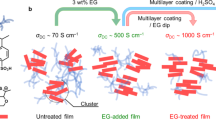
Abstract
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly(4-styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT: PSS) films have strong potential for application in flexible transparent conductive electrodes. As secondary dopants, some polar solvents, such as methanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, and N,N-dimethylformamide, have been revealed to enhance the electrical conductivity of PEDOT: PSS by orders of magnitude. In this study, the electrical conductivity of PEDOT: PSS is shown to be enhanced by a bisphenol additive, bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) sulfone (BPS). The effects of BPS on the chemical structure of PEDOT: PSS were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The PEDOT: PSS conformation is found to undergo a transformation into a highly conductive structure following the addition of BPS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou J, Fukawa T, Kimura M. Directional electromechanical properties of PEDOT/PSS films containing aligned electrospun nanofibers. Polym J. 2011;43:849–54.
Groenendaal LB, Jonas F, Freitag D, Pielartzik H, Reynolds JR. Poly(3,4‐ethylenedioxythiophene) and its derivatives: past, present, and future. Adv Mater. 2000;12:481–94.
Xi F, Bingang X, Shenghua L, Chaohua C, Jinzhao W, Feng Y. Transfer-printed PEDOT: PSS electrodes using mild acids for high conductivity and improved stability with application to flexible organic solar cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:14029–36.
Wakabayashi T, Katsunuma M, Kudo K, Okuzaki H. pH-tunable high-performance PEDOT: PSS aluminum solid electrolytic capacitors. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2018;1:2157–63.
Takano T, Masunaga H, Fujiwara A, Okuzaki H, Sasaki T. PEDOT nanocrystal in highly conductive PEDOT: PSS polymer films. Macromolecules. 2012;45:3859–65.
Shi H, Liu C, Jiang Q, Xu J. Effective approaches to improve the electrical conductivity of PEDOT:PSS: a review. Adv Electron Mater. 2015;1:1500017.
Pasha A, Roy AS, Murugendrappa MV, Al-Hartomy OA, Khasim S. Conductivity and dielectric properties of PEDOT-PSS doped DMSO nanocomposites thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2016;27:8332–9.
Horii T, Li Y, Okuzaki H. Correlation between the hierarchical structure and electrical conductivity of PEDOT/PSS. Polym J. 2015;47:695–9.
Ouyang J. Secondary doping methods to significantly enhance the conductivity of PEDOT: PSS for its application as transparent electrode of optoelectronic devices. Displays. 2013;34:423–36.
Ichikawa S, Toshima N. Improvement of thermoelectric properties of composite films of PEDOT-PSS with xylitol by means of stretching and solvent treatment. Polym J. 2015;47:522–6.
Okuzaki H, Harashina Y, Yan H. Highly conductive PEDOT/PSS microfibers fabricated by wet-spinning and dip-treatment in ethylene glycol. Europ. Polym J. 2009;45:256–61.
Konagaya S, Tawara Y, Inoue M, Furuhashi H, Terada M, Torimoto T. Effect of phenol derivatives on the conductivity enhancement of poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly (styrene sulfonic acid) (PEDOT: PSS), Proceedings of 18th European conference on composite materials. Applied Mechanics Laboratory: 2019.
Xia Y, Sun K, Ouyang J. Solution-processed metallic conducting polymer films as transparent electrode of optoelectronic devices. Adv Mater. 2012;24:2436–40.
Kim N, Kee S, Lee SH, Lee BH, Kahng YH, Jo YR, et al. Highly conductive PEDOT: PSS nanofibrils induced by solution-processed crystallization. Adv Mater. 2014;26:2268–72.
Panigrahy S, Kandasubramanian B. Polymeric thermoelectric PEDOT: PSS & composites: synthesis, progress, and applications. Eur Polym J. 2020;132:109426.
Ouyang L, Musumeci C, Jafari MJ, Ederth T, Inganäs O. Imaging the phase separation between PEDOT and polyelectrolytes during processing of highly conductive PEDOTPSS film. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:19764–73.
Aasmundtveit KE, Samuelsent EJ, Pettersson LAA, Inganäs O, Johansson T, Feidenhans R. Structure of thin films of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Synth Met. 1999;101:561–4.
Niu L, Kvarnström C, Fröberg K, Ivaska A. Electrochemically controlled surface morphology and crystallinity in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films. Synth Met. 2001;122:425–9.
Kim EG, Brédas JL. Electronic evolution of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT): from the isolated chain to the pristine and heavily doped crystals. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:16880–9.
Chaudhary N, Singh A, Aswal DK, Bharti M, Sharma A, Tillu AR, et al. High energy electron beam induced improved thermoelectric properties of PEDOT:PSS films. Polymer. 2020;202:122645.
