Abstract
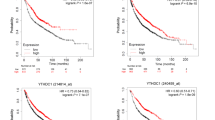
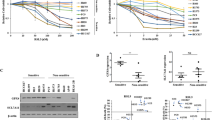
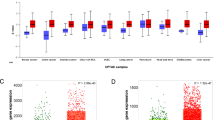
Ferroptosis, a unique form of regulated necrotic cell death, is caused by excessive iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. However, the underlying mechanisms driving ferroptosis in human cancers remain elusive. In this study, we identified TRIM3, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, as a key regulator of ferroptosis. TRIM3 is downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), two major types of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Forced expression of TRIM3 promotes cell death by enhancing the cellular level of ROS and lipid peroxidation. Moreover, our in vivo study determined that TRIM3 overexpression diminishes the tumorigenicity of NSCLC cells, indicating that TRIM3 functions as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC. Mechanistically, TRIM3 directly interacts with SLC7A11/xCT through its NHL domain, leading to SCL7A11 K11-linked ubiquitination at K37, which promotes SLC7A11 proteasome-mediated degradation. Importantly, TRIM3 expression exhibits a negative correlation with SCL7A11 expression in clinical NSCLC samples, and low TRIM3 expression is associated with a worse prognosis. This study reveals that TRIM3 functions as a tumor suppressor that can impede the tumorigenesis of NSCLC by degrading SLC7A11, suggesting a novel therapeutic strategy against NSCLC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brody H. Lung cancer. Nature. 2020;587:S7.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Le X, Nilsson M, Goldman J, Reck M, Nakagawa K, Kato T, et al. Dual EGFR-VEGF pathway inhibition: a promising strategy for patients With EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16:205–15.
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–54.
Wang M, Herbst RS, Boshoff C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med. 2021;27:1345–56.
Abbosh C, Frankell AM, Harrison T, Kisistok J, Garnett A, Johnson L, et al. Tracking early lung cancer metastatic dissemination in TRACERx using ctDNA. Nature. 2023;616:553–62.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33.
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266–82.
Chen J, Li X, Ge C, Min J, Wang F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:467–80.
Zhang Q, Deng T, Zhang H, Zuo D, Zhu Q, Bai M, et al. Adipocyte-derived exosomal MTTP suppresses ferroptosis and promotes chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Adv Sci. 2022;9:e2203357.
Seibt TM, Proneth B, Conrad M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:144–52.
Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H, Liu D, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:43.
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:381–96.
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi AA, et al. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:49.
Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 2021;12:599–620.
Dong H, Xia Y, Jin S, Xue C, Wang Y, Hu R, et al. Nrf2 attenuates ferroptosis-mediated IIR-ALI by modulating TERT and SLC7A11. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:1027.
Gao R, Kalathur RKR, Coto-Llerena M, Ercan C, Buechel D, Shuang S, et al. YAP/TAZ and ATF4 drive resistance to Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by preventing ferroptosis. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13:e14351.
Badeaux AI, Shi Y. Emerging roles for chromatin as a signal integration and storage platform. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:211–24.
Liu T, Jiang L, Tavana O, Gu W. The deubiquitylase OTUB1 mediates ferroptosis via stabilization of SLC7A11. Cancer Res. 2019;79:1913–24.
Li WW, Nie Y, Yang Y, Ran Y, Luo WW, Xiong MG, et al. Ubiquitination of TLR3 by TRIM3 signals its ESCRT-mediated trafficking to the endolysosomes for innate antiviral response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:23707–16.
Yan Q, Sun W, Kujala P, Lotfi Y, Vida TA, Bean AJ. CART: an Hrs/actinin-4/BERP/myosin V protein complex required for efficient receptor recycling. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:2470–82.
Zhuang T, Wang B, Tan X, Wu L, Li X, Li Z, et al. TRIM3 facilitates estrogen signaling and modulates breast cancer cell progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20:45.
Wang X, Zhang Y, Pei X, Guo G, Xue B, Duan X, et al. TRIM3 inhibits P53 signaling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:559.
