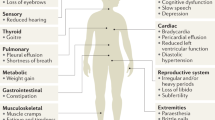
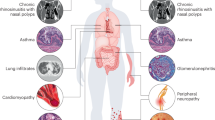
Abstract
Resistant hypertension is associated with a poor prognosis due to organ damage caused by prolonged suboptimal blood pressure control. The concomitant use of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonists with other antihypertensives has been shown to improve blood pressure control in some patients with resistant hypertension, and such patients are considered to have MR-associated hypertension. MR-associated hypertension is classified into two subtypes: one with a high plasma aldosterone level, which includes primary aldosteronism (PA), and the other with a normal aldosterone level. In patients with unilateral PA, adrenalectomy may be the first-choice procedure, while in patients with bilateral PA, MR antagonists are selected. In addition, in patients with other types of MR-associated hypertension with high aldosterone levels, MR antagonists may be selected as a first-line therapy. In patients with normal aldosterone levels, ARBs or ACE inhibitors are used as a first-line therapy, and MR antagonists may be used as an add-on agent. Since MR antagonist therapy may have efficacy as a first-line or add-on agent in these patients, it is important to recognize this type of hypertension. Further studies are needed to elucidate the pathogenesis and management of MR-associated hypertension in more detail to improve the clinical outcomes of patients with MR-associated hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viengchareun S, Le Menuet D, Martinerie L, Munier M, Pascual-Le Tallec L, Lombes M. The mineralocorticoid receptor: insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007;5:e012.
Funder JW. Minireview: aldosterone and the cardiovascular system: genomic and nongenomic effects. Endocrinology. 2006;147:5564–7.
Conn JW. Primary aldosteronism. J Lab Clin Med. 1955;45:661–4.
Mulatero P, Stowasser M, Loh KC, Fardella CE, Gordon RD, Mosso L, et al. Increased diagnosis of primary aldosteronism, including surgically correctable forms, in centers from five continents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1045–50.
Funder JW, Carey RM, Mantero F, Murad MH, Reincke M, Shibata H, et al. The management of primary aldosteronism: case detection, diagnosis, and treatment: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:1889–916.
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, et al. The Japanese society of hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–481.
Monticone S, Burrello J, Tizzani D, Bertello C, Viola A, Buffolo F, et al. Prevalence and clinical manifestations of primary aldosteronism encountered in primary care practice. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69:1811–20.
Monticone S, D’Ascenzo F, Moretti C, Williams TA, Veglio F, Gaita F, et al. Cardiovascular events and target organ damage in primary aldosteronism compared with essential hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:41–50.
Sechi LA, Di Fabio A, Bazzocchi M, Uzzau A, Catena C. Intrarenal hemodynamics in primary aldosteronism before and after treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1191–7.
Akehi Y, Yanase T, Motonaga R, Umakoshi H, Tsuiki M, Takeda Y, et al. High prevalence of diabetes in patients with primary aldosteronism (pa) associated with subclinical hypercortisolism and prediabetes more prevalent in bilateral than unilateral PA: a large, multicenter cohort study in Japan. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:938–45.
Velema M, Dekkers T, Hermus A, Timmers H, Lenders J, Groenewoud H, et al. Quality of life in primary aldosteronism: a comparative effectiveness study of adrenalectomy and medical treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:16–24.
Reincke M. Anxiety, depression, and impaired quality of life in primary aldosteronism: why we shouldn’t ignore it! J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:1–4.
Rocha R, Stier CT Jr., Kifor I, Ochoa-Maya MR, Rennke HG, Williams GH, et al. Aldosterone: a mediator of myocardial necrosis and renal arteriopathy. Endocrinology. 2000;141:3871–8.
El-Gharbawy AH, Nadig VS, Kotchen JM, Grim CE, Sagar KB, Kaldunski M, et al. Arterial pressure, left ventricular mass, and aldosterone in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2001;37:845–50.
Rocha R, Funder JW. The pathophysiology of aldosterone in the cardiovascular system. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;970:89–100.
Blasi ER, Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Blomme EA, Polly ML, McMahon EG. Aldosterone/salt induces renal inflammation and fibrosis in hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1791–800.
Rossi GP, Cesari M, Pessina AC. Left ventricular changes in primary aldosteronism. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:96–8.
Dartsch T, Fischer R, Gapelyuk A, Weiergraeber M, Ladage D, Schneider T, et al. Aldosterone induces electrical remodeling independent of hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2013;164:170–8.
