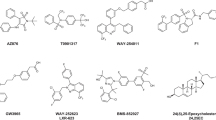
Abstract
Liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is a ligand-regulated transcription factor that plays crucial roles in metabolism, development, and immunity. Despite being classified as an ‘orphan’ receptor due to the ongoing debate surrounding its endogenous ligands, recent researches have demonstrated that LRH-1 can be modulated by various synthetic ligands. This highlights the potential of LRH-1 as an attractive drug target for the treatment of inflammation, metabolic disorders, and cancer. In this review, we provide an overview of the structural basis, functional activities, associated diseases, and advancements in therapeutic ligand research targeting LRH-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Luo XY, Wu DH, Xu Y. ROR nuclear receptors: structures, related diseases, and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36:71–87.
Wärnmark A, Treuter E, Wright AP, Gustafsson JA. Activation functions 1 and 2 of nuclear receptors: molecular strategies for transcriptional activation. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1901–9.
Sar P. Nuclear receptor: structure and function. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2023;196:209–27.
Weikum ER, Liu X, Ortlund EA. The nuclear receptor superfamily: a structural perspective. Protein Sci. 2018;27:1876–92.
Giguère V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:689–725.
Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL. How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:993–96.
Fayard E, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K. LRH-1: an orphan nuclear receptor involved in development, metabolism and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:250–60.
Zerlotin R, Arconzo M, Piccinin E, Moschetta A. Another one bites the gut: nuclear receptor LRH-1 in intestinal regeneration and cancer. Cancers. 2021;13:896.
Sun Y, Demagny H, Schoonjans K. Emerging functions of the nuclear receptor LRH-1 in liver physiology and pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867:166145.
Michalek S, Brunner T. Nuclear-mitochondrial crosstalk: on the role of the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (NR5A2) in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, cell survival, and cancer. IUBMB Life. 2021;73:592–610.
Yazawa T, Imamichi Y, Miyamoto K, Khan MR, Uwada J, Umezawa A, et al. Regulation of steroidogenesis, development, and cell differentiation by steroidogenic factor-1 and liver receptor homolog-1. Zool Sci. 2015;32:323–30.
Mouzat K, Baron S, Marceau G, Caira F, Sapin V, Volle DH, et al. Emerging roles for LXRs and LRH-1 in female reproduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;368:47–58.
Sandhu N, Rana S, Meena K. Nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2 (NR5A2): role in health and diseases. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48:8155–70.
Meinsohn M-C, Smith OE, Bertolin K, Murphy BD. The orphan nuclear receptors steroidogenic factor-1 and liver receptor homolog-1: structure, regulation, and essential roles in mammalian reproduction. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1249–79.
Li LA, Chiang EFL, Chen JC, Hsu NC, Chen YJ, Chung BC. Function of steroidogenic factor 1 domains in nuclear localization, transactivation, and interaction with transcription factor TFIIB and c-Jun. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:1588–98.
Solomon IH, Hager JM, Safi R, McDonnell DP, Redinbo MR, Ortlund EA. Crystal structure of the human LRH-1 DBD-DNA complex reveals Ftz-F1 domain positioning is required for receptor activity. J Mol Biol. 2005;354:1091–102.
Seacrist CD, Kuenze G, Hoffmann RM, Moeller BE, Burke JE, Meiler J, et al. Integrated structural modeling of full-length LRH-1 reveals inter-domain interactions contribute to receptor structure and function. Structure. 2020;28:830–46.
Lu Y, Anderson WR, Zhang H, Feng S, Pick L. Functional conservation of drosophila FTZ-F1 and its mammalian homologs suggests ligand-independent regulation of NR5A family transcriptional activity. Dev Genes Evol. 2013;223:199–205.
Steinmetz AC, Renaud JP, Moras D. Binding of ligands and activation of transcription by nuclear receptors. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2001;30:329–59.
Sablin EP, Krylova IN, Fletterick RJ, Ingraham HA. Structural basis for ligand-independent activation of the orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1575–85.
Nagy L, Schwabe JW. Mechanism of the nuclear receptor molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:317–24.
Busby S, Nuhant P, Cameron M, Mercer BA, Hodder P, Roush WR, et al. Discovery of inverse agonists for the liver receptor homologue-1 (LRH1; NR5A2). Probe reports from the NIH molecular libraries program. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010.
Forman BM. Are those phospholipids in your pocket? Cell Metab. 2005;1:153–55.
