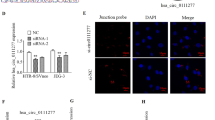
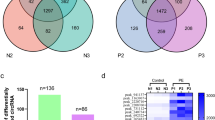
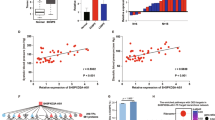
Abstract
Preeclampsia (PE) is a multiple organ and system disease that seriously threatens the safety of the mother and infant during pregnancy, and has a profound impact on the morbidity and mortality of the mother and new babies. Presently, there are no remedies for cure of PE as to the mechanisms of PE are still unclear, and the only way to eliminate the symptoms is to deliver the placenta. Thus, new therapeutic targets for PE are urgently needed. Approximately 95% of human transcripts are thought to be non-coding RNAs, and the roles of them are to be increasingly recognized of great importance in various biological processes. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs, with no 5′ caps and 3′ polyadenylated tails, commonly produced by back-splicing of exons. The structure of circRNAs makes them more stable than their counterparts. Increasing evidence shows that circRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of PE, but the biogenesis, functions, and mechanisms of circRNAs in PE are poorly understood. In the present review, we mainly summarize the biogenesis, functions, and possible mechanisms of circRNAs in the development and progression of PE, as well as opportunities and challenges in the treatment and prevention of PE.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Espinoza J, Vidaeff A, Pettker CM, Simhan H. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e1–e25.
Homer CS, Brown MA, Mangos G, Davis GK. Nonproteinuric pre-eclampsia: a novel risk indicator in women with gestational hypertension. J Hypertens. 2008;26:295–302.
Poon LC, Shennan A, Hyett JA, Kapur A, Hadar E, Divakar H, et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on pre-eclampsia: a pragmatic guide for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2019;145:1–33.
Amaral L, Cunningham MW Jr, Cornelius DC, Lamarca B. Preeclampsia: long-term consequences for vascular health. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015;11:403–15.
Kumari P, Sampath K. cncRNAs: Bi-functional RNAs with protein coding and non-coding functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;47-48:40–51.
Vo JN, Cieslik M, Zhang YJ, Shukla S, Xiao LB, Zhang YP, et al. The landscape of circular RNA in cancer. Cell. 2019;176:869–81.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013;495:333–38.
Suzuki H, Tsukahara T. A view of pre-mRNA splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:9331–42.
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1976;73:3852–56.
Kos A, Dijkema R, Arnberg AC, van der Meide PH, Schellekens H. The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature. 1986;323:558–60.
Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, Oliner JD, et al. Scrambled exons. Cell 1991;64:607–13.
Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, et al. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell. 1993;73:1019–30.
Cocquerelle C, Daubersies P, Majerus MA, Kerckaert JP, Bailleul B. Splicing with inverted order of exons occurs proximal to large introns. EMBO J. 1992;11:1095–98.
Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hetuin D, Bailleul B. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993;7:155–60.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu JZ, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–57.
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu XH, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159:134–47.
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, Bartel DP. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15:409.
Westholm JO, Miura P, Olson S, Shenker S, Joseph B, Sanfilippo P, et al. Genome-wide analysis of Drosophila circular RNAs reveals their structural and sequence properties and age-dependent neural accumulation. Cell Rep. 2014;9:1966–80.
Ivanov A, Memczak S, Wyler E, Torti F, Porath HT, Orejuela MR, et al. Analysis of intron sequences reveals hallmarks of circular RNA biogenesis in animals. Cell Rep. 2015;10:170–77.
Zhang YS, Zhu M, Zhang X, Dai K, Liang Z, Pan J, et al. Micropeptide vsp21 translated by Reovirus circular RNA 000048 attenuates viral replication. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;209:1179–87.
Zhu M, Liang Z, Pan J, Zhang X, Xue RY, Cao GL, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma progression mediated by hepatitis B virus-encoded circRNA HBV_circ_1 through interaction with CDK1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;25:668–82.
Zhang YM, Zhao YY, Yu FF, Li X, Chen XH, Zhu D, et al. CircRNA_06354 might promote early-onset preeclampsia in humans via hsa-miR-92a-3p/vascular endothelial growth factor-A. J Hypertens. 2023;41:494–507.
Zhang YG, Yang HL, Long Y, Li WL. Cicular RNA in blood corpuscles combined with plasmaprotein factor for early pr-ediction of pre-eclampsia. BJOG. 2016;123:2113–18.
