Abstract
Study design
Systematic review.
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity due to SCI or MS.
Methods
A comprehensive search of the Pubmed, Cochrane, Scopus, and Embase databases was performed. Studies evaluating adult patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity due to SCI or MS were analyzed according to clinical and urodynamic outcome parameters.
Results
A total of 488 patients were included in 11 studies, with sample sizes ranging from 15 to 91. The duration of the treatments varied from 4 weeks to 12 months. Mirabegron was used as a secondline treatment after anticholinergics in most of the studies. While clinical outcome parameters are used in studies involving only MS patients, urodynamic outcome parameters are also used in studies involving patients with SCI. The efficacy of mirabegron was found not to be different than anticholinergics when compared in MS patients. Comprehensive urodynamic evaluation was performed in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies and no satisfactory results were obtained compared to placebo. In retrospective studies there were some significant improvements in Pdet(max), MCC and compliance. The major safety concern with mirabegron is cardiovascular safety. In one study, tachyarrhythmia and palpitations reported in a patient with SCI at C6 level, in another study tachycardia reported in one patient with MS.
Conclusions
Although mirabegron demonstrates similar clinical efficacy to anticholinergics in MS patients, its effect on urodynamic parameters in patients with SCI cannot be considered satisfactory. It has a good safety profile with mild cardiovascular side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) is characterized by reduced bladder capacity, elevated detrusor pressure (Pdet) during the storage phase and/or reduced bladder compliance [1]. NDO can lead to deterioration of the upper urinary tract (UUT) with subsequent renal failure, so an adequate treatment of the elevated Pdet is necessary to protect the UUT. All guidelines are in agreement with the use of anticholinergics as first-line treatment for NDO [2].
Combined treatment with anticholinergics and clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) is still the mainstay of urological management for most spinal cord injury (SCI) patients with NDO. In patients affected by the side effects and those unresponsive to anticholinergics, usually the first treatment option is intradetrusor onabotulinumtoxin-A injection which is an invasive treatment modality [3]. Mirabegron is a β3-agonist that relaxes the bladder and facilitates the filling phase by stimulating the β3-adrenoreceptors [4]. Yet, it remains to be proven whether mirabegron alone or in combination with anticholinergics is a preferable treatment option before application of intradetrusor onabotulinumtoxin-A injection for patients with an inadequate response or intolerance to anticholinergics. Due to lack of robust data in the literature, none of the guidelines have included mirabegron as first-line therapy for neurogenic bladder (NB).
El Helou et al. [5] published the first systematic review on the efficacy of mirabegron in patients with NB. They analyzed a total of seven studies, with only two of the studies having a RCT design. These studies enrolled 302 patients having NB with various underlying neurologic disorders including SCI [6,7,8], Multiple Sclerosis (MS) [7,8,9], cerebrovascular diseases [10], Parkinson’s disease [10], dementia [10], HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) [11] and spina bifida [12]. Patients with NB due to cerebrovascular diseases, Parkinson’s disease and dementia may differ from SCI patients in many aspects. Results of pediatric patients with spina bifida may have no real analogy to those observed in adult patients with SCI. Ideally, the patients with SCI who are known to be at a high risk of renal complications ought to be analyzed separately from the other neurologic disorders. Lowering or normalizing the detrusor pressure is an important treatment goal to prevent UUT deterioration and potentially improve long-term outcomes in patients with SCI [13, 14]. International guidelines recommend urodynamic studies as the most important tool to monitor risk factors for renal deterioration secondary to SCI [15, 16]. Thus, a treatment modality claimed to be efficacious in patients with SCI need to be proven by urodynamic studies.
A very recent systematic review [17] providing a meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) analyzed a total of four RCTs. Of the trials, two included patients with SCI or MS [7, 8], one included only MS patients [9] and the remaining one enrolled only Parkinsonism patients with OAB symptoms [18]. This systematic review evaluated only the bladder compliance data from two RCTs but neglected the data regarding the other urodynamic variables provided in the same trials. Patients with Parkinson’s disease constituted almost half of the analyzed patients in the study by Cho et al. [18]. However, LUTD in patients with Parkinson’s disease is not driven exclusively by neurogenic mechanisms [19, 20] and neurogenic DO may not be the only cause of OAB symptoms in these patients [21].
