Abstract
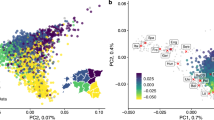
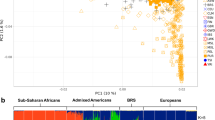
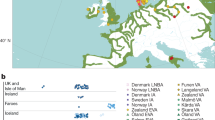
Selection on standing genetic variation is important for rapid local genetic adaptation when the environment changes. We report that, for the prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) gene, different populations have different target haplotypes, even though haplotypes are shared among populations. The C-C-A haplotype, whereby the first C is located at rs2294008 of PSCA and is a low risk allele for gastric cancer, has become a target of positive selection in Asia. Conversely, the C-A-G haplotype carrying the same C allele has become a selection target mainly in Africa. However, Asian and African share both haplotypes, consistent with the haplotype divergence time (170 kya) prior to the out-of-Africa dispersal. The frequency of C-C-A/C-A-G is 0.344/0.278 in Asia and 0.209/0.416 in Africa. Two-dimensional site frequency spectrum analysis revealed that the extent of intra-allelic variability of the target haplotype is extremely small in each local population, suggesting that C-C-A or C-A-G is under ongoing hard sweeps in local populations. From the time to the most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) of selected haplotypes, the onset times of positive selection were recent (3–55 kya), concurrently with population subdivision from a common ancestor. Additionally, estimated selection coefficients from ABC analysis were up to ~3%, similar to those at other loci under recent positive selection. Phylogeny of local populations and TMRCA of selected haplotypes revealed that spatial and temporal switching of positive selection targets is a unique and novel feature of ongoing selection at PSCA. This switching may reflect the potential of rapid adaptability to distinct environments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium (2015) A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15393
Albers PK, McVean G (2020) Dating genomic variants and shared ancestry in population-scale sequencing data. PLoS Biol 18:e3000586. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000586
Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, Alves I, Martinho C, Cameron E et al. (2013) The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol 30:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B57:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Brown MB (1975) 400: a method for combining non-independent, one-sided tests of significance. Biometrics 31:987–992. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529826
Busby GB, Band G, Si Le Q, Jallow M, Bougama E, Mangano VD et al. (2016) Malaria genomic epidemiology network. Admixture into and within sub-Saharan Africa. Elife 5:e15266. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.15266
Colosimo PF, Hosemann KE, Balabhadra S, Villarreal GJ, Dickson M, Grimwood J et al. (2005) Widespread parallel evolution in sticklebacks by repeated fixation of Ectodysplasin alleles. Science 307:1928–1933. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1107239
Engelken J, Espadas G, Mancuso FM, Bonet N, Scherr AL, Jímenez-Álvarez V et al. (2016) Signatures of evolutionary adaptation in quantitative trait loci influencing trace element homeostasis in liver. Mol Biol Evol 33:738–754. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv267
Evans PD, Gilbert SL, Mekel-Bobrov N, Vallender EJ, Anderson JR, Vaez-Azizi LM et al. (2005) Microcephalin, a gene regulating brain size, continues to evolve adaptively in humans. Science 309:1717–1720. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113722
Excoffier L, Dupanloup I, Huerta-Sánchez E, Sousa VC, Foll M (2013) Robust demographic inference from genomic and SNP data. PLoS Genet 9:e1003905. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003905
Fan S, Kelly DE, Beltrame MH, Hansen MEB, Mallick S, Ranciaro A et al. (2019) African evolutionary history inferred from whole genome sequence data of 44 indigenous African populations. Genome Biol 20:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1679-2
Fenner JN (2005) Cross-cultural estimation of the human generation interval for use in genetics-based population divergence studies. Am J Phys Anthropol 128:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.20188
Ferrer-Admetlla A, Liang M, Korneliussen T, Nielsen R (2014) On detecting incomplete soft or hard selective sweeps using haplotype structure. Mol Biol Evol 31:1275–1291. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu077
Fujito NT, Satta Y, Hayakawa T, Takahata N (2018a) A new inference method for detecting an ongoing selective sweep. Genes Genet Syst 93:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.18-00008
Fujito NT, Satta Y, Hane M, Matsui A, Yashima K, Kitajima K, Sato C, Takahata N, Hayakawa T (2018b) Positive selection on schizophrenia-associated ST8SIA2 gene in post-glacial Asia. PLoS One 13:e0200278. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200278
Gakuhari T, Nakagome S, Rasmussen S, Allentoft ME, Sato T, Korneliussen T et al. (2020) Ancient Jomon genome sequence analysis sheds light on migration patterns of early East Asian populations. Commun Biol 3:437. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01162-2
