Abstract
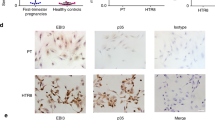
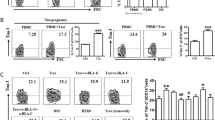
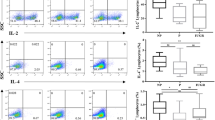
The disturbance of maternal immune tolerance to a semiallogeneic fetus is recognized as one of the key pathologies of preeclampsia (PE), in which an imbalance between the inflammation-limiting regulatory T cells (Tregs) and the inflammation-mediating Th17 cells plays an essential role. Previously, we reported that the abnormal upregulation of tetraspannin CD81 in trophoblast cells (fetal component) participated in the pathogenesis of PE. However, as one of the potential immune regulatory molecules, whether CD81 induces PE by interfering with the balance of the maternal immune system has not yet been clarified. Thus, we investigated the relationship between the upregulation of CD81 in trophoblast cells and the imbalance of Treg and Th17 cells in mothers. Here, we demonstrated that upregulation of CD81 in trophoblast cells was accompanied by a decrease in Treg cells and an increase in Th17 cells in both the basal plate (placental maternal side) and peripheral blood of patients with PE. In vitro culture of naïve T cells with medium from the CD81-overexpressing trophoblast cell line HTR-8 resulted in enhanced differentiation of T cells into Th17 cells and decreased the formation of Tregs, which was dependent on the paracrine signaling of IL-6 in trophocytes, induced by CD81. In a CD81-induced PE rat model, we found a significant shift of T cell differentiation towards Th17 cells, and administration of IL-6 antibody mitigated the PE phenotype and the imbalance of the Treg/Th17 cells. These results define a vital regulatory cascade involving trophocyte-derived CD81, IL-6, and maternal Treg/Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of PE and suggests new therapeutic approaches based on CD81 and IL-6 downregulation to prevent human PE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mol, B. W. J. et al. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 387, 999–1011 (2016).
Buurma, A. J. et al. Genetic variants in pre-eclampsia: a meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 19, 289–303 (2013).
Rana, S., Karumanchi, S. A. & Lindheimer, M. D. Angiogenic factors in diagnosis, management, and research in preeclampsia. Hypertension 63, 198–202 (2014).
McGinnis, R., Steinthorsdottir, V., Williams, N. O., Thorleifsson, G. & Shooter, S. Variants in the fetal genome near FLT1 are associated with risk of preeclampsia. Nat. Genet. 49, 1255–1260 (2017).
Redman, C. W. & Sargent, I. L. Immunology of pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 63, 534–543 (2010).
Gobert, M. & Lafaille, J. Maternal-fetal immune tolerance, block by block. Cell 150, 7–9 (2012).
Kimura, A. & Kishimoto, T. IL-6: regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 40, 1830–1835 (2010).
Fu, B. et al. Natural killer cells promote immune tolerance by regulating inflammatory TH17 cells at the human maternal-fetal interface. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, E231–E240 (2013).
Jianjun, Z., Yali, H., Zhiqun, W., Mingming, Z. & Xia, Z. Imbalance of T-cell transcription factors contributes to the Th1 type immunity predominant in pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 63, 38–45 (2010).
Zhang, Y. et al. The altered PD-1/PD-L1 pathway delivers the ‘one-two punch’ effects to promote the Treg/Th17 imbalance in pre-eclampsia. Cell Mol. Immunol. 15, 710–723 (2018).
Erlebacher, A. Mechanisms of T cell tolerance towards the allogeneic fetus. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 23–33 (2013).
Du, M. et al. Embryonic trophoblasts induce decidual regulatory T cell differentiation and maternal-fetal tolerance through thymic stromal lymphopoietin instructing dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 192, 1502–1511 (2014).
Shen, L. et al. Up-regulation of CD81 inhibits cytotrophoblast invasion and mediates maternal endothelial cell dysfunction in preeclampsia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 1940–1945 (2017).
Cunningham, F., Leveno, K., Bloom, S., Hauth, J., Rouse, D. & Spong, C. Williams Obstetrics 23rd edn (McGraw-Hill Education, New York, USA, 2009).
Laurence, A. et al. Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell generation. Immunity 26, 371–381 (2007).
Gong, P. et al. Curcumin improves LPS-induced preeclampsia-like phenotype in rat by inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway. Placenta 41, 45–52 (2016).
Nozu, T., Miyagishi, S., Nozu, R., Takakusaki, K. & Okumura, T. Repeated water avoidance stress induces visceral hypersensitivity: Role of interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and peripheral corticotropin-releasing factor. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 32, 1958–1965 (2017).