This review aims at analyzing the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in adult patients with NDO due to SCI or MS. Most of the studies of mirabegron performed in patients with SCI also included patients with MS, and studies including patients with SCI alone are scarce. Therefore studies involving patients with MS were also included in this systematic review.
Methods
This study is a systematic review designed to collect published literature and articles on the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in SCI or MS patients with NDO. This study was conducted following the PRISMA(Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) reporting guidelines [22] and was aimed at exploring the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in SCI or MS patients with NDO. A search strategy based on a combination of the following terms was used: [(mirabegron) and [(neurogenic bladder) or (Spinal Cord Injury) or (Multiple Sclerosis)]. This strategy was run in various electronic databases; including PubMed, Cochrane, Scopus and Embase to identify articles published up to December 31 2021, with no language restriction. The details of the search strategy are shown in online Supplementary File-1. Relevant reviews and the reference lists of the original articles for further suitable publications were also screened.
From these, all original research articles and reviews reported in English and published on the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with NDO were included in this analysis. All of the abstracts and titles were reviewed by the author. The studies without control group and retrospective studies were also included in this review, as the number of studies on this topic is very limited. Further, only studies involving SCI, MS or both groups together were included in this systematic review. Studies involving patients with NDO diagnoses other than SCI or MS, studies involving pediatric patients and studies performed in non-neurogenic bladder patients were excluded. Full-text articles were obtained and examined for the subjective and objective outcome parameters, noting also safety considerations.
Results
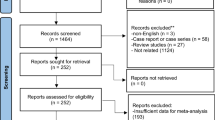
Searching the databases using specific keywords yielded 290 articles. Among the 186 studies, 11 were included according to the PRISMA protocols (Fig. 1).
A total of 488 patients were included in 11 studies that satisfied the inclusion criteria, with the number of patients ranging from 15 to 91. Two of these studies were randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies [7, 8], two were randomized comparative studies [9, 23], three were prospective cohort studies [11, 24, 25], one was a prospective comparative non-randomized study [26] and three were retrospective studies [6, 27, 28]. The duration of the treatments ranged from 4 weeks to 12 months [5, 25]. In all of the studies, mirabegron was taken orally in daily dosages of either 25 mg or 50 mg. Two studies conducted in MS patients [23, 26] compared the efficacy of mirabegron and that of anticholinergics but without including a placebo group. Another study also in MS patients, provided comparative data for mirabegron and solifenacin [9]. This study primarily aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of combined mirabegron and desmopressin treatment as compared to monotherapy, which included groups of patients using only mirabegron or only solifenacin or only desmopressin. In a study with almost all included patients with SCI [27] 73% of patients received mirabegron in combination with an established anticholinergic or onabotulinum-toxin therapy. In another study performed in SCI patients [28], mirabegron was added to the pre-existing anticholinergics. Clinical and urodynamic outcome parameters used in all these studies were different (Table 1).
Clinical outcome parameters
The clinical outcome parameters used in the reviewed studies are shown in Table 1.
Welk et al. found significant difference only in Neurogenic Bladder Symptom Score (NBSS) (total NBSS marginal means 29 vs. 34, p = 0.04) among those treated with mirabegron as compared to the placebo group [7]. Another study performed by Trbovich et al. [25] three subscores within NBSS (total incontinence, total storage and voiding, total consequences) significantly improved (p = 0.01) and the frequency of incontinence decreased (p = 0.03) on mirabegron.
Krhut et al. [8] reported significant differences in all of the patient-reported outcomes in favor of the mirabegron group relative to the placebo group [The Patient Perception of Bladder Condition (PPBC), P = 0.0013; Incontinence-Quality of Life (I-QoL), P = 0.006; Treatment Satisfaction-Visual Analog Scale (TS-VAS), P = 0.00045].
There was a significant improvement with the use of mirabegron, in all of the bladder diary (BD) parameters including the mean CIC frequency/24 h (6.63 at the baseline to 5.37 at 6 weeks, p = 0.002), the mean CIC volume (275 to 341 ml, p = 0.0002), the mean number of incontinence episodes per 24 h (3.97 to 2.27, p < 0.0001), and the mean time from CIC to leakage (1.73 to 2.75 h, p < 0.0001) in the study performed by Vasudeva et al. [24].
Wöllner and Pannek [6] reported that frequency of bladder evacuation/24 h (8.1 vs. 6.4, P = 0.003) and incontinence episodes/24 h (2.9 vs. 1.3, P = 0.027) were significantly decreased during mirabegron treatment.