Rossi GP, Seccia TM, Gallina V, Muiesan ML, Leoni L, Pengo M, et al. Prospective appraisal of the prevalence of primary aldosteronism in hypertensive patients presenting with atrial flutter or fibrillation (PAPPHY Study): rationale and study design. J Hum Hypertens. 2013;27:158–63.
Rossi GP, Bolognesi M, Rizzoni D, Seccia TM, Piva A, Porteri E, et al. Vascular remodeling and duration of hypertension predict outcome of adrenalectomy in primary aldosteronism patients. Hypertension. 2008;51:1366–71.
Martinez-Aguayo A, Carvajal CA, Campino C, Aglony M, Bolte L, Garcia H, et al. Primary aldosteronism and its impact on the generation of arterial hypertension, endothelial injury and oxidative stress. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010;23:323–30.
Farquharson CA, Struthers AD. Spironolactone increases nitric oxide bioactivity, improves endothelial vasodilator dysfunction, and suppresses vascular angiotensin I/angiotensin II conversion in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 2000;101:594–7.
Rocha R, Stier CT Jr. Pathophysiological effects of aldosterone in cardiovascular tissues. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;12:308–14.
Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Frierdich GE, Nachowiak DA, Kekec BK, Blomme EA, et al. Aldosterone induces a vascular inflammatory phenotype in the rat heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283:H1802–10.
Takeda Y. Role of cardiovascular aldosterone in hypertension. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2005;3:261–6.
Yugar-Toledo JC, Bonalume Tacito LH, Ferreira-Melo SE, Sousa W, Consolin-Colombo F, Irigoyen MC, et al. Low-renin (volume dependent) mild-hypertensive patients have impaired flow-mediated and glyceryl-trinitrate stimulated vascular reactivity. Circ J. 2005;69:1380–5.
Schiffrin EL. Effects of aldosterone on the vasculature. Hypertension. 2006;47:312–8.
Ruilope LM. Aldosterone, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an endless story. Hypertension. 2008;52:207–8.
Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, et al. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:709–17.
Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, et al. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1309–21.
Zannad F, McMurray JJ, Krum H, van Veldhuisen DJ, Swedberg K, Shi H, et al. Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:11–21.
Goette A, Hoffmanns P, Enayati W, Meltendorf U, Geller JC, Klein HU. Effect of successful electrical cardioversion on serum aldosterone in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2001;88:906–9, A8.
Chung YW, Yang YH, Wu CK, Yu CC, Juang JM, Wang YC, et al. Spironolactone is associated with reduced risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients receiving renal replacement therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2016;202:962–6.
Simopoulos V, Tagarakis G, Hatziefthimiou A, Skoularigis I, Triposkiadis F, Trantou V, et al. Effectiveness of aldosterone antagonists for preventing atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery in patients with systolic heart failure: a retrospective study. Clin Res Cardiol. 2015;104:31–7.
Wei J, Ni J, Huang D, Chen M, Yan S, Peng Y. The effect of aldosterone antagonists for ventricular arrhythmia: a meta-analysis. Clin Cardiol. 2010;33:572–7.
Beygui F, Labbe JP, Cayla G, Ennezat PV, Motreff P, Roubille F, et al. Early mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction is associated with a reduction of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:73–9.
Bolignano D, Palmer SC, Navaneethan SD, and Strippoli GF. Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;4:CD007004.
Currie G, Taylor AH, Fujita T, Ohtsu H, Lindhardt M, Rossing P, et al. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on proteinuria and progression of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17:127.
Myat A, Redwood SR, Qureshi AC, Spertus JA, Williams B. Resistant hypertension. BMJ. 2012;345:e7473.
Williams B. Resistant hypertension: an unmet treatment need. Lancet. 2009;374:1396–8.
Dahal K, Kunwar S, Rijal J, Alqatahni F, Panta R, Ishak N, et al. The effects of aldosterone antagonists in patients with resistant hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized studies. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28:1376–85.
Nishizaka MK, Zaman MA, Calhoun DA. Efficacy of low-dose spironolactone in subjects with resistant hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:925–30.
Williams B, MacDonald TM, Morant S, Webb DJ, Sever P, McInnes G, et al. Spironolactone versus placebo, bisoprolol, and doxazosin to determine the optimal treatment for drug-resistant hypertension (PATHWAY-2): a randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet. 2015;386:2059–68.