Zhang, Y. et al. MicroRNA-155 contributes to preeclampsia by down-regulating CYR61. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 202, 466.e461–467 (2010).
Littman, D. R. & Rudensky, A. Y. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell 140, 845–858 (2010).
Knochelmann, H. M. et al. When worlds collide: Th17 and Treg cells in cancer and autoimmunity. Cell Mol. Immunol. 15, 458–469 (2018).
Fu, B., Tian, Z. & Wei, H. TH17 cells in human recurrent pregnancy loss and pre-eclampsia. Cell Mol. Immunol. 11, 564–570 (2014).
Moffett, A. & Loke, C. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 584–594 (2006).
Li, L., Tu, J., Jiang, Y., Zhou, J. & Schust, D. J. Regulatory T cells decrease invariant natural killer T cell-mediated pregnancy loss in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 10, 613–623 (2017).
Wu, L. et al. IL-7/IL-7R signaling pathway might play a role in recurrent pregnancy losses by increasing inflammatory Th17 cells and decreasing Treg cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 76, 454–464 (2016).
Rahimzadeh, M., Norouzian, M., Arabpour, F. & Naderi, N. Regulatory T-cells and preeclampsia: an overview of literature. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 12, 209–227 (2016).
Trowsdale, J. & Betz, A. G. Mother’s little helpers: mechanisms of maternal-fetal tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 7, 241–246 (2006).
Arck, P. C. & Hecher, K. Fetomaternal immune cross-talk and its consequences for maternal and offspring’s health. Nat. Med. 19, 548–556 (2013).
Varghese, S., Crocker, I., Bruce, I. N. & Tower, C. Systemic lupus erythematosus, regulatory T cells and pregnancy. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 7, 635–648 (2011).
Toldi, G. et al. Decreased number of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in preeclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 87, 1229–1233 (2008).
Prins, J. et al. Preeclampsia is associated with lower percentages of regulatory T cells in maternal blood. Hypertens. Pregnancy 28, 300–311 (2009).
Wang, J., Ioan-Facsinay, A., van der Voort, E. I., Huizinga, T. W. & Toes, R. E. Transient expression of FOXP3 in human activated nonregulatory CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 37, 129–138 (2007).
Miyao, T. et al. Plasticity of Foxp3(+) T cells reflects promiscuous Foxp3 expression in conventional T cells but not reprogramming of regulatory T cells. Immunity 36, 262–275 (2012).
Zhang, Y. et al. Human trophoblast cells induced MDSCs from peripheral blood CD14(+) myelomonocytic cells via elevated levels of CCL2. Cell Mol. Immunol. 13, 615–627 (2016).
Levy, S. Function of the tetraspanin molecule CD81 in B and T cells. Immunol. Res. 58, 179–185 (2014).
Sagi, Y., Landrigan, A., Levy, R. & Levy, S. Complementary costimulation of human T-cell subpopulations by cluster of differentiation 28 (CD28) and CD81. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 1613–1618 (2012).
Li, P., Spolski, R., Liao, W. & Leonard, W. J. Complex interactions of transcription factors in mediating cytokine biology in T cells. Immunol. Rev. 261, 141–156 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571462, 81600353, and 81701472), Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Center (YXZXB2016004), Jiangsu Biobank of Clinical Resources (BM2015004), and Jiangsu Province Grant for Science and Technology (BK20161106). We would like to thank our patients and our colleagues at the Biobank of Nanjing for the donation and collection of placental tissues and blood samples in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.D. and Y.D designed and performed the experiments, data analysis, and manuscript drafting. Y.L. and Z.W. helped to construct the PE rat model and performed part of the flow cytometry analysis. D.L. and N.G. analyzed data and drew the graphs. R.L. and M.Z. summarized the data and wrote the manuscript. L.S. and X.Z designed the study and collected clinical samples. G.Z. and Y.H. planned and supervised this study. All authors have approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Dai, Y., Lei, Y. et al. Upregulation of CD81 in trophoblasts induces an imbalance of Treg/Th17 cells by promoting IL-6 expression in preeclampsia. Cell Mol Immunol 16, 302–312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-018-0186-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-018-0186-9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Diagnostic signature composed of seven genes in HIF-1 signaling pathway for preeclampsia
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2023)
-
IL-32-driven neutrophil activation in preeclampsia
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
Hydroxychloroquine induces apoptosis of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via up-regulation of CD81 contributing to alleviate lupus symptoms
Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Select Early-Life Environmental Exposures and DNA Methylation in the Placenta
Current Environmental Health Reports (2022)
-
Continuous activation of polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells during pregnancy is critical for fetal development
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)