Gerbault P, Moret C, Currat M, Sanchez-Mazas A (2009) Impact of selection and demography on the diffusion of lactase persistence. PLoS One 4:e6369. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006369
Gurdasani D, Carstensen T, Tekola-Ayele F, Pagani L, Tachmazidou I, Hatzikotoulas K et al. (2015) The African genome variation project shapes medical genetics in Africa. Nature 517:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13997
Haber M, Jones AL, Connell BA, Asan, Arciero E, Yang H et al. (2019) A rare deep-rooting D0 African Y-chromosomal haplogroup and its implications for the expansion of modern humans out of Africa. Genetics 212:1421–1428. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.119.302368
Henn BM, Gignoux CR, Jobin M, Granka JM, Macpherson JM, Kidd JM et al. (2011) Hunter-gatherer genomic diversity suggests a southern African origin for modern humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5154–5162. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1017511108
Hudson RR (2002) Generating samples under a Wright-Fisher neutral model of genetic variation. Bioinformatics 18:337–338. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.337
Ishikawa A, Kabeya N, Ikeya K, Kakioka R, Cech JN, Osada N et al. (2019) A key metabolic gene for recurrent freshwater colonization and radiation in fishes. Science 364:886–889. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau5656
Itan Y, Powell A, Beaumont MA, Burger J, Thomas MG (2009) The origins of lactase persistence in Europe. PLoS Comput Biol 5:e1000491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000491
Iwasaki RL, Ishiya K, Kanzawa-Kiriyama H, Kawai Y, Gojobori J, Satta Y (2020) Evolutionary history of the risk of SNPs for diffuse-type gastric cancer in the Japanese population. Genes (Basel) 11:775. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070775
Jones DA, Wakeley J (2008) The influence of gene conversion on linkage disequilibrium around a selective sweep. Genetics 180:1251–1259. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.092270
Kamberov YG, Wang S, Tan J, Gerbault P, Wark A, Tan L (2013) Modeling recent human evolution in mice by expression of a selected EDAR variant. Cell 152:691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.016
Kanzawa-Kiriyama H, Jinam TA, Kawai Y, Sato T, Hosomichi K, Tajima A et al. (2019) Late Jomon male and female genome sequences from the Funadomari site in Hokkaido, Japan. Anthropos Sci 127:83–109. https://doi.org/10.1537/ase.190415
Key FM, Abdul-Aziz MA, Mundry R, Peter BM, Sekar A, D’Amato M et al. (2018) Human local adaptation of the TRPM8 cold receptor along a latitudinal cline. PLoS Genet 14:e1007298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007298
Lachance J, Vernot B, Elbers CC, Ferwerda B, Froment A, Bodo JM et al. (2012) Evolutionary history and adaptation from high-coverage whole-genome sequences of diverse African hunter-gatherers. Cell 150:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.009
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski R, Sitarz R (2020) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci 21:4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114012
McManus KF, Taravella AM, Henn BM, Bustamante CD, Sikora M, Cornejo OE (2017) Population genetic analysis of the DARC locus (Duffy) reveals adaptation from standing variation associated with malaria resistance in humans. PLoS Genet 13:e1006560. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006560
Miller CT, Beleza S, Pollen AA, Schluter D, Kittles RA, Shriver MD et al. (2007) cis-Regulatory changes in Kit ligand expression and parallel evolution of pigmentation in sticklebacks and humans. Cell 131:1179–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.055
Nakagome S, Hudson RR, Di Rienzo A (2019) Inferring the model and onset of natural selection under varying population size from the site frequency spectrum and haplotype structure. Proc Biol Sci 286:20182541. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.2541
Oleksyk TK, Smith MW, O’Brien SJ (2010) Genome-wide scans for footprints of natural selection. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365:185–205. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0219
Osada N, Kawai Y (2021) Exploring models of human migration to the Japanese archipelago using genome-wide genetic data. Anthropol Sci 129:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1537/ase.201215
Peter BM, Heurta-Sanchez E, Nielsen R (2012) Distinguishing between selective sweeps from standing variation and from a de novo mutation. PLoS Genet 8:e1003011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003011
Pickrell JK, Coop G, Novembre J, Kudaravalli S, Li JZ, Absher D et al. (2009) Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations. Genome Res 19:826–837. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.087577.108
Rees JS, Castellano S, Andrés AM (2020) The genomics of human local adaptation. Trends Genet 36:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2020.03.006
Satta Y, Zheng W, Nishiyama KV, Iwasaki RL, Hayakawa T, Fujito NT et al. (2020) Two-dimensional site frequency spectrum for detecting, classifying and dating incomplete selective sweeps. Genes Genet Syst 94:283–300. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.19-00012
Saunders MA, Slatkin M, Garner C, Hammer MF, Nachman MW (2005) The extent of linkage disequilibrium caused by selection on G6PD in humans. Genetics 171:1219–1229. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.048140
