Abstract
Introduction
Focal therapy (FT) is a promising alternative with curative intent for Low- to Intermediate-risk localized Prostate Cancer (PCa), claiming better functional outcomes and safety profile than standard whole-gland treatments. Ten different FT modalities have been described in the literature. The objective of our narrative review is to evaluate the safety profile and functional outcomes of these different modalities and the current most used tools of assessment for those outcomes.
Material and methods
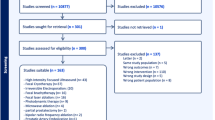
Literature search was performed on 21st February 2023 using PubMed, EMBASE, and Scopus, following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement (PRISMA). Articles reporting whole-gland treatments were excluded. All articles reporting functional outcomes were included.
Results
One-hundred-seven studies, reporting data on 6933 patients, were included (26 on High Intensity Focal Ultrasound, 22 on Focal Cryotherapy, 14 on Irreversible Electroporation, 11 on Focal brachytherapy, 10 on Focal Laser Ablation, 8 on Photodynamic Therapy, 3 on Microwave ablation, 3 on Robotic Partial Prostatectomy, 2 on bipolar Radio Frequency Ablation, 1 on Prostatic Artery Embolization, and 7 studies comparing different FTs). Post-operative pad-free rate ranged between 92.3–100%. Greater heterogeneity exists considering the Change in Erectile Function, with Changing in Erectile function- rates ranging between 0–94.4% (Cryotherapy). The most used Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) were the International Prostate Symptom Score and the International Index of Erectile Function for incontinence/urinary function and potency, respectively. The most common reported complications were hematuria, infections, and urethral strictures, with rates widely ranging among different treatments. The Clavien–Dindo Classification was the most used (40/88 papers) to describe adverse events.
Conclusion
FT is a promising treatment for localized PCa, achieving excellent results in terms of safety and functional outcomes. There is a wide heterogeneity in the definition of PROMS and time of collection between studies. High quality comparative studies with standard treatments are needed to reinforce these findings.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The online version contains supplementary material, including the list of all articles retrieved and tables reporting information about these studies.
References
Ficarra V, Novara G, Rosen RC, Artibani W, Carroll PR, Costello A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:405–17.
Resnick MJ, Koyama T, Fan KH, Albertsen PC, Goodman M, Hamilton AS, et al. Long-term functional outcomes after treatment for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:436–45.
Boorjian SA, Eastham JA, Graefen M, Guillonneau B, Karnes RJ, Moul JW, et al. A critical analysis of the long-term impact of radical prostatectomy on cancer control and function outcomes. Eur Urol. 2012;61:664–75.
Wilt TJ. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and harms of treatments for clinically localized prostate cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:435.
Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1250–61.
Ahmed HU. The index lesion and the origin of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1704–6.
Mottet N et al. EAU Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. (2023). EAU Guidelines. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Milan 2023.
Beerlage HP, Thüroff S, Debruyne FM, Chaussy C, de la Rosette JJ. Transrectal high-intensity focused ultrasound using the Ablatherm device in the treatment of localized prostate carcinoma. Urology. 1999;54:273–7.
Valerio M, Cerantola Y, Eggener SE, Lepor H, Polascik TJ, Villers A, et al. New and established technology in focal ablation of the prostate: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2017;71:17–34.
Hopstaken JS, Bomers JGR, Sedelaar MJP, Valerio M, Futterer JJ, Rovers MM. An updated systematic review on focal therapy in localized prostate cancer: what has changed over the past 5 years? Eur Urol. 2022;81:5–33.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Monaco A, Sommer J, Akerman M, Joshi P, Corcoran A, Katz A. Effect of prostate volume and minimum tumor temperature on 4-year quality-of-life after focal cryoablation compared with active surveillance in men with prostate cancer. J Endourol. 2022;36:1625–31.
Azzouzi A-R, Vincendeau S, Barret E, Cicco A, Kleinclauss F, van der Poel HG, et al. Padeliporfin vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy versus active surveillance in men with low-risk prostate cancer (CLIN1001 PCM301): an open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:181–91.
Scheltema MJ, Chang JI, Böhm M, van den Bos W, Blazevski A, Gielchinsky I, et al. Pair-matched patient- reported quality of life and early oncological control following focal irreversible electroporation versus robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. World J Urol. 2018;36:1383–9.
Garcia-Barreras S, Sanchez-Salas R, Sivaraman A, Barret E, Secin F, Nunes-Silva I, et al. Comparative analysis of partial gland ablation and radical prostatectomy to treat low and intermediate risk prostate cancer: oncologic and functional outcomes. J Urol. 2018;199:140–6.
Tourinho-Barbosa RR, Sanchez-Salas R, Claros OR, Collura-Merlier S, Bakavicius A, Carneiro A, et al. Focal therapy for localized prostate cancer with either HIFU or cryoablation: a single institution experience. J Urol. 2020;203:320–30.
