704–8.
Austoni E, Colombo F, Romanò AL, Guarneri A, Goumas IK, Cazzaniga A. Soft prosthesis implant and relaxing albugineal incision with saphenous grafting for surgical therapy of Peyronie’s disease: A 5-year experience and long-term follow-up on 145 operated patients. Eur Urol. 2005;47:223–9.
Silvani M, Pecoraro S, Zucchi A. Corporoplasty for induratio penis plastica with soft axial tutors, single relaxing albugineal incision and safenous grafting. A 3-year follow up. Arch Ital di Urol Androl organo Uff [di] Soc Ital di Ecogr Urol e Nefrol. 2012;84:84–8.
Craatz S, Spanel-Borowski K, Begemann JF, Olianas R, Fisch M, Hohenfellner R. The dorsal lamina of the rectus sheath: A suitable grafting material for the penile tunica albuginea in Peyronie’s disease? BJU Int. 2006;97:134–7.
Kadioglu A, Sanli O, Akman T, Cakan M, Erol B, Mamadov F. Surgical Treatment of Peyronie’s Disease: A Single Center Experience with 145 Patients. Eur Urol. 2008;53:432–40. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17467161/.
Pathak AS, Chang JH, Parekh AR, Aboseif SR. Use of rectus fascia graft for corporeal reconstruction during placement of penile implant. Urology. 2005;65:1198–201.
Perovic SV, Djinovic RP. Current surgical management of severe Peyronie’s disease. Arch Esp Urol. 2010;63:755–70.
Konstantinovic ML, Ozog Y, Spelzini F, Pottier C, De Ridder D, Deprest J. Biomechanical findings in rats undergoing fascial reconstruction with graft materials suggested as an alternative to polypropylene. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29:488–93.
Ozog Y, Konstantinovic M, Zheng F, Spelzini F, Verbist G, Luyten C, et al. Porous acellular porcine dermal collagen implants to repair fascial defects in a rat model: biomechanical evaluation up to 180 days. Gynecol Obstet Investig. 2009;68:205–12.
Winters JC. InteXen tissue processing and laboratory study. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2006;17:S34–8.
Sansalone S, Garaffa G, Djinovic R, Egydio P, Vespasiani G, Miano R, et al. Simultaneous penile lengthening and penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease, refractory erectile dysfunction, and severe penile shortening. J Sex Med. 2012;9:316–21.
Althof SE, Corty EW, Levine SB, Levine F, Burnett AL, McVary K, et al. EDITS: development of questionnaires for evaluating satisfaction with treatments for erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1999;53:793–9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10197859.
Levine LA, Estrada CR. Human cadaveric pericardial graft for the surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2003;170:2359–62.
Usta MF, Bivalacqua TJ, Sanabria J, Koksal IT, Moparty K, Hellstrom WJG. Patient and partner satisfaction and long-term results after surgical treatment for Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 2003;62:105–9.
Otero JR, Gómez BG, Polo JM, Mateo CP, Barreras SG, Cruz EG, et al. Use of a lyophilized bovine pericardium graft to repair tunical defect in patients with Peyronie’s disease: Experience in a clinical setting. Asian J Androl. 2017;19:316–20. https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.pros.lib.unimi.it/26806077/.
Farrell MR, Abdelsayed GA, Ziegelmann MJ, Levine LA. A Comparison of Hemostatic Patches Versus Pericardium Allograft for the Treatment of Complex Peyronie’s Disease With Penile Prosthesis and Plaque Incision. Urology 2019;129:113–8.
Zucchi A, Silvani M, Pecoraro S. Corporoplasty with small soft axial prostheses (VIRILIS I®) and bovine pericardial graft (HYDRIX®) in Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:275–9.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Sansalone S. Penile length and girth restoration in severe Peyronie’s disease using circular and longitudinal grafting. BJU Int. 2013;111:E213–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11582.x.
Egydio PH, Sansalone S. Peyronie’s Reconstruction for Maximum Length and Girth Gain: Geometrical Principles. Adv Urol. 2008;2008.
Clavell-Hernández J, Wang R. Penile Size Restoration With Nondegloving Approach for Peyronie’s Disease: Initial Experience. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1506–13.
Cocci A, Ralph D, Djinovic R, Hatzichristodoulou G, Morelli G, Salonia A, et al. Surgical outcomes after collagenase Clostridium histolyticum failure in patients with Peyronie’s disease in a multicenter clinical study. Sci Rep. 2021;11:166.
Voytik-Harbin SL, Brightman AO, Kraine MR, Waisner B, Badylak SF. Identification of extractable growth factors from small intestinal submucosa. J Cell Biochem. 1997;67:478–91. https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.pros.lib.unimi.it/doi/full/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-4644%2819971215%2967%3A4%3C478%3A%3AAID-JCB6%3E3.0.CO%3B2-P.