Shibata H, Itoh H. Mineralocorticoid receptor-associated hypertension and its organ damage: clinical relevance for resistant hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2012;25:514–23.
Bertocchio JP, Warnock DG, Jaisser F. Mineralocorticoid receptor activation and blockade: an emerging paradigm in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011;79:1051–60.
Sato A, Saruta T. Aldosterone breakthrough during angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:781–8.
MacFadyen RJ, Lee AF, Morton JJ, Pringle SD, Struthers AD. How often are angiotensin II and aldosterone concentrations raised during chronic ACE inhibitor treatment in cardiac failure? Heart. 1999;82:57–61.
Horita Y, Taura K, Taguchi T, Furusu A, Kohno S. Aldosterone breakthrough during therapy with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in proteinuric patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology. 2006;11:462–6.
Sato A, Saruta T. Aldosterone escape during angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy in essential hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. J Int Med Res. 2001;29:13–21.
Cicoira M, Zanolla L, Franceschini L, Rossi A, Golia G, Zeni P, et al. Relation of aldosterone “escape” despite angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor administration to impaired exercise capacity in chronic congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:403–7.
Narayan H, Webb DJ. New evidence supporting the use of mineralocorticoid receptor blockers in drug-resistant hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016;18:34.
Sato A, Saruta T, Funder JW. Combination therapy with aldosterone blockade and renin-angiotensin inhibitors confers organ protection. Hypertens Res. 2006;29:211–6.
Kaplan NM. The current epidemic of primary aldosteronism: causes and consequences. J Hypertens. 2004;22:863–9.
Racine MC, Douville P, Lebel M. Functional tests for primary aldosteronism: value of captopril suppression. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2002;4:245–9.
Sartori M, Calo LA, Mascagna V, Realdi A, Macchini L, Ciccariello L, et al. Aldosterone and refractory hypertension: a prospective cohort study. Am J Hypertens. 2006;19:373–9.
Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Lamounier-Zepter V, Schraven A, Langenbach J, Willenberg HS, Barthel A, et al. Human adipocytes secrete mineralocorticoid-releasing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:14211–6.
Goodfriend TL, Egan BM, Kelley DE. Plasma aldosterone, plasma lipoproteins, obesity and insulin resistance in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids. 1999;60:401–5.
Engeli S, Bohnke J, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Schling P, Bader M, et al. Weight loss and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Hypertension. 2005;45:356–62.
Harada E, Mizuno Y, Katoh D, Kashiwagi Y, Morita S, Nakayama Y, et al. Increased urinary aldosterone excretion is associated with subcutaneous not visceral, adipose tissue area in obese individuals: a possible manifestation of dysfunctional subcutaneous adipose tissue. Clin Endocrinol. 2013;79:510–6.
Huby AC, Antonova G, Groenendyk J, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Bollag WB, Filosa JA, et al. Adipocyte-derived hormone leptin is a direct regulator of aldosterone secretion, which promotes endothelial dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis. Circulation. 2015;132:2134–45.
Krug AW, Vleugels K, Schinner S, Lamounier-Zepter V, Ziegler CG, Bornstein SR, et al. Human adipocytes induce an ERK1/2 MAP kinases-mediated upregulation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and an angiotensin II-sensitization in human adrenocortical cells. Int J Obes. 2007;31:1605–16.
Pedrosa RP, Drager LF, Gonzaga CC, Sousa MG, de Paula LK, Amaro AC, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea: the most common secondary cause of hypertension associated with resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;58:811–7.
Florczak E, Prejbisz A, Szwench-Pietrasz E, Sliwinski P, Bielen P, Klisiewicz A, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with resistant hypertension: the RESIST-POL study. J Hum Hypertens. 2013;27:678–85.
Logan AG, Perlikowski SM, Mente A, Tisler A, Tkacova R, Niroumand M, et al. High prevalence of unrecognized sleep apnoea in drug-resistant hypertension. J Hypertens. 2001;19:2271–7.
Martinez-Garcia MA, Navarro-Soriano C, Torres G, Barbe F, Caballero-Eraso C, Lloberes P, et al. Beyond resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2018;72:618–24.
Gonzaga CC, Gaddam KK, Ahmed MI, Pimenta E, Thomas SJ, Harding SM, et al. Severity of obstructive sleep apnea is related to aldosterone status in subjects with resistant hypertension. J Clin Sleep Med. 2010;6:363–8.