Qian YT, Lu YQ, Rui C, Qian YJ, Cai MH, Jia RZ. Potential significance of circular RNA in human placental tissue for patients with preeclampsia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39:1380–90.
Hu XP, Ao JP, Li XY, Zhang HJ, Wu J, Cheng W. Competing endogenous RNA expression profiling in pre-eclampsia identifies hsa_circ_0036877 as a potential novel blood biomarker for early pre-eclampsia. Clin Epigenetics. 2018;10:48.
Ma B, Zhao HQ, Gong LL, Xiao XR, Zhou QJ, Lu HQ, et al. Differentially expressed circular RNAs and the competing endogenous RNA network associated with preeclampsia. Placenta. 2021;103:232–41.
Li XP, Yang R, Xu Y, Zhang YS. Circ_0001438 participates in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia via the circ_0001438/miR-942/NLRP3 regulatory network. Placenta. 2021;104:40–50.
Gao X, Qu HN, Zhang Y. Circ_0001326 suppresses trophoblast cell proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in preeclampsia by miR-188-3p/HtrA serine peptidase 1 axis. J Hypertens. 2023;41:587–96.
Hu XM, Xia WL. Circ_0005714/miR-223-3p/ADAM9 regulatory axis affects proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiopoiesis in trophoblast cells. Autoimmunity. 2022;55:640–49.
Zhou FM, Liu HX, Zhang RR, Sun YL. Circ_0007121 facilitates trophoblastic cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via the regulation of the miR-421/ZEB1 axis in preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2022;29:100–09.
Ren JL, Cai J. Circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia. Open Med (Wars). 2023;18:20230645.
Hu ZY, Dong CM, Dong Q. Circ_0015382 is associated with preeclampsia and regulates biological behaviors of trophoblast cells through miR-149-5p/TFPI2 axis. Placenta. 2021;108:73–80.
Li W, Yu N, Fan L, Chen SH, Wu JL. Circ_0063517 acts as ceRNA, targeting the miR-31-5p-ETBR axis to regulate angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells in preeclampsia. Life Sci. 2020;244:117306.
Zhang LP, Liu MX. Circ_0077109 sponges miR-139-5p and upregulates HOXD10 in trophoblast cells as potential mechanism for preeclampsia progression. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2022;88:e13609.
Zhu HL, Niu X, Li QH, Zhao YH, Chen X, Sun HS. Circ_0085296 suppresses trophoblast cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via modulating miR-144/E-cadherin axis. Placenta. 2020;97:18–25.
Zhang SQ, Guo GX. Circ_FURIN promotes trophoblast cell proliferation, migration and invasion in preeclampsia by regulating miR-34a-5p and TFAP2A. Hypertens Res. 2022;45:1334–44.
Zou H, Mao QH. Circ_0037078 promotes trophoblast cell proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis by miR-576-5p/IL1RAP axis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2022;87:e13507.
Liu JY, Yang Y, Liu WL, Lan RL. circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network. Open Med (Wars). 2022;17:577–88.
Zhang YG, Yang HL, Zhang YP, Shi JZ, Chen RG. CircCRAMP1L is a novel biomarker of preeclampsia risk and may play a role in preeclampsia pathogenesis via regulation of the MSP/RON axis in trophoblasts. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:652.
Li K, Lv CY, Zhang WC, Fang J. CircFN1 upregulation initiated oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation and migration in trophoblasts via circFN1-miR-19a/b-3p-ATF2 ceRNA network. Reprod Biol. 2022;22:100631.
Wang WX, Liu JY, Pan E. CircHIPK3 contributes to human villous trophoblast growth, migration and invasion via modulating the pathway of miR-346/KCMF1. Placenta. 2022;118:46–54.
Zhang Y, Cao L, Jia J, Ye L, Wang Y, Zhou B, et al. CircHIPK3 is decreased in preeclampsia and affects migration, invasion, proliferation, and tube formation of human trophoblast cells. Placenta. 2019;85:1–8.
Li Y, Chen JZ, Song SQ. Circ-OPHN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells through mediating miR-558/THBS2 axis. Drug Dev Res. 2022;83:1034–46.
Li J, Han JY, Zhao AM, Zhang GX. CircPAPPA regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and cell cycle of trophoblast cells through the mir-3127-5p/hoxa7 axis. Reprod Sci. 2022;29:1215–25.
Wu SY, Liu LY, Tao T, Xiao JY, Yang HZ, Yu XS, et al. circPTK2 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells through the miR-619/WNT7B pathway in preeclampsia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478:2621–7.
