Abstract
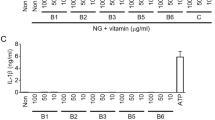
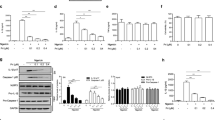
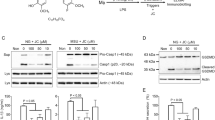
Vitamin K refers to a group of structurally similar vitamins that are essential for proper blood coagulation, as well as bone and cardiovascular health. Previous studies have indicated that vitamin K may also have anti-inflammatory properties, although the underlying mechanisms of its anti-inflammatory effects remain unclear. The NLRP3 inflammasome is a multiprotein complex, and its activation leads to IL-1β and IL-18 secretion and contributes to the pathogenesis of various human inflammatory diseases. Here, we show that synthetic vitamins K3 and K4 are selective, potent inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome and specifically block the interaction between NLRP3 and ASC, thereby inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. Moreover, we show that treatment with vitamin K3 or K4 attenuates the severity of inflammation in a mouse model of peritonitis. Our results demonstrate that vitamins K3 and K4 exert their anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and indicate that vitamin K supplementation may be a treatment option for NLRP3-associated inflammatory diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ivanova, D. et al. Vitamin K: Redox-modulation, prevention of mitochondrial dysfunction and anticancer effect. Redox Biol. 16, 352–358 (2018).
DiNicolantonio, J. J., Bhutani, J. & O’Keefe, J. H. The health benefits of vitamin K. Open Heart 2, e000300 (2015).
Thijssen, H. H., Vervoort, L. M., Schurgers, L. J. & Shearer, M. J. Menadione is a metabolite of oral vitamin K. Br. J. Nutr. 95, 260–266 (2006).
Hirota, Y. et al. Menadione (vitamin K3) is a catabolic product of oral phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in the intestine and a circulating precursor of tissue menaquinone-4 (vitamin K2) in rats. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 33071–33080 (2013).
Thijssen, H. H. & Drittij-Reijnders, M. J. Vitamin K distribution in rat tissues: dietary phylloquinone is a source of tissue menaquinone-4. Br. J. Nutr. 72, 415–425 (1994).
Rosati, M. Saunders handbook of veterinary drugs: small and large animals. Can. Vet. J. 58, 728 (2017).
Wen, L., Chen, J., Duan, L. & Li, S. Vitamin Kdependent proteins involved in bone and cardiovascular health (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 18, 3–15 (2018).
Li, Y., Chen, J. P., Duan, L. & Li, S. Effect of vitamin K2 on type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 136, 39–51 (2018).
Nowak, J. K. et al. Prevalence and correlates of vitamin K deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 4, 4768 (2014).
Cozzolino, M. et al. Vitamin K in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 11, 168 (2019).
Ohsaki, Y. et al. Vitamin K suppresses the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines in cultured macrophage-like cells via the inhibition of the activation of nuclear factor kappaB through the repression of IKKalpha/beta phosphorylation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 21, 1120–1126 (2010).
Ohsaki, Y. et al. Vitamin K suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the rat. Biosci., Biotechnol., Biochem. 70, 926–932 (2006).
Gong, T., Yang, Y., Jin, T., Jiang, W. & Zhou, R. Orchestration of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by ion fluxes. Trends Immunol. 39, 393–406 (2018).
Gong, T., Jiang, W. & Zhou, R. Control of inflammasome activation by phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 43, 685–699 (2018).
Tang, T., Gong, T., Jiang, W. & Zhou, R. GPCRs in NLRP3 inflammasome activation, regulation, and therapeutics. Trends Pharm. Sci. 39, 798–811 (2018).
Mortimer, L., Moreau, F. & MacDonald, J. A. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition is disrupted in a group of auto-inflammatory disease CAPS mutations. Nat. Immunol. 17, 1176–1186 (2016).
Jiang, H. et al. Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders. J. Exp. Med. 214, 3219–3238 (2017).
Huang, Y. et al. Tranilast directly targets NLRP3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 10, e8689 (2018).
He, H. et al. Oridonin is a covalent NLRP3 inhibitor with strong anti-inflammasome activity. Nat. Commun. 9, 2550 (2018).
Yan, Y. et al. Omega-3 fatty acids prevent inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 38, 1154–1163 (2013).
Kayagaki, N. et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 526, 666–671 (2015).
Kayagaki, N. et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 479, 117–121 (2011).
Broz, P. & Dixit, V. M. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 407–420 (2016).
Xu, H. et al. Innate immune sensing of bacterial modifications of Rho GTPases by the Pyrin inflammasome. Nature 513, 237–241 (2014).
Gurung, P., Lukens, J. R. & Kanneganti, T. D. Mitochondria: diversity in the regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Trends Mol. Med. 21, 193–201 (2015).
He, Y., Zeng, M. Y., Yang, D., Motro, B. & Nunez, G. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 530, 354–357 (2016).
Shi, H. et al. NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component. Nat. Immunol. 17, 250–258 (2016).
Swanson, K. V. & Deng, M. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19, 477–489 (2019).
So, A. K. & Martinon, F. Inflammation in gout: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 13, 639–647 (2017).
Tanaka, S. et al. Vitamin K3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 160, 283–292 (2010).
Harshman, S. G. & Shea, M. K. The role of vitamin K in chronic aging diseases: inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and osteoarthritis. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 5, 90–98 (2016).
Hodges, S. J., Pilkington, M. J., Shearer, M. J., Bitensky, L. & Chayen, J. Age-related changes in the circulating levels of congeners of vitamin K2, menaquinone-7 and menaquinone-8. Clin. Sci. (Lond., Engl.: 1979). 78, 63–66 (1990).
Shearer, M. J. Vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB) in early infancy. Blood Rev. 23, 49–59 (2009).
Conly, J. & Stein, K. Reduction of vitamin K2 concentrations in human liver associated with the use of broad spectrum antimicrobials. Clin. Invest. Med. Med. Clin. et. Exp. 17, 531–539 (1994).
Kuwabara, A. et al. High prevalence of vitamin K and D deficiency and decreased BMD in inflammatory bowel disease. Osteoporos. Int. 20, 935–942 (2009).
Misra, D. et al. Vitamin K deficiency is associated with incident knee osteoarthritis. Am. J. Med. 126, 243–248 (2013).
Wolf, P., Hupfeld, C., Dorrestein, G. & Kamphues, J. Investigations in pet birds (Agapornis spp.) fed different vitamin K contents in the diet. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 89, 222–228 (2005).
Ho, P. C. & Wong, V. K. Influence of DL methionine and sodium metabisulphite on the photostability of vitamin k1. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 52, 129–133 (1998).
Hassan G. S. Menadione. Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology. 227–313, Vol. 38 (Elsevier; 2013).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2019YFA0508503), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant number XDB29030102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81701549, 91742202, 81525013, 81722022, and 81821001), the Young Talent Support Program and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2019-026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Z., Y.H., B.H., Y.C., and X.W. performed the experiments. R.Z., X.W., T.G., and W.J. designed the research. T.G., W.J., and R.Z. wrote the manuscript. W.J. supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Hou, Y., He, H. et al. Synthetic vitamin K analogs inhibit inflammation by targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol Immunol 18, 2422–2430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-00545-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-00545-z