Sim JJ, Yan EH, Liu IL, Rasgon SA, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Calhoun DA, et al. Positive relationship of sleep apnea to hyperaldosteronism in an ethnically diverse population. J Hypertens. 2011;29:1553–9.
Gaddam K, Pimenta E, Thomas SJ, Cofield SS, Oparil S, Harding SM, et al. Spironolactone reduces severity of obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with resistant hypertension: a preliminary report. J Hum Hypertens. 2010;24:532–7.
Wolley MJ, Pimenta E, Calhoun D, Gordon RD, Cowley D, Stowasser M. Treatment of primary aldosteronism is associated with a reduction in the severity of obstructive sleep apnoea. J Hum Hypertens. 2017;31:561–7.
Furlan R, Barbic F, Piazza S, Tinelli M, Seghizzi P, Malliani A. Modifications of cardiac autonomic profile associated with a shift schedule of work. Circulation. 2000;102:1912–6.
Bradley TD, Floras JS. Sleep apnea and heart failure: Part II: central sleep apnea. Circulation. 2003;107:1822–6.
Suwazono Y, Dochi M, Sakata K, Okubo Y, Oishi M, Tanaka K, et al. Shift work is a risk factor for increased blood pressure in Japanese men: a 14-year historical cohort study. Hypertension. 2008;52:581–6.
Scheer FA, Hilton MF, Mantzoros CS, Shea SA. Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:4453–8.
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Fuentes-Broto L. Melatonin: a multitasking molecule. Prog Brain Res. 2010;181:127–51.
Dubocovich ML, Markowska M. Functional MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in mammals. Endocrine. 2005;27:101–10.
Borjigin J, Zhang LS, Calinescu AA. Circadian regulation of pineal gland rhythmicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;349:13–9.
Doi M, Takahashi Y, Komatsu R, Yamazaki F, Yamada H, Haraguchi S, et al. Salt-sensitive hypertension in circadian clock-deficient Cry-null mice involves dysregulated adrenal Hsd3b6. Nat Med. 2010;16:67–74.
Grossman E, Messerli FH. Management of blood pressure in patients with diabetes. Am J Hypertens. 2011;24:863–75.
Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P, Vega GL, Toto RD. Addition of angiotensin receptor blockade or mineralocorticoid antagonism to maximal angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:2641–50.
Gu Q, Burt VL, Dillon CF, Yoon S. Trends in antihypertensive medication use and blood pressure control among United States adults with hypertension: the National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001 to 2010. Circulation. 2012;126:2105–14.
van den Meiracker AH, Baggen RG, Pauli S, Lindemans A, Vulto AG, Poldermans D, et al. Spironolactone in type 2 diabetic nephropathy: effects on proteinuria, blood pressure and renal function. J Hypertens. 2006;24:2285–92.
Sato A, Hayashi K, Naruse M, Saruta T. Effectiveness of aldosterone blockade in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension. 2003;41:64–8.
Jansen PM, Danser AH, Imholz BP, van den Meiracker AH. Aldosterone-receptor antagonism in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2009;27:680–91.
Greene EL, Kren S, Hostetter TH. Role of aldosterone in the remnant kidney model in the rat. J Clin Investig. 1996;98:1063–8.
Bianchi S, Bigazzi R, Campese VM. Long-term effects of spironolactone on proteinuria and kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;70:2116–23.
Volk MJ, Bomback AS, Klemmer PJ. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in chronic kidney disease. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011;13:282–8.
Bomback AS, Kshirsagar AV, Amamoo MA, Klemmer PJ. Change in proteinuria after adding aldosterone blockers to ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers in CKD: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51:199–211.
Bomback AS, Toto R. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: beyond the ACE inhibitor and angiotensin-II receptor blocker combination. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22:1032–40.
Toto RD. Aldosterone blockade in chronic kidney disease: can it improve outcome? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010;19:444–9.
Zulian E, Sartorato P, Benedini S, Baro G, Armanini D, Mantero F, et al. Spironolactone in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: effects on clinical features, insulin sensitivity and lipid profile. J Endocrinol Investig. 2005;28:49–53.
Dona G, Sabbadin C, Fiore C, Bragadin M, Giorgino FL, Ragazzi E, et al. Inositol administration reduces oxidative stress in erythrocytes of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;166:703–10.
Cascella T, Palomba S, Tauchmanova L, Manguso F, Di Biase S, Labella D, et al. Serum aldosterone concentration and cardiovascular risk in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:4395–400.
