Abstract
Purpose
To compare the safety and efficacy of subconjunctival injection of Mitomycin C(MMC) with sponge-applied MMC during trabeculectomy.
Methods
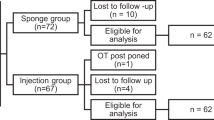
This prospective, randomised, interventional study was conducted on consecutive patients with uncontrolled glaucoma. 137 patients were randomised into an Injection group (Group 1, n = 66) and a sponge group (Group 2, n = 71). Trabeculectomy was performed in all patients who were followed up on days 1, 15, 30, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 2 years & 3 years postoperatively. Baseline & follow-up visits were compared to find out difference in the number of antiglaucoma medications (AGM), Intraocular pressure (IOP), and Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA). In Group 1, the surgeon used MMC 0.2 mg/ml as subconjunctival injection and two separate semicircular surgical sponges soaked with MMC solution of 0.2 mg/mL were inserted subconjunctivally in Group 2.
Results
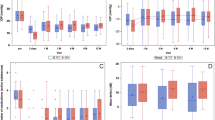
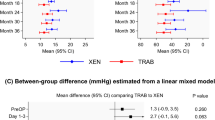
Mean preop IOP was 34.21 ± 13.3 mmHg & 34.17 ± 10.6 mmHg in group 1 & 2 respectively, which reduced to 11.34 ± 3.7& 12.57 ± 4.7 mmHg(6 months),11.97 ± 4.2 & 13.60 ± 5.3 mmHg(1 year),12.42 ± 4.4 & 11.77 ± 2.8 mmHg (2 years) &11.25 ± 3.2 & 11.81 ± 3.2 mmHg at final visit(P < 0.001 in both groups)with no significant difference between the groups. The mean number of preoperative AGM was 2.32 ± 0.7 & 2.32 ± 0.8 in group1 & 2 respectively which reduced to 0.78 ± 0.9 (P < 0.001) & 1.13 ± 1.1(P = 0.930) at 3 years. Overall success rates were 75.3% in group 1 and 70.7% in group 2 at 3 years(p = 0.512). Postoperative complications and the final post-operative visual outcomes were similar between the groups.
Conclusion
Subconjunctival Injection of MMC is as safe and effective as sponge application with comparable surgical outcomes and complications in the long term.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author and approval by the Clinical Audit Committee of the institute. The data are not publicly available due to them containing information that could compromise research participant privacy.
References
Cairns JE. Trabeculectomy. Preliminary report of a new method. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968;66:673–9.
Wilkins, M, Indar, A & Wormald, R Intra-operative mitomycin C for glaucoma surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD002897 (2001) https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002897.
Khaw PT, Chiang M, Shah P, Sii F, Lockwood A, Khalili A. Enhanced trabeculectomy: the moorfields safer surgery system. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;59:15–35.
Robin AL, Ramakrishnan R, Krishnadas R, Smith SD, Katz JD, Selvaraj S, et al. A long-term dose-response study of mitomycin in glaucoma filtration surgery. Arch Ophthalmol Chic Ill 1960. 1997;115:969–74.
Neelakantan A, Rao BS, Vijaya L, Grandham SB, Krishnan N, Priya VS, et al. Effect of the concentration and duration of application of mitomycin C in trabeculectomy. Ophthalmic Surg. 1994;25:612–5.
Shin DH, Tsai CS, Kupin TH, Olivier MM. Retained cellulose sponge after trabeculectomy with adjunctive subconjunctival mitomycin C. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994;118:111–2.
Choudhary S, Sen S, Gupta O. An unusual case of posttrabeculectomy conjunctival granuloma. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2018;11:52–4.
Khamar M, Bhojwani D, Patel P, Vasavada A. Leftover mitomycin-c sponge causing blebitis. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1753–5.
Lim MC, Hom B, Watnik MR, Brandt JD, Altman AR, Paul T, et al. A comparison of trabeculectomy surgery outcomes With Mitomycin-C applied by intra-tenon injection versus sponge. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;216:243–56.
Pakravan M, Esfandiari H, Yazdani S, Douzandeh A, Amouhashemi N, Yaseri M, et al. Mitomycin C-augmented trabeculectomy: subtenon injection versus soaked sponges: a randomised clinical trial. Br J Ophthalmol. 2017;101:1275–80.