Xu D, Jiang X, Wang Y, Song S. Liver receptor homolog-1 regulates apoptosis of bovineovarian granulosa cells by progestogen receptor signaling pathway. Animals. 2022;12:1213.
Mays SG, Okafor CD, Whitby RJ, Goswami D, Stec J, Flynn AR, et al. Crystal structures of the nuclear receptor, liver receptor homolog 1, bound to synthetic agonists. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:25281–91.
Wu X, Zhang Y, Xu Y. Discovery of the first low nanomolar liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) agonist. J Med Chem. 2019;62:11019–21.
Cornelison JL, Cato ML, Johnson AM, D’Agostino EH, Melchers D, Patel AB, et al. Development of a new class of liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) agonists by photoredox conjugate addition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020;30:127293.
Cato ML, D’Agostino EH, Spurlin RM, Flynn AR, Cornelison JL, Johnson AM, et al. Comparison of activity, structure, and dynamics of SF-1 and LRH-1 complexed with small molecule modulators. J Biol Chem. 2023;299:104921.
Cato ML, Cornelison JL, Spurlin RM, Courouble VV, Patel AB, Flynn AR, et al. Differential modulation of nuclear receptor LRH-1 through targeting buried and surface regions of the binding pocket. J Med Chem. 2022;65:6888–902.
Mays SG, Hercules D, Ortlund EA, Okafor CD. The nuclear receptor LRH-1 discriminates between ligands using distinct allosteric signaling circuits. Protein Sci. 2023;32:e4754.
Lazarus KA, Wijayakumara D, Chand AL, Simpson ER, Clyne CD. Therapeutic potential of liver receptor homolog-1 modulators. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;130:138–46.
Lonard DM, O’malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators: judges, juries, and executioners of cellular regulation. Mol Cell. 2007;27:691–700.
Zhao H, Li Z, Cooney AJ, Lan ZJ. Orphan nuclear receptor function in the ovary. Front Biosci. 2007;12:3398–405.
Suzuki T, Kasahara M, Yoshioka H, Morohashi K, Umesono K. LXXLL-related motifs in Dax-1 have target specificity for the orphan nuclear receptors Ad4BP/SF-1 and LRH-1. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:238–49.
Yazawa T, Inaoka Y, Okada R, Mizutani T, Yamazaki Y, Usami Y, et al. PPAR-gamma coactivator-1alpha regulates progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells with SF-1 and LRH-1. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24:485–96.
Darimont BD, Wagner RL, Apriletti JW, Stallcup MR, Kushner PJ, Baxter JD, et al. Structure and specificity of nuclear receptor-coactivator interactions. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3343–56.
Stein S, Schoonjans K. Molecular basis for the regulation of the nuclear receptor LRH-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:26–34.
Gu P, Goodwin B, Chung AC, Xu X, Wheeler DA, Price RR, et al. Orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1 is required to maintain oct4 expression at the epiblast stage of embryonic development. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:3492–505.
Heng JC, Feng B, Han J, Jiang J, Kraus P, Ng JH, et al. The nuclear receptor Nr5a2 can replace Oct4 in the reprogramming of murine somatic cells to pluripotent cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:167–74.
Paré JF, Malenfant D, Courtemanche C, Jacob-Wagner M, Roy S, Allard D, et al. The fetoprotein transcription factor (FTF) gene is essential to embryogenesis and cholesterol homeostasis and is regulated by a DR4 element. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:21206–16.
Meinsohn MC, Morin F, Bertolin K, Duggavathi R, Schoonjans K, Murphy BD. The orphan nuclear receptor liver homolog receptor-1 (Nr5a2) regulates ovarian granulosa cell proliferation. J Endocr Soc. 2018;2:24–41.
Higashiyama H, Kinoshita M, Asano S. Expression profiling of liver receptor homologue 1 (LRH-1) in mouse tissues using tissue microarray. J Mol Histol. 2007;38:45–52.
Nadolny C, Dong X. Liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1): a potential therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16:997–1004.
Kramer HB, Lai CF, Patel H, Periyasamy M, Lin ML, Feller SM, et al. LRH-1 drives colon cancer cell growth by repressing the expression of the CDKN1A gene in a p53-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:582–94.
Xiao L, Wang Y, Xu K, Hu H, Xu Z, Wu D, et al. Nuclear receptor LRH-1 functions to promote castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer via its promotion of intratumoral androgen biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 2018;78:2205–18.
Faber C, Kirchner T, Hlubek F. The impact of microRNAs on colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2009;454:359–67.
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Michalek J, Vyzula R. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: translation of molecular biology into clinical application. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:102.