Armanini D, Bordin L, Dona G, Sabbadin C, Bakdounes L, Ragazzi E, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome: implications of measurement of plasma aldosterone, renin activity and progesterone. Steroids. 2012;77:655–8.
Rafiq K, Hitomi H, Nakano D, Nishiyama A. Pathophysiological roles of aldosterone and mineralocorticoid receptor in the kidney. J Pharm Sci. 2011;115:1–7.
Baker ME, Funder JW, Kattoula SR. Evolution of hormone selectivity in glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;137:57–70.
Vitellius G, Trabado S, Bouligand J, Delemer B, Lombes M. Pathophysiology of glucocorticoid signaling. Ann Endocrinol. 2018;79:98–106.
Nishiyama A. Pathophysiological mechanisms of mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:293–300.
Shibata S, Ishizawa K, Uchida S. Mineralocorticoid receptor as a therapeutic target in chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2017;40:221–5.
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawarazaki W, Kurihara H, Tanaka H, et al. Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase: implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:1370–6.
Uddin S, Lekmine F, Sharma N, Majchrzak B, Mayer I, Young PR, et al. The Rac1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is required for interferon alpha-dependent transcriptional activation but not serine phosphorylation of Stat proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27634–40.
Aikawa R, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, Zou Y, Kudoh S, Zhu W, et al. Rho family small G proteins play critical roles in mechanical stress-induced hypertrophic responses in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1999;84:458–66.
Shibata S, Mu S, Kawarazaki H, Muraoka K, Ishizawa K, Yoshida S, et al. Rac1 GTPase in rodent kidneys is essential for salt-sensitive hypertension via a mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent pathway. J Clin Investig. 2011;121:3233–43.
Nagase M, Ayuzawa N, Kawarazaki W, Ishizawa K, Ueda K, Yoshida S, et al. Oxidative stress causes mineralocorticoid receptor activation in rat cardiomyocytes: role of small GTPase Rac1. Hypertension. 2012;59:500–6.
Duncan JL 3rd, Fuhrman GM, Bolton JS, Bowen JD, Richardson WS. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy is superior to an open approach to treat primary hyperaldosteronism. Am Surg. 2000;66:932–5. discussion 935–6
Meria P, Kempf BF, Hermieu JF, Plouin PF, Duclos JM. Laparoscopic management of primary hyperaldosteronism: clinical experience with 212 cases. J Urol. 2003;169:32–5.
Rossi H, Kim A, Prinz RA. Primary hyperaldosteronism in the era of laparoscopic adrenalectomy. Am Surg. 2002;68:253–6. discussion 256–7
Hundemer GL, Curhan GC, Yozamp N, Wang M, Vaidya A. Renal outcomes in medically and surgically treated primary aldosteronism. Hypertension. 2018;72:658–66.
Hundemer GL, Curhan GC, Yozamp N, Wang M, Vaidya A. Cardiometabolic outcomes and mortality in medically treated primary aldosteronism: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:51–9.
Hundemer GL, Curhan GC, Yozamp N, Wang M, Vaidya A. Incidence of atrial fibrillation and mineralocorticoid receptor activity in patients with medically and surgically treated primary aldosteronism. JAMA Cardiol. 2018;3:768–74.
Pelliccia F, Patti G, Rosano G, Greco C, Gaudio C. Efficacy and safety of eplerenone in the management of mild to moderate arterial hypertension: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177:219–28.
Roush GC, Ernst ME, Kostis JB, Yeasmin S, Sica DA. Dose doubling, relative potency, and dose equivalence of potassium-sparing diuretics affecting blood pressure and serum potassium: systematic review and meta-analyses. J Hypertens. 2016;34:11–9.
Arai K, Homma T, Morikawa Y, Ubukata N, Tsuruoka H, Aoki K, et al. Pharmacological profile of CS-3150, a novel, highly potent and selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;761:226–34.
Ito S, Itoh H, Rakugi H, Okuda Y, Yoshimura M, Yamakawa S. Double-Blind Randomized Phase 3 Study Comparing Esaxerenone (CS-3150) and eplerenone in patients with essential hypertension (ESAX-HTN Study). Hypertension. 2020;75:51–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morimoto, S., Ichihara, A. Management of primary aldosteronism and mineralocorticoid receptor-associated hypertension. Hypertens Res 43, 744–753 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0468-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0468-3