Babaie A, Bakhshandeh B, Abedi A, Mohammadnejad J, Shabani I, Ardeshirylajimi A. et al. Synergistic effects of conductive PVA/PEDOT electrospun scaffolds and electrical stimulation for more effective neural tissue engineering. Eur Polym J. 2020;140:110051.
Sakunpongpitiporn PK, Phasuksom K, Paradee N, Sirivat A. Facile synthesis of highly conductive PEDOT:PSS via surfactant templates. RSC Adv. 2019;9:6363–78.
Li X, Jiang Y, Shuai L, Wang L, Meng L, Mu X. Sulfonated copolymers with SO3H and COOH groups for the hydrolysis of polysaccharides. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:1283–9.
Khong SH, Sivaramakrishnan S, Png RQ, Wong LY, Chia PJ, Chua LL, et al. General photo-patterning of polyelectrolyte thin films via efficient ionic bis(fluorinated phenyl azide) photo-crosslinkers and their post-deposition modification. Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17:2490–9.
Koizumi Y, Ohira M, Watanabe T, Nishiyama H, Tomita I, Inagi S. Synthesis of Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–platinum and poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) –poly(styrenesulfonate) hybrid fibers by alternating current bipolar electropolymerization. Langmuir. 2018;34:7598–603.
Liu Y, Weng B, Razal JM, Xu Q, Zhao C, Hou Y, et al. High-performance flexible allsolid-state supercapacitor from large free-standing graphene PEDOT/PSS Films. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17045.
He H, Zhang L, Guan X, Cheng H, Liu X, Yu S, et al. Biocompatible conductive polymers with high conductivity and high stretchability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:26185–19.
Mikhaylova Y, Adam G, Haussler L, Eichhorn KJ, Voit B. Temperature-dependent FTIR spectroscopic and thermoanalytic studies of hydrogen bonding of hudroxyl (phenolic group) terminated hyperbranched aromatic polyesters. J, Mol Struct. 2006;788:80–88.
Coleman MM, Skrovanek DJ, Hu J, Painter PC. Hydrogen bonding in polymer blends. 1. FTIR studies of urethane-ether blends. Macromolecules. 1988;21:59–65.
Carmo M, Roepke T, Roth C, dos Santos AM, Poco JGR, Linardi MA. Novel electrocatalyst support with proton conductive properties for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications. J Power Sources. 2009;191:330–7.
Al-Graiti W, Foroughi J, Liu Y, Chen J. Hybrid graphene/conducting polymer strip sensors for sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of serotonin. ACS Omega. 2019;4:22169–77.
Yin C, Yang C, Jiang M, Deng C, Yang L, Li J, et al. A novel and facile one-pot solvothermal synthesis of PEDOT–PSS/Ni–Mn–Co–O hybrid as an advanced supercapacitor electrode material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:2741–52.
Ravit R, Abdullah J, Ahmad I, Sulaiman Y. Electrochemical performance of poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythipohene)/nanocrystalline cellulose (PEDOT/NCC) film for supercapacitor. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;203:128–38.
Zhao Z, Moussa M, Shi G, Meng Q, Wang R, Ma J. Compressible, electrically conductive, fibre-like, three-dimensional PEDOT-based composite aerogels towards energy storage applications. Comp Sci Technol. 2016;127:36–46.
Ely F, Matsumoto A, Zoetebier B, Peressinotto VS, Hirata MK, de Sousa DA. Handheld and automated ultrasonic spray deposition of conductive PEDOT: PSS films and their application in AC EL devices. Org Electron. 201;15:1062–70.
Zhou T, Orcid GX, Orcid SG, Huang M, Huang M, Luo J, et al. Simple InCl3 Doped PEDOT: PSS and UV–ozone treatment strategy: external quantum efficiency up to 21% for solution-processed organic light-emitting devices with a thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitter. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:34139–45.
Ouyang J, Xu Q, Chu CW, Yang Y, Li G, Shinar J. On the mechanism of conductivity enhancement in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly (styrene sulfonate) film through solvent treatment. Polymer. 2004;45:8443–50.
Mitraka E, Jafari MJ, Vagin M, Liu X, Fahlman M, Ederth T, et al. Oxygen-induced doping on reduced PEDOT. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5:4404–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Foundation for the Electrotechnology of Chubu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morimune-Moriya, S., Tanahashi, H., Sasaki, K. et al. Effect of bisphenols on the electrical conductivity and structure of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly(styrene sulfonate). Polym J 54, 707–713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00617-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00617-z
This article is cited by
-
PJ ZEON award for outstanding papers in Polymer Journal 2022
Polymer Journal (2023)