Abstract
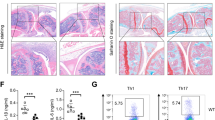
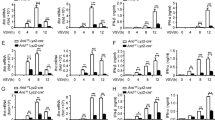
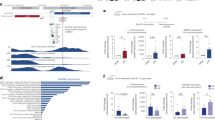
IL-6 plays important and pleiotropic roles in infection and inflammatory diseases, and its production needs to be tightly regulated. However, the epigenetic mechanism underlying Il6 gene transcription remains to be fully elucidated. Here, we report that lysine-specific demethylase 2b (KDM2B), which demethylates H3K4me3 and H3K36me2, is required in macrophages and dendritic cells for the induction of IL-6 but not TNF-α, IL-1, and IFN-β. Compared to wild-type mice, KDM2B-deficient mice were more resistant to endotoxin shock and colitis, with a less severe inflammatory pathogenesis phenotype and decreased IL-6 production in sera. KDM2B selectively bound the Il6 promoter but did not alter histone demethylation; instead, KDM2B interacted with Brahma-related gene 1 (Brg1), the core ATPase subunit of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes, to facilitate chromatin accessibility of the Il6 promoter. Furthermore, KDM2B directly recruited RNA Polymerase II to further initiate and promote Il6 transcription. Thus, our finding identifies a novel nonclassical function of KDM2B in gene-specific transcription initiation and enhancement of Il6 independent of its demethylase activity and adds new insight into the specific epigenetic modification mechanism of inflammatory immune responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Shea, J. J., Ma, A. & Lipsky, P. Cytokines and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 37–45 (2002).
Takeuchi, O. & Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 (2010).
Medzhitov, R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 449, 819–826 (2007).
Cao, X. Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 35–50 (2016).
Zhang, Q., Raoof, M., Chen, Y., Sumi, Y. & Hauser, C. J. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature 464, 104–107 (2010).
Harris, H. E., Andersson, U. & Pisetsky, D. S. HMGB1: a multifunctional alarmin driving autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Rheum. 8, 195–202 (2012).
Mills, K. H. TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 807–822 (2011).
Rosser, E. C. et al. Regulatory B cells are induced by gut microbiota-driven interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 production. Nat. Med. 20, 1334–1339 (2014).
Kopf, M. et al. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature 368, 339–342 (1994).
Tanaka, Y. & Martin Mola, E. IL-6 targeting compared to TNF targeting in rheumatoid arthritis: studies of olokizumab, sarilumab and sirukumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 1595–1597 (2014).
Atreya, R. et al. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat. Med. 6, 583–588 (2000).
Jones, S. A., Scheller, J. & Rose-John, S. Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 3375–3383 (2011).
Smith, Z. D. & Meissner, A. DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 204–220 (2013).
Ventham, N. T., Kennedy, N. A., Nimmo, E. R. & Satsangi, J. Beyond gene discovery in inflammatory bowel disease: the emerging role of epigenetics. Gastroenterology 145, 293–308 (2013).
Narlikar, G. J., Sundaramoorthy, R. & Owen-Hughes, T. Mechanisms and functions of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling enzymes. Cell 154, 490–503 (2013).
Black, J. C., Van Rechem, C. & Whetstine, J. R. Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact. Mol. Cell 48, 491–507 (2012).
Kooistra, S. M. & Helin, K. Molecular mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 297–311 (2012).
Park, S. Y., Park, J. W. & Chun, Y. S. Jumonji histone demethylases as emerging therapeutic targets. Pharm. Res. 105, 146–151 (2016).
Shi, Y. Histone lysine demethylases: emerging roles in development, physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 829–833 (2007).
Tsukada, Y. I., Fang, J., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Warren, M. E. & Tempst, P. Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Nature 439, 811–816 (2006).
Jin, H. et al. Kdm2b maintains murine embryonic stem cell status by recruiting PRC1 complex to CpG islands of developmental genes. Nat. Cell. Biol. 15, 373–384 (2013).
Liang, G., He, J. & Zhang, Y. Kdm2b promotes induced pluripotent stem cell generation by facilitating gene activation early in reprogramming. Nat. Cell. Biol. 14, 457–466 (2012).
Janzer, A. et al. The H3K4me3 histone demethylase Fbxl10 is a regulator of chemokine expression, cellular morphology, and the metabolome of fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 30984–30992 (2012).
Han, X. R. et al. KDM2B/FBXL10 targets c-Fos for ubiquitylation and degradation in response to mitogenic stimulation. Oncogene 35, 4179–4190 (2016).
Wirtz, S., Neufert, C., Weigmann, B. & Neurath, M. F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat. Protoc. 2, 541–546 (2007).
Liu, X. et al. Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining activation of the kinase Btk. Nat. Immunol. 12, 416–424 (2011).
Zhang, Q. et al. Tet2 is required to resolve inflammation by recruiting Hdac2 to specifically repress IL-6. Nature 525, 389–393 (2015).
Simon, J. M., Giresi, P. G., Davis, I. J. & Lieb, J. D. Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA. Nat. Protoc. 7, 256–267 (2012).
Ramirezcarrozzi, V. R. et al. Selective and antagonistic functions of SWI/SNF and Mi-2beta nucleosome remodeling complexes during an inflammatory response. Genes Dev. 20, 282–296 (2006).
Hunter, C. A. & Jones, S. A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 16, 448–457 (2015).
Tanaka, T., Narazaki, M. & Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. CSH Perspect. Biol. 6, a016295 (2014).
Hargreaves, D. C., Horng, T. & Medzhitov, R. Control of inducible gene expression by signal-dependent transcriptional elongation. Cell 138, 129–145 (2009).
Iglesias, M. J. et al. Combined chromatin and expression analysis reveals specific regulatory mechanisms within cytokine genes in the macrophage early immune response. PLoS ONE 7, e32306 (2012).
Fowler, T., Sen, R. & Roy, A. L. Regulation of primary response genes. Mol. Cell 44, 348–360 (2011).
Ramirez-Carrozzi, V. R. et al. A unifying model for the selective regulation of inducible transcription by CpG islands and nucleosome remodeling. Cell 138, 114–128 (2009).
Euskirchen, G., Auerbach, R. K. & Snyder, M. SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factors: multiscale analyses and diverse functions. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 30897–30905 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank X. Sun and M. Jin for technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570871, 81571541, 81771695, 31770970, and 81770094), Program of Shanghai Chief Scientist of Medical and Health Subject (2018BR16), and Shuguang Program sponsored by the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (18SG33).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, B. et al. KDM2B promotes IL-6 production and inflammatory responses through Brg1-mediated chromatin remodeling. Cell Mol Immunol 17, 834–842 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0251-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0251-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Captive ERVWE1 triggers impairment of 5-HT neuronal plasticity in the first-episode schizophrenia by post-transcriptional activation of HTR1B in ALKBH5-m6A dependent epigenetic mechanisms
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
H3K4me3-related lncRNAs signature and comprehensive analysis of H3K4me3 regulating tumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma
Respiratory Research (2023)
-
Histone demethylases in the regulation of immunity and inflammation
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Histone demethylase KDM5B licenses macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses by repressing Nfkbia transcription
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
OTUD6A promotes prostate tumorigenesis via deubiquitinating Brg1 and AR
Communications Biology (2022)