Schetter AJ, Okayama H, Harris CC. The role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Cancer J. 2012;18:244–52.
Qu R, Hao S, Jin X, Shi G, Yu Q, Tong X, et al. MicroRNA-374b reduces the proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cells by regulation of LRH-1/Wnt signaling. Gene. 2018;642:354–61.
Liang Y, Zhao Q, Fan L, Zhang Z, Tan B, Liu Y, et al. Down-regulation of MicroRNA-381 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in colon cancer through up-regulation of LRH-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;75:137–41.
Yuan Q, Cao G, Li J, Zhang Y, Yang W. MicroRNA-136 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting liver receptor homolog-1/Wnt signaling. Gene. 2017;628:48–55.
Yan L, Qiu J, Yao J. Downregulation of microRNA-30d promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting LRH-1 in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39:1371–80.
Lai HT, Chiang CT, Tseng WK, Chao TC, Su Y. GATA6 enhances the stemness of human colon cancer cells by creating a metabolic symbiosis through upregulating LRH-1 expression. Mol Oncol. 2020;14:1327–47.
Wilde L, Roche M, Domingo-Vidal M, Tanson K, Philp N, Curry J, et al. Metabolic coupling and the reverse warburg effect in cancer: implications for novel biomarker and anticancer agent development. Semin Oncol. 2017;44:198–203.
Sidler D, Renzulli P, Schnoz C, Berger B, Schneider-Jakob S, Flück C, et al. Colon cancer cells produce immunoregulatory glucocorticoids. Oncoimmunology. 2012;1:529–30.
Schoonjans K, Dubuquoy L, Mebis J, Fayard E, Wendling O, Haby C, et al. Liver receptor homolog 1 contributes to intestinal tumor formation through effects on cell cycle and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:2058–62.
Miki Y, Clyne CD, Suzuki T, Moriya T, Shibuya R, Nakamura Y, et al. Immunolocalization of liver receptor homologue-1 (LRH-1) in human breast carcinoma: possible regulator of insitu steroidogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2006;244:24–33.
Thiruchelvam PT, Lai CF, Hua H, Thomas RS, Hurtado A, Hudson W, et al. The liver receptor homolog-1 regulates estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;127:385–96.
Annicotte JS, Chavey C, Servant N, Teyssier J, Bardin A, Licznar A, et al. The nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 is an estrogen receptor target gene. Oncogene. 2005;24:8167–75.
Bianco S, Jangal M, Garneau D, Gévry N. LRH-1 controls proliferation in breast tumor cells by regulating CDKN1A gene expression. Oncogene. 2015;34:4509–18.
Lazarus KA, Brown KA, Young MJ, Zhao Z, Coulson RS, Chand AL, et al. Conditional overexpression of liver receptor homolog-1 in female mouse mammary epithelium results in altered mammary morphogenesis via the induction of TGF-β. Endocrinology. 2014;155:1606–17.
Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Lorenzo PI, Gauthier BR. Targeting LRH-1/NR5A2 to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cell Stress. 2018;2:141–43.
Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Lorenzo PI, Rodríguez NG, Herrera Gómez IG, Fuente-Martin E, López-Noriega L, et al. LRH-1 agonism favours an immune-islet dialogue which protects against diabetes mellitus. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1488.
Martin Vázquez E, Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Araujo Legido R, Marín-Cañas S, Nola E, Dorronsoro A, et al. NR5A2/LRH-1 regulates the PTGS2-PGE(2)-PTGER1 pathway contributing to pancreatic islet survival and function. iScience. 2022;25:104345.
Baquié M, St-Onge L, Kerr-Conte J, Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Lorenzo PI, Jimenez Moreno CM, et al. The liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) is expressed in human islets and protects {beta}-cells against stress-induced apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20:2823–33.
Hu J, Zhang Z, Hu H, Yang K, Zhu Z, Yang Q, et al. LRH-1 activation alleviates diabetes-induced podocyte injury by promoting GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis. Cell Prolif. 2023;56:e13479.
Oosterveer MH, Mataki C, Yamamoto H, Harach T, Moullan N, van Dijk TH, et al. LRH-1-dependent glucose sensing determines intermediary metabolism in liver. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2817–26.
Miranda DA, Krause WC, Cazenave-Gassiot A, Suzawa M, Escusa H, Foo JC, et al. LRH-1 regulates hepatic lipid homeostasis and maintains arachidonoyl phospholipid pools critical for phospholipid diversity. JCI Insight. 2018;3:e96151.
