Abstract
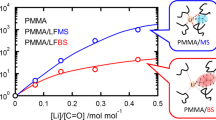
Lithium halides are easily dispersed in poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and lead to strong physical crosslinking with PMMA. We investigated the additional effects of various lithium halides, such as LiCl, LiBr, and LiI salts, on the rheological and mechanical properties of PMMA. The salts were homogeneously dispersed in the PMMA matrix, and the flow zone expanded owing to the pinning effects of the molten PMMA chains as the anion size increased. Furthermore, the brittleness of the PMMA solids doped with LiX (X = Cl, Br, and I) was analyzed using the Griffith theory, which suggested that the stress concentration around the salts in the PMMA matrix leads to the initiation of macroscopic fractures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe M, Itoh M, Sanui K, Ogata N. Carrier transport and generation processes in polymer electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) networks. Macromolecules. 1987;20:569–73.
Yang Y, Zhang J, Zhou C, Wu S, Xu S, Liu W, et al. Effect of lithium iodide addition on polyethylene oxide-poly(vinylidene fluoride) polymer-blend electrolyte for dye-sensitized nanocrystalline solar cell. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112:6594–602.
Zhang LZ, Wang YY, Wang CL, Xiang H. Synthesis and characterization of a PVA/LiCl blend membrane for air dehumidification. J Membr Sci. 2008;308:198–206.
Idris A, Ahmed I, Limin MA. Influence of lithium chloride, lithium bromide and lithium fluoride additives on performance of polyethersulfone membranes and its application in the treatment of palm oil mill effluent. Desalination. 2010;250:805–9.
Jiang X, Li H, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Hou L. Studies of the plasticizing effect of different hydrophilic inorganic salts on starch/poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;82:223–30.
Saari RA, Maeno R, Tsuyuguchi R, Marujiwat W, Phulkerd P, Yamaguchi M. Impact of Lithium halides on rheological properties of aqueous solution of poly(vinyl alcohol). J Polym Res. 2020;27:218.
Bianchi E, Ciferri A, Tealdi A, Torre R, Valenti B. Bulk properties of synthetic polymer/inorganic salt systems. II. Crystallization kinetics of salted polycaproamide. 1974;7:495–500.
Xu Y, Sun W, Li W, Hu X, Zhou H, Weng S. Investigation on the Interaction between polyamide and lithium salts. Polymer. 1999;77:2685–90.
Wu Y, Xu Y, Wang D, Zhao Y, Weng S, Xu D, et al. FT-IR spectroscopic investigation on the interaction between nylon 66 and lithium salts. J Appl Polym Sci 2004;91:2869–75.
Hofmeister F. Zur Lehre von der Wirkung der Salze -. Zweite Mittheilung. Arch Exp Pathol und Pharmakologie. 1888;24:247–60.
Saari RA, Nasri MS, Marujiwat W, Maeno R, Yamaguchi M. Application of the Hofmeister series to the structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) films containing metal salts. Polym J 2021;53:557–64.
Sato Y, Ito A, Maeda S, Yamaguchi M. Structure and optical properties of transparent polyamide 6 containing lithium bromide. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 2018;56:1513–20.
Miyagawa A, Ayerdurai V, Nobukawa S, Yamaguchi M. Viscoelastic properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) with high glass transition temperature by lithium salt addition. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 2016;54:2388–94.
Ito A, Phulkerd P, Ayerdurai V, Soga M, Courtoux A, Miyagawa A, et al. Enhancement of the glass transition temperature of poly(methyl methacrylate) by salt. Polym J 2018;50:857–63.
Ito A, Maeno R, Yamaguchi M. Control of optical and mechanical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) by introducing lithium salt. Opt Mater. 2018;83:152–6.
Ito A, Shin A, Nitta K. Rheological and mechanical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) doped with lithium salts. Polym J. 2022;54:41–6.
Ito A, Nitta KH. Rheological and mechanical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) associated with lithium salts. Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi. 2022;50:87–93.
Ito A, Nitta KH. Additive effects of lithium salts with various anionic species in poly (Methyl methacrylate). Molecules. 2021;26:4096.
Custelcean R, Moyer BA. Anion separation with metal-organic frameworks. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2007;1321–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200700018.
Griffith AA. The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philosophical Transactions of the royal society A. 1921;221:163–198.
Griffits AA. Fracture mechanics of polymers. Polym Eng Sci. 1977;17:144.
Saito Y, Yamamoto H, Nakamura O, Kageyama H, Ishikawa H, Miyoshi T, et al. Determination of ionic self-diffusion coefficients of lithium electrolytes using the pulsed field gradient NMR. J Power Sources. 1999;81–82:772–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. H. Uchida, Institute of Science and Engineering, Kanazawa University, for experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, A., Shin, A. & Nitta, Kh. Additive effects of lithium halides on the tensile and rheological properties of poly(methyl methacrylate). Polym J 54, 1279–1285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00691-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00691-3