Xu XH, Teng H. CircRNA circ_0055724 inhibits trophoblastic cell line htr-8/svneo’s invasive and migratory abilities via the miR-136/N-Cadherin axis. Dis Markers. 2022;2022:9390731.
Zhang YG, Yang HL, Long Y, Zhang YP, Chen RG, Shi JZ, et al. CircRNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in preeclampsia and the potential role of N6-methyladenosine-modified circPAPPA2 in trophoblast invasion. Sci Rep. 2021;11:24357.
Wang D, Guan HB, Wang Y, Song GY, Xia YJ. N6-methyladenosine modification in trophoblasts promotes circSETD2 expression, inhibits miR-181a-5p, and elevates MCL1 transcription to reduce apoptosis of trophoblasts. Environ Toxicol. 2023;38:422–35.
Zhang YG, Yang HL, Zhang YP, Shi JZ, Chen RG, Xiao XQ. CircSFXN1 regulates the behaviour of trophoblasts and likely mediates preeclampsia. Placenta. 2020;101:115–23.
Dai W, Liu XH. Circular RNA 0004904 promotes autophagy and regulates the fused in sarcoma/vascular endothelial growth factor axis in preeclampsia. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47:111.
Mao QH, Zou H. Circular RNA circ_0032962 promotes trophoblast cell progression as ceRNA to target PBX3 via sponging miR-326 in preeclampsia. Reprod Biol. 2021;21:100571.
Ou YH, Zhu LQ, Wei XC, Bai SY, Chen MQ, Chen H, et al. Circular RNA circ_0111277 attenuates human trophoblast cell invasion and migration by regulating miR-494/HTRA1/Notch-1 signal pathway in pre-eclampsia. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:479.
Li CH, Li Q. Circular RNA circ_0111277 serves as ceRNA, targeting the miR-424-5p/NFAT5 axis to regulate the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2022;29:923–35.
Gai SK, Sun L, Wang HY, Yang P. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia. Open Med (Wars). 2020;15:1061–71.
Shan L, Hou XF. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0026552 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells via the miR-331-3p/TGF-βR1 axis in pre-eclampsia. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24:798.
Li ZW, Zhou XY, Gao WY, Sun MN, Chen HY, Meng T. Circular RNA VRK1 facilitates pre-eclampsia progression via sponging miR-221-3P to regulate PTEN/Akt. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26:1826–41.
Su S, Yang F, Zhong LL, Pang LH. Circulating noncoding RNAs as early predictive biomarkers in preeclampsia: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021;19:177.
Qi TT, Zhang D, Shi XT, Li MH, Xu HB. Decreased circUBAP2 expression is associated with preeclampsia by limiting trophoblast cell proliferation and migration. Reprod Sci. 2021;28:2237–45.
Cao MK, Wen J, Bu CZ, Li CY, Lin Y, Zhang H, et al. Differential circular RNA expression profiles in umbilical cord blood exosomes from preeclampsia patients. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21:303.
Zhou WB, Wang HY, Yang JY, Long W, Zhang B, Liu JB, et al. Down-regulated circPAPPA suppresses the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells via the miR-384/STAT3 pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39:BSR20191965.
Shi YB, Zhang LX, Wang LL, Ding HQ. Downregulation of Circ_0088196 contributes to the development of trophoblastic cells through mir-133b sponging function to affect the AHNAK expression. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2022;87:305–15.
Song MY, Xu P, Wang L, Liu J, Hou XF. Hsa_circ_0001326 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells via miR-145-5p/TGFB2 axis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2023;89:e13682.
Zhang YY, Fang S, Wang JY, Chen SQ, Xuan RR. Hsa_circ_0008726 regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia through modulating the miR-1290-LHX6 signaling pathway. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022;36:e24540.
Shi FL, Li L. Hsa_circ_0088196 suppresses trophoblast migration and invasion by the miR-525-5p/ABL1 axis and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022;36:e23150.
Liu Y, Ma XM, Liu YY. Hsa_circ_0001326 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of HTR-8/SVneo cells via increasing IL16 expression. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021;86:e13484.
Wang WZ, Shi JY, Zheng L. Identification of circular rna circ_0017068 as a regulator of proliferation and apoptosis in trophoblast cells by miR-330-5p/XIAP axis. Reprod Sci. 2022;29:2414–27.
Shang J, Lin L, Huang XM, Zhou LH, Huang Q. Re-expression of circ_0043610 contributes to trophoblast dysfunction through the miR-558/RYBP pathway in preeclampsia. Endocr J. 2022;69:1373–85.