In the study performed by Krebs et al. [27] the percentage of patients suffering from urinary incontinence (UI) significantly decreased from 60.3% to 33.3% and 38.1% at the first and second follow-up visits, respectively (p ≤ 0.005). There was no change in the number of daily bladder evacuations during mirabegron treatment.
Matsuo et al. [11] reported that mirabegron treatment improved OAB symptom score in terms of night-time frequency, urgency, total score (P < 0.001) and urgency incontinence (p = 0.004). Mirabegron therapy also improved the total International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), as well as the urgency, nocturia, storage symptoms subscale scores and the IPSS-QoL (P < 0.001).
Brucker et al. [26] used patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) including OAB Questionnaire Short Form (OAB-q SF), Patient Global Impression of Severity (PGI-S) and Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI-I). There was no statistically significant difference between mirabegron and solifenacin groups in achieving minimal clinically important difference (MCID) for any of these 3 PROMs.
In a randomized study performed by Glycas et al. [23] all patients completed specific validated questionnaires including the Multiple Sclerosis International Quality of Life (MusiQoL) and NBSS questionnaires and BD. No difference was found in LUTD improvement between mirabegron and anticholinergics regarding the assessed clinical outcome parameters.
In the study performed by Zachariou et al. [9] the combination of mirabegron and desmopressin in patients with MS, resulted in a statistically significant improvement in the 3 day BD components composed of micturition episodes (3.5 ± 0.4 micturition/24 h), urgency episodes (2.3 ± 0.2) and the number of UI (1.0 ± 0.2 episodes/24 h). There was no significant change from baseline when mirabegron was used as a monotherapy. The combination of mirabegron and desmopressin resulted in fewer urinary tract infections during treatment period as compared to baseline (1.2 vs. 3.2; p < 0.01). But mirabegron did not show a significant change as a monotherapy.
Urodynamic outcome parameters
The urodynamic outcome parameters used in the reviewed studies are shown in Table 1.
In the study performed by Zachariou et al. [9] in which MS patients were recruited, only voided volume (VV) was examined and there was no significant change from baseline when mirabegron was used as a monotherapy. However, when combined with desmopressin, it was associated with an increase of VV (189 vs. 104 ml; p < 0.01).
In the study performed by Welk et al. [7] there was no significant difference in maximum cystometric capacity (MCC), volume at first detrusor contraction (VFDC) and Pdet(max) between mirabegron and placebo (p > 0.05). Krhut et al. [8] reported a statistically significant increase in VFDC (P = 0.00047) and an improvement in bladder compliance (P = 0.0041) in the mirabegron group compared with the placebo group, whereas the increase in MCC in the mirabegron group did not reach statistical significance and no significant change in Pdet(max) was detected in either group of patients (p > 0.05).
Vasudeva et al. [24] reported that the mean CC increased significantly from 348 to 406 ml and Pdet(max) decreased significantly from 54 cmH2O to 41 cmH2O after mirabegron treatment. However, VFDC and bladder compliance did not improve significantly. In another study performed by Matsuo et al. [11] there were no significant changes in VV, Qmax, and post-void residual volume (PVR) after mirabegron treatment (p < 0.01).
Wöllner and Pannek [6] noted a significant decrease in the Pdet(max) during the storage phase (45.8 vs. 30 cmH2O, p = 0.018) with the use of mirabegron. The MCC increased from 365 to 419 ml, (P = 0.084) and the compliance increased from 28 to 45 ml /cmH2O (P = 0.069).
Krebs et al. [27] reported that the Pdet(max) was significantly decreased (p = 0.04); MCC (p = 0.005) and detrusor compliance (p = 0.0001) were significantly increased with the use of mirabegron in combination with an established antimuscarinic or onabotulinum-toxin therapy in 73% of the patients.
In the study performed by Han et al. [28] urodynamic evaluation showed a significant increase in CC (mean, 362 to 424 ml; p = 0.03) when mirabegron was added to the pre-existing antimuscarinic drug. In addition, a significant increase in reflex volume (mean, 251 to 329 ml; p = 0.02) and improvement in bladder compliance (median, 12 to 18 ml/cmH2O; p = 0.04) were also reported. Furthermore, there was a non-significant decrease in Pdet(max) (mean, 31 to 27 cmH2O; p = 0.39) after mirabegron treatment.