Kandarakis SA, Papakonstantinou E, Petrou P, Diagourtas A, Ifantides C, Georgalas I, Serle J. One-year randomized comparison of safety and efficacy of trabeculectomy with mitomycin C sub-tenon injection versus Mitomycin C-Infused Sponges. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2022;5:77–84.
Maheshwari D, Kanduri S, Rengappa R, Kadar MA. Intraoperative injection versus sponge-applied mitomycin C during trabeculectomy: one-year study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:615–9.
Lee E, Doyle E, Jenkins C. Trabeculectomy surgery augmented with intra-Tenon injection of mitomycin C. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008;86:866–70.
S Khouri A, Huang G, Y Huang L. Intraoperative injection vs sponge-applied Mitomycin C during trabeculectomy: one-year study. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2017;11:101–6.
Esfandiari H, Pakravan M, Yazdani S, Doozandeh A, Yaseri M, Conner IP. Treatment outcomes of Mitomycin C-Augmented trabeculectomy, sub-tenon injection versus soaked sponges, after 3 years of Follow-up. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2018;1:66–74.
Swogger J, Conner IP, Rosano M, Kemmerer M, Happ-Smith C, Wells A, et al. Injected versus sponge-applied Mitomycin C (MMC) during modified trabeculectomy in New Zealand White Rabbit Model. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020;9:23.
Guimarães ME, de Pádua Soares Bezerra B, de Miranda Cordeiro F, Carvalho CH, Danif DN, Prata TS, et al. Glaucoma surgery with soaked sponges with Mitomycin C vs sub-tenon injection: short-term outcomes. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2019;13:50–54.
Kalarn S, Le T, Rhee DJ. The role of trabeculectomy in the era of minimally invasive glaucoma surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022;33:112–8.
Sawchyn AK, Slabaugh MA. Innovations and adaptations in trabeculectomy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2016;27:158–63.
You Y, Gu Y, Fang C, Ma X. Long-term effects of simultaneous subconjunctival and subscleral Mitomycin C application in repeat trabeculectomy. J Glaucoma. 2002;11:110–8.
Holló G. Wound healing and glaucoma surgery: modulating the scarring process with conventional antimetabolites and new molecules. Dev Ophthalmol. 2012;50:79–89.
Georgopoulos M, Vass C, Vatanparast Z. Impact of irrigation in a new model for in vitro diffusion of mitomycin-C after episcleral application. Curr Eye Res. 2002;25:221–5.
Mehel E, Weber M, Stork L, Péchereau A. A novel method for controlling the quantity of mitomycin-C applied during filtering surgery for glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 1998;14:491–6.
Mietz H, Diestelhorst M, Rump AF, Theisohn M, Klaus W, Krieglstein GK. Ocular concentrations of mitomycin C using different delivery devices. Ophthalmologica. 1998;212:37–42.
Chiew W, Guo X, Ang BH, Lim AH, Yip LL. Comparison of surgical outcomes of sponge application versus subconjunctival injection of Mitomycin-C during combined phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy surgery in Asian eyes. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2021;33:253–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CONCEPTION: Constructing an idea or hypothesis for research and/or manuscript: DM, MRP. DESIGN: Planning methodology to reach the conclusion: DM, MRP. SUPERVISION: Organising and supervising the course of the project or the article and taking the responsibility: DM, MRP, RR, MAK, NP. FUNDINGS: Providing personnel, environmental and financial support and tools and instruments that are vital for the project: NIL. MATERIALS: Biological materials, reagents and referred patients: DM, RR, MAK. DATA COLLECTION AND/OR PROCESSING: Taking responsibility in execution of the experiments, patient follow-up, data management and reporting: DM, MRP, PHM. ANALYSIS AND/OR INTERPRETATION: Taking responsibility in logical interpretation and presentation of the results: DM, MRP. LITERATURE REVIEW: Taking responsibility in this necessary function: DM, MRP, PHM. WRITER: Taking responsibility in the construction of the whole or body of the manuscript: DM, MRP. CRITICAL REVIEW: Reviewing the article before submission not only for spelling and grammar but also for its intellectual content.: DM, MRP, NP. OTHER.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maheshwari, D., Pillai, M.R., HM, P. et al. Long-term outcomes of Mitomycin-C augmented trabeculectomy using subconjunctival injections versus soaked sponges: a randomised controlled trial. Eye 38, 968–972 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02816-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02816-1