Knoll LD. Use of Small Intestinal Submucosa Graft for the Surgical Management of Peyronie’s Disease. J Urol. 2007;178:2474–8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17976656/.
Rolle L, Falcone M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Sedigh O, Ralph DJ, et al. A prospective multicentric international study on the surgical outcomes and patients’ satisfaction rates of the ‘sliding’ technique for end-stage Peyronie’s disease with severe shortening of the penis and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2016;117:814–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13371.
Rolle L, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Sedigh O, Destefanis P, Galletto E, et al. A New, Innovative, Lengthening Surgical Procedure for Peyronie’s Disease by Penile Prosthesis Implantation with Double Dorsal-Ventral Patch Graft: The “Sliding Technique”. J Sex Med. 2012;9:2389–95. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22429331/.
Falcone M, Preto M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Garaffa G, Sedigh O, et al. A Comparative Study Between 2 Different Grafts Used as Patches After Plaque Incision and Inflatable Penile Prosthesis Implantation for End-Stage Peyronie’s Disease. J Sex Med. 2018;15:848–52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29753801/.
Hatzichristodoulou G. Partial Plaque Excision and Grafting With Collagen Fleece in Peyronie Disease. J Sexual Med. 2016;13:277–81. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26953837/.
Hatzichristodoulou G. The PICS Technique: A Novel Approach for Residual Curvature Correction During Penile Prosthesis Implantation in Patients With Severe Peyronie’s Disease Using the Collagen Fleece TachoSil. J Sex Med. 2018;15:416–21.
Hatzichristodoulou G, Yang DY, Ring JD, Hebert KJ, Ziegelman MJ, Köhler TS. Multicenter Experience Using Collagen Fleece for Plaque Incision With Grafting to Correct Residual Curvature at the Time of Inflatable Penile Prosthesis Placement in Patients With Peyronie’s Disease. J Sex Med. 2020. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32198103/.
Fernández-Pascual E, Gonzalez-García FJ, Rodríguez-Monsalve M, Turo J, Martínez-Ballesteros C, Carballido J, et al. Surgical Technique for Complex Cases of Peyronie’s Disease With Implantation of Penile Prosthesis, Multiple Corporeal Incisions, and Grafting With Collagen Fleece. J Sex Med. 2019;16:323–32. http://www.jsm.jsexmed.org/article/S1743609518313857/fulltext.
Chierigo F, Capogrosso P, Dehò F, Pozzi E, Schifano N, Belladelli F, et al. Long-Term Follow-Up After Penile Prosthesis Implantation—Survival and Quality of Life Outcomes. J Sex Med. 2019;16:1827–33. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31501062/.
Deveci S, Martin D, Parker M, Mulhall JP. Penile Length Alterations Following Penile Prosthesis Surgery. Eur Urol. 2007;51:1128–31.
Kueronya V, Miernik A, Stupar S, Kojovic V, Hatzichristodoulou G, Egydio PH, et al. International multicentre psychometric evaluation of patient-reported outcome data for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2015;115:822–8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25327685/.
Khera M, Bella A, Karpman E, Brant W, Christine B, Kansas B, et al. Penile Prosthesis Implantation in Patients With Peyronie’s Disease: Results of the PROPPER Study Demonstrates a Decrease in Patient-Reported Depression. J Sex Med. 2018;15:786–8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29653913.
Hellstrom WJG, Feldman R, Rosen RC, Smith T, Kaufman G, Tursi J. Bother and distress associated with Peyronie’s disease: Validation of the Peyronie’s disease questionnaire. J Urol. 2013;190:627–34.
Caraceni E, Utizi L. A Questionnaire for the Evaluation of Quality of Life after Penile Prosthesis Implant: Quality of Life and Sexuality with Penile Prosthesis (QoLSPP). J Sex Med. 2014;11:1005–12. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548771.
Acknowledgements
This project is endorsed by the European Association of Urology Research Foundation. FC, MD is supported by The Margaret Spittle Research Fellowship, University College London Hospital, London UK. AM is supported by the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre University College London Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
FCh—conception and design, data acquisition, drafting and revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, CB—revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, FC-J—data acquisition, revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, FC—conception and design, data acquisition, revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, LAK—revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, CT—revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version, AM—revision of the manuscript, approval of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chierigo, F., Bettocchi, C., Campos-Juanatey, F. et al. Use of grafting materials during penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease—a systematic review. Int J Impot Res 34, 534–542 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-021-00479-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-021-00479-8