Safety parameters
In a study performed by Vasudeva et al. [24] mirabegron was well tolerated and no severe side effects were reported. They reported a clinically insignificant but statistically significant change in heart rate (HR). There was no significant change in blood pressure (BP).
Krhut et al. [29] investigated cardiovascular (CV) safety of mirabegron. They used 24 h BP, electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring and echocardiographic examination. They did not observe any significant change in QT interval in the mirabegron group. They reported tachyarrhythmia and palpitations in a patient who has SCI at C6 level.
In the study performed by Welk et al. [7] there were no clinically concerning safety findings related to BP, HR, ECG, PVR, or liver or renal function.
In the study performed by Krebs et al. [27] four patients (6%) had reported side effects including dry skin, tachycardia, headache and stomach pain during mirabegron treatment. Three of the four patients were treated with anticholinergics concomitantly except the patient complaining of stomach pain. In the study performed by Zachario et al. [9] in one patient with MS out of 30 patients receiving mirabegron (alone or in combination with desmopressin) developed tachycardia.
Matsuo et al. [11] reported that one patient (5.3%) complained of dry mouth. In a study performed by Trbovich et al. [25] no significant changes in HR or BP were found. ECG monitoring also showed no change in rhythm. The Neurogenic bowel dysfunction assessment did not show any change in bowel function. Wöllner and Pannek [6] reported constipation in 1 patient with SCI (%7).
Brucker et al. [26] reported that 30% of patients in the anticholinergic group were experiencing worsening constipation vs. 3% in the mirabegron group (P < 0.01), according to the Patient Assessment of Constipation Symptoms (PACSYM) evaluation.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first review of the literature evaluating the efficacy of mirabegron in adult patients with NDO due to SCI or MS.
Apparently, it seems that studies assessing the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in only MS patients, clinical variables alone were used for assessment, without any urodynamic evaluation. However, in studies involving SCI patients urodynamic variables have been included as outcome measures to monitor risk factors for renal deterioration secondary to SCI as recommended by international guidelines [15, 16]. Intravesical filling pressures of <40 cm H2O have traditionally been considered safe as suggested by the results of a study conducted in myelodysplastic children [30]. However, the corresponding cut-off value in adults has been proposed as of <25 cm H2O [15]. Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies assessed the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in the treatment of NB dysfunction in patients with SCI or MS [7, 8]. One of these RCTs found no significant improvement in any of the urodynamic parameters, but noted a significantly lower NB symptom burden with mirabegron [7]. In the other RCT, mirabegron improved some urodynamic variables (VFDC and bladder compliance) and also the PROMs [8]. However, it should be noted that neither of these studies showed any decrease in Pdet(max) with mirabegron treatment. Considering that Pdet(max) is regarded as a major risk factor for renal deterioration, patients may need additional or an alternative treatment for controlling Pdet(max) values within a safe limit. No significant change in MCC [7] or CC [8] was recorded with mirabegron in these RCTs [7, 8]. These results do not in general indicate a considerable improvement in urodynamic parameters with mirabegron.
In the literature review, there were two prospective cohort studies performed in patients with SCI [24, 25]. Vasudeva et al. [24] reported that mirabegron is effective in adult patients with SCI. The authors did not use a specific questionnaire for the evaluation of QoL instead they stated that leakage and CIC frequency are the most important parameters that affect the patient’s QoL. It is much better to use a 24 h pad-weight test to determine the amount of leakage compared to the number of incontinence episodes between CIC. The symptoms of lower urinary tract pathology are subjective, and the perception of their severity is influenced by many factors. SCI patients may also not show symptoms because of impaired or altered sensation. Furthermore, patients might find symptoms difficult to define, such as the timing of incontinence and describing whether leakage is associated with urinary urgency or with stress maneuvers.
Self-completed and interviewer-administered patient questionnaires can be a suitable method for monitoring patients’ perspectives of bothersome symptoms and their impact on QoL and it might even help to quantitate patients’ responses to treatment [15].
