Abstract
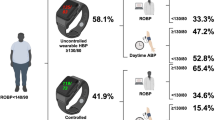
This study sought to evaluate the relationship between blood pressure (BP) taken by a new wrist-cuff oscillometric wearable BP monitoring device and left ventricular mass index measured by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI-LVMI) in 50 hypertensive patients (mean age 60.5 ± 8.9 years, 92.0% men, 96% treated for hypertension) with regular employment. Participants were asked to self-measure their wearable BPs twice in the morning and evening under a guideline-recommended standardized home BP measurement, and once each at five predetermined times and any additional time points under an ambulatory condition for a maximum of 7 days. In total, 2105 wearable BP measurements (home BP: 747 [morning: 409, evening: 338], ambulatory condition: 1358 [worksite: 942]) were collected over 5.5 ± 1.2 days. The average of all wearable systolic BP (SBP) readings (129.8 ± 11.0 mmHg) was weakly correlated with cMRI-LVMI (r = 0.265, p = 0.063). Morning home wearable SBP average (128.5 ± 13.8 mmHg) was significantly correlated with cMRI-LVMI (r = 0.378, p = 0.013), but ambulatory wearable SBP average (132.5 ± 12.7 mmHg) was not (r = 0.215, p = 0.135). The averages of the highest three values of all wearable SBPs (153.3 ± 13.9 mmHg) and ambulatory wearable SBPs (152.9 ± 13.9 mmHg) were 16 mmHg higher than that of the morning home wearable SBPs (137.0 ± 15.9 mmHg). Those peak values were significantly correlated with cMRI-LVMI (r = 0.320, p = 0.023; r = 0.310, p = 0.029; r = 0.451, p = 0.002, respectively). In conclusion, an increased number of wearable BP measurements, which could detect individual peak BP, might add to the clinical value of these measurements as a complement to the guideline-recommended home BP measurements, but further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–104.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr., Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: a Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:2199–269.
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–481.
Stergiou GS, Palatini P, Parati G, O’Brien E, Januszewicz A, Lurbe E, et al. 2021 European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for office and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. J Hypertens. 2021;39:1293–1302.
Kario K, Park S, Chia YC, Sukonthasarn A, Turana Y, Shin J, et al. 2020 Consensus summary on the management of hypertension in Asia from the HOPE Asia Network. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020;22:351–62.
Park S, Buranakitjaroen P, Chen CH, Chia YC, Divinagracia R, Hoshide S, et al. Expert panel consensus recommendations for home blood pressure monitoring in Asia: the Hope Asia Network. J Hum Hypertens. 2018;32:249–58.
Kario K, Shimbo D, Hoshide S, Wang JG, Asayama K, Ohkubo T, et al. Emergence of Home Blood Pressure-Guided Management of Hypertension Based on Global Evidence. Hypertension. 2019:HYPERTENSIONAHA11912630.
Shimbo D, Artinian NT, Basile JN, Krakoff LR, Margolis KL, Rakotz MK, et al. Self-Measured Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home: A Joint Policy Statement From the American Heart Association and American Medical Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e42–e63.
Kario K, Shin J, Chen CH, Buranakitjaroen P, Chia YC, Divinagracia R, et al. Expert panel consensus recommendations for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in Asia: the HOPE Asia Network. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019;21:1250–83.
Kario K. Nocturnal hypertension: new technology and evidence. Hypertension. 2018;71:997–1009.
Asayama K, Fujiwara T, Hoshide S, Ohkubo T, Kario K, Stergiou GS, et al. Nocturnal blood pressure measured by home devices: evidence and perspective for clinical application. J Hypertens. 2019;37:905–16.
Kario K, Kanegae H, Tomitani N, Okawara Y, Fujiwara T, Yano Y, et al. Nighttime Blood Pressure Measured by Home Blood Pressure Monitoring as an Independent Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in General Practice. Hypertension. 2019;73:1240–8.
Hoshide S, Kanegae H, Kario K. Nighttime home blood pressure as a mediator of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular events. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:1138–46.
Kuwabara M, Harada K, Hishiki Y, Kario K. Validation of a wrist-type home nocturnal blood pressure monitor in the sitting and supine position according to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO81060-2:2013 guidelines: Omron HEM-9600T. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019;21:463–9.
Kuwabara M, Harada K, Hishiki Y, Ohkubo T, Kario K, Imai Y. Validation of a wrist-type home nocturnal blood pressure monitor in the sitting and supine position according to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO81060-2:2013 guidelines: Omron HEM-9601T. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020;22:970–8.
Kario K, Tomitani N, Iwashita C, Shiga T, Kanegae H. Simultaneous self-monitoring comparison of a supine algorithm-equipped wrist nocturnal home blood pressure monitoring device with an upper arm device. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021;23:793–801.
Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Kario K. Comparison of nighttime measurement schedules using a wrist-type nocturnal home blood pressure monitoring device. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021;23:1144–49.