Schaffner SF, Foo C, Gabriel S, Reich D, Daly MJ, Altshuler D (2005) Calibrating a coalescent simulation of human genome sequence variation. Genome Res 15:1576–1583. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.3709305
Scally A, Durbin R (2012) Revising the human mutation rate: implications for understanding human evolution. Nat Rev Genet 13:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3295
Schlebusch CM, Sjödin P, Skoglund P, Jakobsson M (2012) Stronger signal of recent selection for lactase persistence in Maasai than in Europeans. Eur J Hum Genet 21:550–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.199
Schrider DR, Kern AD (2017) Soft sweeps are the dominant mode of adaptation in the human genome. Mol Biol Evol 34:1863–1877. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx154
Smith J, Coop G, Stephens M, Novembre J (2018) Estimating time to the common ancestor for a beneficial allele. Mol Biol Evol 35:1003–1017. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy006
Soares P, Alshamali F, Pereira JB, Fernandes V, Silva NM, Afonso C et al. (2012) The expansion of mtDNA Haplogroup L3 within and out of Africa. Mol Biol Evol 29:915–927. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr245
Szpiech ZA, Hernandez RD (2014) selscan: an efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection. Mol Biol Evol 31:2824–2827. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu211
Tanikawa C, Urabe Y, Matsuo K, Kubo M, Takahashi A, Ito H et al. (2012) A genome-wide association study identifies two susceptibility loci for duodenal ulcer in the Japanese population. Nat Genet 44:430–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1109
Terhorst J, Kamm JA, Song YS (2017) Robust and scalable inference of population history from hundreds of unphased whole genomes. Nat Genet 49:303–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3748
The Study Group of Millennium Genome Project for Cancer (2008) Genetic variation in PSCA is associated with susceptibility to diffuse-type gastric cancer. Nat Genet 40:730–740. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.152
Tishkoff SA, Reed FA, Ranciaro A, Voight BF, Babbitt CC, Silverman JS et al. (2007) Convergent adaptation of human lactase persistence in Africa and Europe. Nat Genet 39:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1946
Tishkoff SA, Varkonyi R, Cahinhinan N, Abbes S, Argyropoulos G, Destro-Bisol G et al. (2001) Haplotype diversity and linkage disequilibrium at human G6PD: recent origin of alleles that confer malarial resistance. Science 293:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061573
Wang X, Grus WE, Zhang J (2006) Gene losses during human origins. PLoS Biol 4:e52. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040052
Wang Y, Lu D, Chung YJ, Xu S (2018) Genetic structure, divergence and admixture of Han Chinese, Japanese and Korean populations. Hereditas 155:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41065-018-0057-5
Xue Y, Daly A, Yngvadottir B, Liu M, Coop G, Kim Y (2006) Spread of an inactive form of caspase-12 in humans is due to recent positive selection. Am J Hum Genet 78:659–670. https://doi.org/10.1086/503116
Yang MA, Fan X, Sun B, Chen C, Lang J, Ko YC et al. (2020) Ancient DNA indicates human population shifts and admixture in northern and southern China. Science 369:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba0909
Yang Z, Shi H, Ma P, Zhao S, Kong Q, Bian T et al. (2018) Darwinian positive selection on the pleiotropic effects of KITLG explain skin pigmentation and winter temperature adaptation in Eurasians. Mol Biol Evol 35:2272–2283. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy136
Yasukochi Y, Satta Y (2013) Current perspectives on the intensity of natural selection of MHC loci. Immunogenetics 65:479–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0693-x
Zhang C, Li J, Tian L, Lu D, Yuan K, Yuan Y et al. (2015) Differential natural selection of human zinc transporter genes between African and non-African populations. Sci Rep 5:9658. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09658
Acknowledgements
We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. We would also like to thank Drs. Shigeki Nakagome, Naoki Osada, Hie Lim Kim, Tatsuya Ota and Jun Gojobori for valuable advice and discussion in this project, as well as colleagues in our department. Furthermore, we thank Dr. Quintin Lau for English editing. This work has been supported in part by the Graduate University for Advanced Studies, SOKENDAI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RLI was responsible for conducting the research, extracting and analyzing data, interpreting results, reviewing the literature and writing the manuscript. YS was responsible for extracting and analyzing data, interpretation and discussion of results and amending the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Associate editor Giorgio Bertorelle.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasaki, R.L., Satta, Y. Spatial and temporal diversity of positive selection on shared haplotypes at the PSCA locus among worldwide human populations. Heredity 131, 156–169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-023-00631-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-023-00631-8