In the study by Vasudeva et al. [24] 5 patients (17.3%) were completely dry at the end of 6 weeks and the authors commented that this is a significant finding. Absence of leakage is an important factor for QoL, but it is not predictive of good urodynamic results that is required for the prevention of UUT. There may be no incontinence although there are high detrusor pressures in the presence of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia in suprasacral SCI patients, so continence is not a security indicator for UUT protection, which is the primary goal for NB treatment. As stated by the authors of the study [24] among the urodynamic parameters, the MCC, Pdet(max) and compliance are important markers to assess the risk to the UUT. They noted a significant decrease in the Pdet(max) during the storage phase after mirabegron treatment. However, mean value for Pdet(max) at the end of treatment was above the Pdet(max) <25 cmH2O cut-off level proposed for adults. The proportion of patients achieving the target Pdet(max) <25 cmH2O (or <40 cmH2O) after mirabegron treatment was not reported.
A retrospective single center study evaluated the efficacy of anticholinergic drugs either in monotherapy, or in combination with an existing anticholinergic drug in chronic suprasacral SCI patients [31]. They demonstrated that clinical balance (absence of leakage) is not predictive of urodynamic balance because one-third of the fully continent patients showed persistent involuntary detrusor contractions. They then defined the urodynamic balance as the combination of MCC greater than 400 ml and amplitude of idiopathic detrusor contractions lower than 20 cmH2O. This study shows that the absence of leakage, which is an important factor for QoL, is not sufficient for urodynamic safety and targeted clinical and, especially, urodynamic balance criteria should be defined for interpreting whether the outcome of therapy is sufficient or not. Therefore, it is important to determine target urodynamic outcome measures when designing studies to evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic agents for NB, particularly in patients with SCI.
A prospective cohort study conducted in an old (>60 y/o) patient population with SCI [25], revealed that switching to mirabegron after at least 6 months of treatment with anticholinergics results in improvement in cognitive test scores. They concluded mirabegron should be preferred over anticholinergics in older SCI patients to preserve cognition. It should be pointed out that this study did not include any urodynamic outcome measure for assessment of efficacy. In the absence of such information, a recommendation for treatment choice solely based on positive effect on cognitive functions will not be appropriate.
Three retrospective uncontrolled studies evaluated the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with SCI [6, 27, 28]. Some favorable results on urodynamic outcomes were reported in these studies, including a significant decrease in Pdet(max) in two of them [6, 28]. Of note, all participants in one of the two studies received mirabegron on top of anticholinergics. No significant change in Pdet(max) was observed in the third study where the majority of patients (73%) received mirabegron in combination with an established anticholinergic drug or onabotulinum-toxin therapy [27].
Because the studies investigating the efficacy and safety of mirabegron in patients with SCI are very limited, the prospective open-label study performed by Matsuo et al. [11] was also evaluated in this review. They investigated the efficacy of mirabegron in patients diagnosed with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). HAM/TSP is characterized by slow progression of lower limb sensory disturbances and movement disorder accompanied by NB dysfunction caused by chronic inflammation in the central nervous system, especially the lower thoracic spinal cord [32]. It should be noted that it was an open-label study, including only female patients who received mirabegron after a short washout period, and that urodynamic pressure-flow studies were not performed in the study.
The efficacy and safety of Mirabegron was compared with anticholinergics in patients with MS in two randomized [9, 23] and one non-randomized [26] controlled studies. None or only one urodynamic variable was assessed in these studies. No difference was found between mirabegron and anticholinergics in terms of LUTD improvement in the study by Glykas et al. [23] and in terms of achieving each PROMs’ MCID in the study by Brucker et al. [26]. In the study by Zachariou et al. mirabegron monotherapy did not demonstrate significant change in clinical outcome measures at the end of the treatment period [9].
The major safety concern with mirabegron is CV safety. There were no clinically concerning safety findings related to BP, HR and ECG [7, 25]. In clinical practice, lower initial dose of mirabegron should be considered in patients with cervical and high thoracic level of SCI patients, since tachyarrhythmia and palpitations has been reported in a patient with SCI at C6 level [8]. The lower prevalence of worsening in constipation with mirabegron as compared to anticholinergics that has been noted in a comparative study in MS patients (30% versus 3%) may provide a safety advantage for mirabegron [26].
Multicenter randomized prospective studies comparing the efficacy of mirabegron as a monotherapy or in combination with anticholinergics are needed to determine the place of mirabegron in patients with NDO. There is yet no evidence concerning the use of mirabegron as a first-line therapy for NDO except for the two studies performed in MS patients [9, 27]. Consequently, there is also need for prospective comparative studies exploring the efficacy of mirabegron in treatment-naive patients.