Kario K, Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Yasui N, Nishizawa M, Fujiwara T, et al. Development of a New ICT-Based Multisensor Blood Pressure Monitoring System for Use in Hemodynamic Biomarker-Initiated Anticipation Medicine for Cardiovascular Disease: the National IMPACT Program Project. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;60:435–49.
Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Suzuki Y, Kuwabara M, Kario K. Stress-Induced Blood Pressure Elevation Self-Measured by a Wearable Watch-Type Device. Am J Hypertens. 2021;34:377–82.
Tomitani N, Hoshide S, Kario K. Self-measured worksite blood pressure and its association with organ damage in working adults: Japan Morning Surge Home Blood Pressure (J-HOP) worksite study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021;23:53–60.
Kario K. Management of hypertension in the digital era: small wearable monitoring devices for remote blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension. 2020;76:640–50.
Omboni S, McManus RJ, Bosworth HB, Chappell LC, Green BB, Kario K, et al. Evidence and Recommendations on the Use of Telemedicine for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: an international expert position paper. Hypertension. 2020;76:1368–83.
Kuwabara M, Harada K, Hishiki Y, Kario K. Validation of two watch-type wearable blood pressure monitors according to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO81060-2:2013 guidelines: Omron HEM-6410T-ZM and HEM-6410T-ZL. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019;21:853–8.
Kario K, Shimbo D, Tomitani N, Kanegae H, Schwartz JE, Williams B. The first study comparing a wearable watch-type blood pressure monitor with a conventional ambulatory blood pressure monitor on in-office and out-of-office settings. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020;22:135–41.
Kario K, Hoshide S, Saito K, Sato K, Hamasaki H, Suwa H, et al. Validation of the TM-2441 ambulatory blood pressure measurement device according to the ISO 81060-2: 2013 standard. Blood Press Monit. 2019;24:38–41.
Schulz-Menger J, Bluemke DA, Bremerich J, Flamm SD, Fogel MA, Friedrich MG, et al. Standardized image interpretation and post-processing in cardiovascular magnetic resonance - 2020 update: Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR): Board of Trustees Task Force on Standardized Post-Processing. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020;22:19.
Kario K, Saito I, Kushiro T, Teramukai S, Ishikawa Y, Mori Y, et al. Home blood pressure and cardiovascular outcomes in patients during antihypertensive therapy: primary results of HONEST, a large-scale prospective, real-world observational study. Hypertension. 2014;64:989–96.
Hoshide S, Yano Y, Haimoto H, Yamagiwa K, Uchiba K, Nagasaka S, et al. Morning and Evening Home Blood Pressure and Risks of Incident Stroke and Coronary Artery Disease in the Japanese General Practice Population: the Japan Morning Surge-Home Blood Pressure Study. Hypertension. 2016;68:54–61.
Kario K, Saito I, Kushiro T, Teramukai S, Tomono Y, Okuda Y, et al. Morning Home Blood Pressure Is a Strong Predictor of Coronary Artery Disease: The HONEST Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:1519–27.
Kario K. Time for focus on morning hypertension: pitfall of current antihypertensive medication. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:149–51.
Schwartz JE, Muntner P, Kronish IM, Burg MM, Pickering TG, Bigger JT, et al. Reliability of Office, Home, and Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurements and Correlation With Left Ventricular Mass. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:2911–22.
Anstey DE, Muntner P, Bello NA, Pugliese DN, Yano Y, Kronish IM, et al. Diagnosing Masked Hypertension Using Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring, Home Blood Pressure Monitoring, or Both? Hypertension. 2018;72:1200–7.
Acknowledgements
The HeartGuide device was supplied by Omron Healthcare Co., Ltd., who also provided funding for the study. However, the collection and analysis of BP data in this study were entirely independent of Omron Healthcare Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.K. supervised the conduct of the study and data analysis, and had primary responsibility of writing this paper. N.T. analyzed the data and wrote the paper with input from all authors. T.M. supported study data collection at Washiya Hospital. H.K. contributed to the analysis. P.L. and B.W. contributed to the study design. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Omron Healthcare.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KK has received a research grant from Omron Healthcare, A&D and Fukuda Denshi. NT was the recipient of a JSPS KAKENHI grant (no. 20K17127). BW has received a research grant from Omron Healthcare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kario, K., Tomitani, N., Morimoto, T. et al. Relationship between blood pressure repeatedly measured by a wrist-cuff oscillometric wearable blood pressure monitoring device and left ventricular mass index in working hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 45, 87–96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00758-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00758-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
History and evolution of blood pressure measurement
Clinical Hypertension (2024)
-
Could wristwatch-type wearable oscillometric blood pressure monitoring be a third option for out-of-office blood pressure monitoring?
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Topics 2023 in Hypertension Research leading to guidelines in Asia
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Diagnostic agreement of masked uncontrolled hypertension detected by ambulatory blood pressure and home blood pressure measured by an all-in-one BP monitoring device: The HI–JAMP study
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Effective out-of-office BP monitoring to detect masked hypertension: perspectives for wearable BP monitoring
Hypertension Research (2023)