Abstract
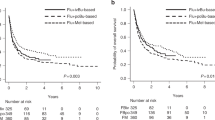
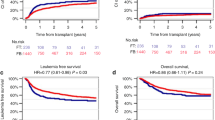
Myeloablative conditioning with fludarabine/busulfan (Flu/Bu4) prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is effective for acute myeloid leukemia. However, the effectiveness of Flu/Bu4 for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) remains poorly understood. Therefore, we retrospectively analyzed nationwide registry data in Japan from 2006 to 2018 and compared transplant outcomes of adult MDS patients receiving Flu/Bu4 and busulfan/cyclophosphamide (Bu4/Cy) using propensity score (PS) matching. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Among 2,482 MDS patients, 153 patients were assigned each to the Flu/Bu4 and Bu4/Cy groups. The 3-year OS rates were 52.7% (95% confidence interval [CI], 43.8–60.8%) and 49.5% (95% CI, 40.8–57.6%) in the Flu/Bu4 and Bu4/Cy group, respectively (P = 0.548). The 3-year progression-free survival (P = 0.858), the cumulative incidence of relapse (P = 0.536), and cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (P = 0.684) were not significantly different between the two groups. According to the findings of subgroup analyses, no patient had a favorable OS when using either of the two regimens. In conclusion, although our PS-matched cohort mainly comprised older patients who had a low hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index and low-risk disease status, Flu/Bu4 could be an alternative to Bu4/Cy for MDS patients prior to allo-HSCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franke GN, Lückemeier P, Platzbecker U. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and prevention of relapse. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021;21:1–7.
Saber W, Horowitz MM. Transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes: who, when, and which conditioning regimens. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ. Program. 2016; 2016: 478–84.
Nagler A, Rocha V, Labopin M, Unal A, Ben Othman T, Campos A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in remission: comparison of intravenous busulfan plus cyclophosphamide (Cy) versus total-body irradiation plus Cy as conditioning regimen-a report from the acute leukemia working party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3549–56.
Copelan EA, Hamilton BK, Avalos B, Ahn KW, Bolwell BJ, Zhu X, et al. Better leukemia-free and overall survival in AML in first remission following cyclophosphamide in combination with busulfan compared with TBI. Blood. 2013;122:3863–70.
Bredeson C, LeRademacher J, Kato K, Dipersio JF, Agura E, Devine SM, et al. Prospective cohort study comparing intravenous busulfan to total body irradiation in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2013;122:3871–8.
Gooley TA, Chien JW, Pergam SA, Hingorani S, Sorror ML, Boeckh M, et al. Reduced mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2091–101.
McSweeney PA, Niederwieser D, Shizuru JA, Sandmaier BM, Molina AJ, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with hematologic malignancies: replacing high-dose cytotoxic therapy with graft-versus-tumor effects. Blood. 2001;97:3390–400.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X, Braunschweig I, Ippolitti C, et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97:631–7.
Itonaga H, Ishiyama K, Aoki K, Aoki J, Ishikawa T, Uchida N, et al. Increased opportunity for prolonged survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients aged 60-69 years with myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:1367–81.
Russell JA, Tran HT, Quinlan D, Chaudhry A, Duggan P, Brown C, et al. Once-daily intravenous busulfan given with fludarabine as conditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation: study of pharmacokinetics and early clinical outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2002;8:468–76.
de Lima M, Couriel D, Thall PF, Wang X, Madden T, Jones R, et al. Once-daily intravenous busulfan and fludarabine: clinical and pharmacokinetic results of a myeloablative, reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and MDS. Blood. 2004;104:857–64.
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Yeshurun M, Yerushalmi R, Avigdor A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in AML and MDS using myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning: the role of dose intensity. Leukemia. 2006;20:322–8.
Chae YS, Sohn SK, Kim JG, Cho YY, Moon JH, Shin HJ, et al. New myeloablative conditioning regimen with fludarabine and busulfan for allogeneic stem cell transplantation: comparison with BuCy2. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2007;40:541–7.
Andersson BS, de Lima M, Thall PF, Wang X, Couriel D, Korbling M, et al. Once daily i.v. busulfan and fludarabine (i.v. Bu-Flu) compares favorably with i.v. busulfan and cyclophosphamide (i.v. BuCy2) as pretransplant conditioning therapy in AML/MDS. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2008;14:672–84.
Lee JH, Choi J, Kwon KA, Lee S, Oh SY, Kwon HC, et al. Fludarabine-based myeloablative regimen as pretransplant conditioning therapy in adult acute leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome: comparison with oral or intravenous busulfan with cyclophosphamide. Korean J Hematol 2010;45:102–8.
Lee JH, Joo YD, Kim H, Ryoo HM, Kim MK, Lee GW, et al. Randomized trial of myeloablative conditioning regimens: busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:701–9.
Liu H, Zhai X, Song Z, Sun J, Xiao Y, Nie D, et al. Busulfan plus fludarabine as a myeloablative conditioning regimen compared with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective and multicenter study. J Hematol Oncol 2013;6:15.