Stein S, Lemos V, Xu P, Demagny H, Wang X, Ryu D, et al. Impaired SUMOylation of nuclear receptor LRH-1 promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:583–92.
Bayrer JR, Wang H, Nattiv R, Suzawa M, Escusa HS, Fletterick RJ, et al. LRH-1 mitigates intestinal inflammatory disease by maintaining epithelial homeostasis and cell survival. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4055.
Coste A, Dubuquoy L, Barnouin R, Annicotte JS, Magnier B, Notti M, et al. LRH-1-mediated glucocorticoid synthesis in enterocytes protects against inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13098–103.
Ahmed A, Schwaderer J, Hantusch A, Kolho KL, Brunner T. Intestinal glucocorticoid synthesis enzymes in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients. Genes Immun. 2019;20:566–76.
Landskron G, Dubois-Camacho K, Orellana-Serradell O, De la Fuente M, Parada-Venegas D, Bitrán M, et al. Regulation of the intestinal extra-adrenal steroidogenic pathway component LRH-1 by glucocorticoids in ulcerative colitis. Cells. 2022;11:1905.
Benod C, Vinogradova MV, Jouravel N, Kim GE, Fletterick RJ, Sablin EP. Nuclear receptor liver receptor homologue 1 (LRH-1) regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth and proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:16927–31.
Sidler D, Renzulli P, Schnoz C, Berger B, Schneider-Jakob S, Flück C, et al. Colon cancer cells produce immunoregulatory glucocorticoids. Oncogene. 2011;30:2411–19.
Zhou J, Suzuki T, Kovacic A, Saito R, Miki Y, Ishida T, et al. Interactions between prostaglandin E(2), liver receptor homologue-1, and aromatase in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:657–63.
Wang Z, Wu D, Ng CF, Teoh JY, Yu S, Wang Y, et al. Nuclear receptor profiling in prostatospheroids and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2018;25:35–50.
Chand AL, Pathirage N, Lazarus K, Chu S, Drummond AE, Fuller PJ, et al. Liver receptor homologue-1 expression in ovarian epithelial and granulosa cell tumours. Steroids. 2013;78:700–06.
Whitby RJ, Dixon S, Maloney PR, Delerive P, Goodwin BJ, Parks DJ, et al. Identification of small molecule agonists of the orphan nuclear receptors liver receptor homolog-1 and steroidogenic factor-1. J Med Chem. 2006;49:6652–55.
Whitby RJ, Stec J, Blind RD, Dixon S, Leesnitzer LM, Orband-Miller LA, et al. Small molecule agonists of the orphan nuclear receptors steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) and liver receptor homologue-1 (LRH-1, NR5A2). J Med Chem. 2011;54:2266–81.
Krylova IN, Sablin EP, Moore J, Xu RX, Waitt GM, MacKay JA, et al. Structural analyses reveal phosphatidyl inositols as ligands for the NR5 orphan receptors SF-1 and LRH-1. Cell. 2005;120:343–55.
Ortlund EA, Lee Y, Solomon IH, Hager JM, Safi R, Choi Y, et al. Modulation of human nuclear receptor LRH-1 activity by phospholipids and SHP. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:357–63.
Lee JM, Lee YK, Mamrosh JL, Busby SA, Griffin PR, Pathak MC, et al. A nuclear-receptor-dependent phosphatidylcholine pathway with antidiabetic effects. Nature. 2011;474:506–10.
Flynn AR, Mays SG, Ortlund EA, Jui NT. Development of hybrid phospholipid mimics as effective agonists for liver receptor homologue-1. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018;9:1051–56.
Mays SG, Flynn AR, Cornelison JL, Okafor CD, Wang H, Wang G, et al. Development of the first low nanomolar liver receptor homolog-1 agonist through structure-guided design. J Med Chem. 2019;62:11022–34.
Corzo CA, Mari Y, Chang MR, Khan T, Kuruvilla D, Nuhant P, et al. Antiproliferation activity of a small molecule repressor of liver receptor homolog 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2015;87:296–304.
Benod C, Carlsson J, Uthayaruban R, Hwang P, Irwin JJ, Doak AK, et al. Structure-based discovery of antagonists of nuclear receptor LRH-1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:19830–44.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Key Research and Development Plan (grant 2022YFE0210600), the Joint Fund of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (grant ZR2022LSW026), the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (grant 202201010138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Lu, Zf., Yu, Hn. et al. Liver receptor homolog-1: structures, related diseases, and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01276-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01276-x