Shu C, Xu P, Han J, Han SM, He J. Upregulation of circRNA hsa_circ_0008726 in pre-eclampsia inhibits trophoblast migration, invasion, and EMT by regulating miR-345-3p/rybp axis. Reprod Sci. 2022;29:2829–41.
Chen LL. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:205–11.
Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA. 2014;20:1829–42.
Wilusz JE. A 360 view of circular RNAs: From biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018;9:e1478.
Aufiero S, van den Hoogenhof MMG, Reckman YJ, Beqqali A, van der Made I, Kluin J, et al. Cardiac circRNAs arise mainly from constitutive exons rather than alternatively spliced exons. RNA. 2018;24:815–27.
Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xaing JF, Yin QF, Xing YH, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51:792–806.
Li ZY, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang XL, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22:256–64.
Li MD, Cui LY, Zhang JP, Wang SC, Du MR. The critical roles of circular RNAs in basic research and clinical application of female reproductive-related diseases. Reprod Sci. 2023;30:1421–34.
Kramer MC, Liang DM, Tatomer DC, Gold B, March ZM, Cherry S, et al. Combinatorial control of Drosophila circular RNA expression by intronic repeats, hnRNPs, and SR proteins. Genes Dev. 2015;29:2168–82.
Liang D, Wilusz JE. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014;28:2233–47.
Barrett SP, Wang PL, Salzman J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. eLife. 2015;4:e07540.
Kelly S, Greenman C, Cook PR, Papantonis A. Exon skipping is correlated with exon circularization. J Mol Biol. 2015;427:2414–17.
Koh W, Gonzalez V, Natarajan S, Carter R, Brown PO, Gawad C. Dynamic ASXL1 Exon skipping and alternative circular splicing in single human cells. PloS One. 2016;11:e0164085.
Suzuki H, Aoki Y, Kameyama T, Saito T, Masuda S, Tanihata J, et al. Endogenous multiple exon skipping and back-splicing at the DMD Mutation Hotspot. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1722.
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM, Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, et al. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell. 2015;160:1125–34.
Errichelli L, Dini Modigliani S, Laneve P, Colantoni A, Legnini I, Capauto D, et al. FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14741.
Khan MA, Reckman YJ, Aufiero S, van den Hoogenhof MM, van der Made I, Beqqali A, et al. RBM20 regulates circular RNA production from the titin gene. Circ Res. 2016;119:996–1003.
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, et al. CircRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014;56:55–66.
Timoteo GD, Dattilo D, entrón-Broco A, Colantoni A, Guarnacci M, Rossi F, et al. Modulation of circRNA metabolism by m6A modification. Cell Rep. 2020;31:107641.
Chen C, Yuan WT, Zhou QB, Shao B, Guo YY, Wang WW, et al. N6-methyladenosine-induced circ1662 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by accelerating YAP1 nuclear localization. Theranostics. 2021;11:4298–315.
Talhouarne GJ, Gall JG. Lariat intronic RNAs in the cytoplasm of Xenopus tropicalisoocytes. RNA. 2014;20:1476–87.
Bao DQ, Zhuang CH, Jiao Y, Yang L. The possible involvement of circRNA DMNT1/p53/JAK/STAT in gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:121.
Deng N, Lei D, Huang JF, Yang ZH, Fan CF, Wang SQ. Circular RNA expression profiling identifies hsa_circ_0011460 as a novel molecule in severe preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2019;17:216–25.
Wei N, Song HB. Circ-0002814 participates in proliferation and migration through miR-210 and FUS/VEGF pathway of preeclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2022;48:1698–709.
Fan XJ, Yang Y, Chen CY, Wang ZF. Pervasive translation of circular RNAs driven by short IRES-like elements. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3751.
Matsumoto A, Nakayama KI. Hidden peptides encoded by putative noncoding RNAs. Cell Struct Funct. 2018;43:75–83.
Pan JC, Meng XD, Jiang N, Jin XF, Zhou CW, Xu DZ, et al. Insights into the noncoding RNA-encoded peptides. Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25:720–27.
Legnini I, Timoteo GD, Rossi F, Morlando M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell. 2017;66:22–37.
Wang Y, Wang ZF. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA. 2015;21:172–79.
Yang Y, Fan XJ, Mao MW, Song XW, Wu P, Zhang Y, et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27:626–41.
Conn VM, Hugouvieux V, Nayak A, Conos SA, Capovilla G, Cildir G, et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat Plants. 2017;3: 17053.