Rambaldi A, Grassi A, Masciulli A, Boschini C, Micò MC, Busca A, et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine as a preparative regimen for allogeneic haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:1525–36.
Pasquini MC, Le-Rademacher J, Zhu X, Artz A, DiPersio J, Fernandez HF, et al. Intravenous busulfan-based myeloablative conditioning regimens prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:1424–30.
Eapen M, Brazauskas R, Hemmer M, Perez WS, Steinert P, Horowitz MM, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplant for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: conditioning regimen intensity. Blood Adv. 2018;2:2095–103.
Patel SS, Rybicki L, Pohlman B, Bolwell B, Gerds AT, Hamilton BK, et al. Comparative effectiveness of busulfan/cyclophosphamide versus busulfan/fludarabine myeloablative conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;13:160–5.
Ben-Barouch S, Cohen O, Vidal L, Avivi I, Ram R. Busulfan fludarabine vs busulfan cyclophosphamide as a preparative regimen before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:232–40.
Atsuta Y. Introduction of Transplant Registry Unified Management Program 2 (TRUMP2): scripts for TRUMP data analyses, part I (variables other than HLA-related data). Int J Hematol. 2016;103:3–10.
Kanda J. Scripts for TRUMP data analyses. Part II (HLA-related data): statistical analyses specific for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2016;103:11–19.
D’Agostino RB. Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group. Stat Med. 1998;17:2265–81.
Klein JP, Rizzo JD, Zhang MJ, Keiding N. Statistical methods for the analysis and presentation of the results of bone marrow transplants. Part 2: regression modeling. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2001;28:1001–11.
Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, Koc ON, Rizzieri DA, Wagner JE, et al. Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1815–22.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1995;15:825–8.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106:2912–9.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89:2079–88.
Cheson BD, Greenberg PL, Bennett JM, Lowenberg B, Wijermans PW, Nimer SD, et al. Clinical application and proposal for modification of the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in myelodysplasia. Blood. 2006;108:419–25.
Austin PC. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar Behav Res. 2011;46:399–424.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:452–8.
Kröger N, Iacobelli S, Franke GN, Platzbecker U, Uddin R, Hübel K, et al. Dose-reduced versus standard conditioning followed by allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a prospective randomized phase III study of the EBMT (RICMAC trial). J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:2157–64.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Saure C, Schroeder T, Zohren F, Groten A, Bruns I, Czibere A, et al. Upfront allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation for patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome or secondary acute myeloid leukemia using a FLAMSA-based high-dose sequential conditioning regimen. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2012;18:466–72.
Damaj G, Mohty M, Robin M, Michallet M, Chevallier P, Beguin Y, et al. Upfront allogeneic stem cell transplantation after reduced-intensity/nonmyeloablative conditioning for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a study by the societe francaise de greffe de moelle et de therapie cellulaire. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2014;20:1349–55.
Nakai K, Kanda Y, Fukuhara S, Sakamaki H, Okamoto S, Kodera Y, et al. Value of chemotherapy before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling donor for myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2005;19:396–401.
Scott BL, Storer B, Loken MR, Storb R, Appelbaum FR, Deeg HJ. Pretransplantation induction chemotherapy and posttransplantation relapse in patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:65–73.
Oran B, Giralt S, Saliba R, Hosing C, Popat U, Khouri I, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of high-risk acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome using reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and melphalan. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2007;13:454–62.
Warlick ED, Cioc A, Defor T, Dolan M, Weisdorf D. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adults with myelodysplastic syndromes: importance of pretransplant disease burden. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009;15:30–8.
Lindsley RC, Saber W, Mar BG, Redd R, Wang T, Haagenson MD, et al. Prognostic mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome after stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl J Med 2017;376:536–47.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Solé F, et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012;120:2454–65.
Rodrigues CA, Sanz G, Brunstein CG, Sanz J, Wagner JE, Renaud M, et al. Analysis of risk factors for outcomes after unrelated cord blood transplantation in adults with lymphoid malignancies: a study by the Eurocord-Netcord and lymphoma working party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:256–63.
Russell JA, Irish W, Balogh A, Chaudhry MA, Savoie ML, Turner AR, et al. The addition of 400 cGY total body irradiation to a regimen incorporating once-daily intravenous busulfan, fludarabine, and antithymocyte globulin reduces relapse without affecting nonrelapse mortality in acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2010;16:509–14.
Aoki J, Seo S, Kanamori H, Tanaka M, Fukuda T, Onizuka M, et al. Impact of low-dose TBI on outcomes of reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for AML. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:604–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all physicians and staff at the transplant centers who contributed to the collection of data for the Transplant Registry Unified Management Program of the Japan Society of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S Kurosawa and YS designed the research, organized the project, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. HI, YN, and JA critically reviewed the analyzed data and manuscript. All authors contributed to data collection and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurosawa, S., Shimomura, Y., Itonaga, H. et al. Fludarabine/busulfan versus busulfan/cyclophosphamide as myeloablative conditioning for myelodysplastic syndrome: a propensity score-matched analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 3008–3015 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01447-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01447-y