Apparently, clinical evaluation parameters are the preferred outcome measures in studies involving only MS patients whereas both clinical and urodynamic evaluation parameters are assessed in studies that involve SCI patients. Since the clinical outcome parameters used in patients with SCI and MS vary, there are also differences across the same patient population. These limitations are a major challenge to do a systematic review on this topic. When evaluating the effectiveness of a drug for NDO, objective cure (including urodynamic parameters), patient-reported cure and QoL assessment using a specific validated questionnaire should all be assessed. Use of similar objective and subjective outcome measures in clinical trials would increase the opportunity for high quality and reliable systematic reviews. For this purpose, it is an urgent task for the researchers in this field to develop consensus based recommendations for a core set of potential outcome domains and outcome measures for use in clinical trials of NDO. Importantly, the target patient population should also be considered in this planning since patients with different neurological disorders are included in the trials of NDO to reach a sufficient sample size. Studies should be planned separately in patients with different causes of NDO, such as traumatic and non-traumatic SCI, MS, Parkinson’s disease and stroke. Trials with sufficient sample sizes that include pre-specified subgroup analysis are needed. In patients with SCI, when evaluating the effects of mirabegron, the results should be analyzed according to the AIS score, time elapsed after injury, initial urodynamic parameters, previous medical treatment and results obtained. For MS patients, measures such as Kurtzke’s EDSS score, time after diagnosis, MS type should also be considered in the analysis.
Conclusions
In two comparative (with no placebo control) studies, one randomized and the other non-randomized, conducted in patients with NDO due to MS, mirabegron treatment did not differ in its effects from anticholinergics. Urodynamic studies in patients with SCI do not so far indicate satisfactory effects of mirabegron for UUT protection, which is the most important aim of NB rehabilitation. No clinically concerning safety findings related to BP, HR, ECG were found in most of the studies. Further studies should be planned separately in patients with different causes of NDO such as traumatic and non-traumatic SCI, MS, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke. There is a need for prospective, multicenter, randomized studies comparing the efficacy of mirabegron as a monotherapy or in combination with anticholinergics, particularly in treatment- naive patients.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information file).
References
Fowler CJ, Dalton C, Panicker JN. Review of neurologic diseases for the urologist. Urol Clin North Am. 2010;37:517–26.
Mete UK, Powell CR. Review of current neurogenic bladder best practices and international guidelines. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2020;15:283–95.
Cooley LF, Kielb S. A review of botulinum toxin a for the treatment of neurogenic bladder. Pmr. 2019;11:192–200.
Kashyap M, Tyagi P. The pharmacokinetic evaluation of mirabegron as an overactive bladder therapy option. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013;9:617–27.
El Helou E, Labaki C, Chebel R, El Helou J, Abi Tayeh G, Jalkh G, et al. The use of mirabegron in neurogenic bladder: a systematic review. World J Urol. 2020;38:2435–42.
Wöllner J, Pannek J. Initial experience with the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity with a new β-3 agonist (mirabegron) in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2016;54:78–82.
Welk B, Hickling D, McKibbon M, Radomski S, Ethans K. A pilot randomized-controlled trial of the urodynamic efficacy of mirabegron for patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37:2810–7.
Krhut J, Borovička V, Bílková K, Sýkora R, Míka D, Mokriš J, et al. Efficacy and safety of mirabegron for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity-Prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37:2226–33.
Zachariou A, Filiponi M, Baltogiannis D, Giannakis J, Dimitriadis F, Tsounapi P, et al. Effective treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in multiple sclerosis patients using desmopressin and mirabegron. Can J Urol. 2017;24:9107–13.
Chen SF, Kuo HC. Therapeutic efficacy of low-dose (25 mg) mirabegron therapy for patients with mild to moderate overactive bladder symptoms due to central nervous system diseases. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019;11:O53–8.
Matsuo T, Miyata Y, Nakamura T, Satoh K, Sakai H. Efficacy of mirabegron for overactive bladder with human T cell lymphotropic virus-1 associated myelopathy. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019;11:O65–70.
Park JS, Lee YS, Lee CN, Kim SH, Kim SW, Han SW. Efficacy and safety of mirabegron, a β3-adrenoceptor agonist, for treating neurogenic bladder in pediatric patients with spina bifida: a retrospective pilot study. World J Urol. 2019;37:1665–70.