Abe N, Matsumoto K, Nishihara M, Nakano M, Shibata A, Maruyama H, et al. Rolling circle translation of circular RNA in living human cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16435.
Perriman R, Ares M Jr. Circular mRNA can direct translation of extremely long repeating-sequence proteins in vivo. RNA. 1998;4:1047–54.
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell. 2017;66:9–21.
Fang L, Du WW, Awan FM, Dong J, Yang BB. The circular RNA circ-Ccnb1 dissociates Ccnb1/Cdk1 complex suppressing cell invasion and tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2019;459:216–26.
Du WW, Fang L, Yang W, Wu N, Awan FM, Yang Z, et al. Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:357–70.
Yang ZG, Awan FM, Du WW, Zeng Y, Lyu J, et al. The circular RNA interacts with STAT3, increasing its nuclear translocation and wound repair by modulating Dnmt3a and miR-17 function. Mol Ther. 2017;25:2062–74.
Song C, Zhang Y, Huang W, Shi J, Huang Q, Jiang M, et al. Circular RNA Cwc27 contributes to Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis by repressing Pur-alpha activity. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:393–406.
Kloc M, Foreman V, Reddy SA. Binary function of mRNA. Biochimie. 2011;93:1955–61.
Jeffares DC, Poole AM, Penny D. Relics from the RNA world. J Mol Evol. 1998;46:18–36.
Poole AM, Jeffares DC, Penny D. The path from the RNA world. J Mol Evol. 1998;46:1–17.
Kloc M, Wilk K, Vargas D, Shirato Y, Bilinski S, Etkin LD. Potential structural role of non-coding and coding RNAs in the organization of the cytoskeleton at the vegetal cortex of Xenopus oocytes. Development. 2005;132:3445–57.
Xin ZY, Ma Q, Ren SC, Wang GQ, Li F. The understanding of circular RNAs as special triggers in carcinogenesis. Brief Funct Genomics. 2017;16:80–6.
Kamrani A, Alipourfard I, Ahmadi-Khiavi H, Yousefi M, Rostamzadeh D, Izadi M, et al. The role of epigenetic changes in preeclampsia. BioFactors. 2019;45:712–24.
Apicella C, Ruano CSM, Méhats C, Miralles F, Vaiman D. The role of epigenetics in placental development and the etiology of preeclampsia. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2837.
Chen XJ, Lu Y. Circular RNA: biosynthesis in vitro. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:787881.
Müller S, Appel B. In Vitro circularization of RNA. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1018–27.
Obi P, Chen YG. The design and synthesis of circular RNAs. Methods 2021;S1046-2023:00065–7.
Puttaraju M, Been M. Group I Permuted Intron-Exon (PIE) sequences self-splice to produce circular exons. Nucl Acids Res. 1992;20:5357–64.
Ford E, Ares M. Synthesis of circular RNA in bacteria and yeast using RNA cyclase ribozymes derived from a group I intron of phage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1994;91:3117–21.
Rausch JW, Heinz WF, Payea MJ, Sherpa C, Gorospe M, Le Grice SF. Characterizing and circumventing sequence restrictions for synthesis of circular RNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:E35.
Jarrell KA. Inverse splicing of a group II intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1993;90:8624–7.
Qu L, Yi ZY, Shen Y, Lin LR, Chen F, Xu YY, et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell. 2022;185:1728–44.
Su P, Zhang L, Zhou FF, Zhang L. Circular RNA vaccine, a novel mRNA vaccine design strategy for SARS-CoV-2 and variants. MedComm. 2022;3:e153.
Jahng JWS, Liu LC, Wu JC. Tumor repressor circular RNA as a new target for preventative gene therapy against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Circ Res. 2020;127:483–5.
Ding N, You AB, Yang H, Hu GS, Lai CP, Liu W, et al. A tumor-suppressive molecular axis EP300/circRERE/miR-6837-3p/MAVS activates type I IFN pathway and antitumor immunity to suppress colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29:2095–109.
Katrekar D, Yen J, Xiang YC, Saha A, Meluzzi D, Savva Y, et al. Efficient in vitro and in vivo RNA editing via recruitment of endogenous ADARs using circular guide RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2022;40:938–45.
Acknowledgements
All authors have significantly contributed to and agree with the content of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFA0802600) and Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center (CXZX202231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Shen, F., Chen, X. et al. Current understanding of circular RNAs in preeclampsia. Hypertens Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-024-01675-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-024-01675-x