Chen G, Kong J, Tucker-Burden C, Anand M, Rong Y, Rahman F, et al. Human Brat ortholog TRIM3 is a tumor suppressor that regulates asymmetric cell division in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2014;74:4536–48.
Li C, Tang Z, Zhang W, Ye Z, Liu F. GEPIA2021: integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W242–W246.
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y, Yu Q. Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:48.
Emdad L, Bhoopathi P, Talukdar S, Pradhan AK, Sarkar D, Wang XY, et al. Recent insights into apoptosis and toxic autophagy: the roles of MDA-7/IL-24, a multidimensional anti-cancer therapeutic. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;66:140–54.
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:528–42.
Li D, Li Y. The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:108.
Xie Y, Wang B, Zhao Y, Tao Z, Wang Y, Chen G, et al. Mammary adipocytes protect triple-negative breast cancer cells from ferroptosis. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:72.
Hornbeck PV, Zhang B, Murray B, Kornhauser JM, Latham V, Skrzypek E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D512–520.
Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, et al. Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:174.
Jia X, Zhao C, Zhao W. Emerging roles of MHC class I region-encoded E3 ubiquitin ligases in innate immunity. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687102.
Chao J, Zhang XF, Pan QZ, Zhao JJ, Jiang SS, Wang Y, et al. Decreased expression of TRIM3 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2014;31:102.
Liu Y, Raheja R, Yeh N, Ciznadija D, Pedraza AM, Ozawa T, et al. TRIM3, a tumor suppressor linked to regulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1.). Oncogene. 2014;33:308–15.
Yan J, Wan P, Choksi S, Liu ZG. Necroptosis and tumor progression. Trends Cancer. 2022;8:21–27.
Levine B, Kroemer G. Biological functions of autophagy genes: a disease perspective. Cell. 2019;176:11–42.
Maremonti F, Meyer C, Linkermann A. Mechanisms and models of kidney tubular necrosis and nephron loss. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022;33:472–86.
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Tang D. Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;66:89–100.
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:34.
Sui S, Xu S, Pang D. Emerging role of ferroptosis in breast cancer: new dawn for overcoming tumor progression. Pharm Ther. 2022;232:107992.
Wang X, Chen Y, Wang X, Tian H, Wang Y, Jin J, et al. Stem cell factor SOX2 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer via upregulation of SLC7A11. Cancer Res. 2021;81:5217–29.
Yang J, Zhou Y, Xie S, Wang J, Li Z, Chen L, et al. Metformin induces ferroptosis by inhibiting UFMylation of SLC7A11 in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:206.
Ouyang S, Li H, Lou L, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Mo J, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Redox Biol. 2022;52:102317.
Shen L, Zhang J, Zheng Z, Yang F, Liu S, Wu Y, et al. PHGDH inhibits ferroptosis and promotes malignant progression by upregulating SLC7A11 in bladder cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:5459–74.
Liu J, Xia X, Huang P. xCT: a critical molecule that links cancer metabolism to redox signaling. Mol Ther. 2020;28:2358–66.
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:280–96.
Acknowledgements
The mechanistic scheme of this study was drawn using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Funding
This work was supported by the “333 projects” of Jiangsu Province (grant numbers: BRA2020190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: ZJW; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation: ZJW, NS; investigation: LY, SY, YW, and YL; acquisition of patient specimens: QZ and GHH; article drafting and revising: ZJW; and article writing: ZJW. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All participants provided informed consent. All human tissue research in this study had the approval of ethics committees of the Affiliated Taizhou People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Taizhou, China) and Shanghai Outdo Biotech (Shanghai, China). All of the animal experiments were performed by the relevant guidelines and regulations and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Nanjing Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Shen, N., Wang, Z. et al. TRIM3 facilitates ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer through promoting SLC7A11/xCT K11-linked ubiquitination and degradation. Cell Death Differ 31, 53–64 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-023-01239-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-023-01239-5