Stohrer M, Blok B, Castro-Diaz D, Chartier-Kastler E, Del Popolo G, Kramer G, et al. EAU guidelines on neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Eur Urol. 2009;56:81–8.
Madersbacher H, Murtz G, Stohrer M. Neurogenic detrusor overactivity in adults: a review on efficacy, tolerability and safety of oral antimuscarinics. Spinal Cord. 2013;51:432–41.
Przydacz M, Chlosta P, Corcos J. Recommendations for urological follow-up of patients with neurogenic bladder secondary to spinal cord injury. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50:1005–16.
Kreydin E, Welk B, Chung D, Clemens Q, Yang C, Danforth T, et al. Surveillance and management of urologic complications after spinal cord injury. World J Urol. 2018;36:1545–53.
Zhang D, Sun F, Yao H, Bao X, Wang D, Cui Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of mirabegron for the treatment of neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:756582.
Cho SY, Jeong SJ, Lee S, Kim J, Lee SH, Choo MS, et al. Mirabegron for treatment of overactive bladder symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial (Parkinson’s Disease Overactive bladder Mirabegron, PaDoMi Study). Neurourol Urodyn. 2021;40:286–94.
Brucker BM, Kalra S. Parkinson’s disease and its effect on the lower urinary tract: evaluation of complications and treatment strategies. Urol Clin North Am. 2017;44:415–28.
Gray R, Stern G, Malone-Lee J. Lower urinary tract dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: changes relate to age and not disease. Age Ageing. 1995;24:499–504.
Vurture G, Peyronnet B, Palma JA, Sussman RD, Malacarne DR, Feigin A, et al. Urodynamic mechanisms underlying overactive bladder symptoms in patients with Parkinson disease. Int Neurourol J. 2019;23:211–8.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1.
Glykas I, Fragkoulis C, Mitsikostas DD, Papatsoris A, Mitsogiannis I, Papadopoulos G, et al. B3 agonists or anticholinergics in the treatment of the lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis? A randomized study. World J Urol. 2021;39:3049–56.
Vasudeva P, Prasad V, Yadav S, Kumar N, Saurav K, Prashanth YM, et al. Efficacy and safety of mirabegron for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity resulting from traumatic spinal cord injury: a prospective study. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021;40:666–71.
Trbovich M, Romo T, Polk M, Koek W, Kelly C, Stowe S, et al. The treatment of neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction in persons with spinal cord injury: an open label, pilot study of anticholinergic agent vs. mirabegron to evaluate cognitive impact and efficacy. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2021;7:50.
Brucker BM, Jericevic D, Rude T, Enemchukwu E, Pape D, Rosenblum N, et al. Mirabegron versus Solifenacin in multiple sclerosis patients with overactive bladder symptoms: a prospective comparative nonrandomized study. Urology. 2020;145:94–9.
Krebs J, Pannek J, Rademacher F, Wöllner J. Real-world effects of mirabegron in patients with chronic neurogenic detrusor overactivity—a retrospective cohort study. Res Rep Urol. 2020;12:187–92.
Han SH, Cho IK, Jung JH, Jang SH, Lee BS. Long-term efficacy of mirabegron add-on therapy to antimuscarinic agents in patients with spinal cord injury. Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43:54–61.
Krhut J, Wohlfahrt P, Pudich J, Kufová E, Borovička V, Bílková K, et al. Cardiovascular safety of mirabegron in individuals treated for spinal cord injury- or multiple sclerosis-induced neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021;53:1089–95.
McGuire EJ, Woodside JR, Borden TA, Weiss RM. Prognostic value of urodynamic testing in myelodysplastic patients. J Urol. 1981;126:205–9.
Hadiji N, Previnaire JG, Benbouzid R, Robain G, Leblond C, Mieusset R, et al. Are oxybutynin and trospium efficacious in the treatment of detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injury patients? Spinal Cord. 2014;52:701–5.
Yamano Y, Sato T. Clinical pathophysiology of human T-lymphotropic virus-type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:389.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akkoc, Y. Efficacy and safety of mirabegron for treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in adults with spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Spinal Cord 60, 854–861 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41393-022-00853-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41393-022-00853-3
This article is cited by
-
Polypharmacy in Multiple Sclerosis: Prevalence, Risks, and Mitigation Strategies
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2023)
-
Unmet needs in the management of neurourological disorders within the last 50 years
World Journal of Urology (2023)