Bakavicius A, Sanchez-Salas R, Muttin F, Sivaraman A, Dell'Oglio P, Barret E, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of focal therapy complications in prostate cancer: a standardized methodology. J Endourol. 2019;33:509–15.
Barret E, Ahallal Y, Sanchez-Salas R, Galiano M, Cosset JM, Validire P, et al. Morbidity of focal therapy in the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2013;63:618–22.
Tay KJ, Cheng CWS, Lau WKO, Khoo J, Thng CH, Kwek JW. Focal therapy for prostate cancer with in-bore mr-guided focused ultrasound: two-year follow-up of a phase I trial-complications and functional outcomes. Radiology. 2017;285:620–8.
Shoji S, Hiraiwa S, Uemura K, Nitta M, Hasegawa M, Kawamura Y, et al. Focal therapy with high-intensity focused ultrasound for the localized prostate cancer for Asian based on the localization with MRI-TRUS fusion image-guided transperineal biopsy and 12-cores transperineal systematic biopsy: prospective analysis of oncolo. Int J Clin Oncol. 2020;25:1844–53.
Yee C-H, Chiu PK-F, Teoh JY-C, Ng C-F, Chan C-K, Hou S-M. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) focal therapy for localized prostate cancer with MRI-US fusion platform. Adv Urol. 2021;2021:7157973.
Dellabella M, Branchi A, Di Rosa M, Pucci M, Gasparri L, Claudini R, et al. Oncological and functional outcome after partial prostate HIFU ablation with focal-one®: a prospective single-center study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021;24:1189–97.
Maestroni U, Dinale F, Minari R, Salsi P, Ziglioli F. High-intensity focused ultrasound for prostate cancer: long-term followup and complications rate. Adv Urol. 2012;2012:960835.
Ward JF, Jones JS. Focal cryotherapy for localized prostate cancer: a report from the national Cryo On-Line Database (COLD) Registry. BJU Int. 2012;109:1648–54.
Aker MN, Brisbane WG, Kwan L, Gonzalez S, Priester AM, Kinnaird A, et al. Cryotherapy for partial gland ablation of prostate cancer: oncologic and safety outcomes. Cancer Med. 2023;12:9351–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.5692.
DiBlasio CJ, Derweesh IH, Malcolm JB, Maddox MM, Aleman MA, Wake RW. Contemporary analysis of erectile, voiding, and oncologic outcomes following primary targeted cryoablation of the prostate for clinically localized prostate cancer. Int Braz J Urol. 2008;34:443–50.
Fernandez-Pascual E, Manfredi C, Martin C, Martinez-Ballesteros C, Balmori C, Lledo-Garcia E, et al. mpMRI-US fusion-guided targeted cryotherapy in patients with primary localized prostate cancer: a prospective analysis of oncological and functional outcomes. Cancers. 2022;14:2988. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122988.
Saito K, Matsuoka Y, Toda K, Yoshida S, Yokoyama M, Yoshimura R, et al. Medium-term oncological and functional outcomes of hemi-gland brachytherapy using iodine-125 seeds for intermediate-risk unilateral prostate cancer. Brachytherapy. 2021;20:842–8.
Ta M-H, Nunes-Silva I, Barret E, Renard-Penna R, Rozet F, Mombet A, et al. Focal brachytherapy for localized prostate cancer: midterm outcomes. Pr Radiat Oncol. 2021;11:e477–e485.
Eggener SE, Yousuf A, Watson S, Wang S, Oto A. Phase II evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging guided focal laser ablation of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2016;196:1670–5.
Oto A, Sethi I, Karczmar G, McNichols R, Ivancevic MK, Stadler WM, et al. MR imaging-guided focal laser ablation for prostate cancer: phase I trial. Radiology. 2013;267:932–40.
Al-Hakeem Y, Raz O, Gacs Z, Maclean F, Varol C. Magnetic resonance image-guided focal laser ablation in clinically localized prostate cancer: safety and efficacy. ANZ J Surg. 2019;89:1610–4.
Walser E, Nance A, Ynalvez L, Yong S, Aoughsten JS, Eyzaguirre EJ, et al. Focal laser ablation of prostate cancer: results in 120 patients with low- to intermediate-risk disease. J Vasc Inter Radio. 2019;30:401–9.e2.
Meneghetti I, Giardino D, Morganti R, Marino V, Menchini Fabris F, Bartoletti R, et al. A single-operator experience using EchoLaser SoracteLiteTM for focal laser ablation of prostate cancer: one more arrow in the quiver for the conservative management of the disease. Arch Ital di Urol Androl organo Uff [di] Soc Ital di Ecogr Urol e Nefrol. 2022;94:406–12.
Chelly S, Maulaz P, Bigot P, Azzouzi AR, Lebdai S. Erectile function after WST11 vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy for low-risk prostate cancer treatment. Asian J Androl. 2020;22:454–8.
Barry Delongchamps N, Schull A, Anract J, Abecassis J-P, Zerbib M, Sibony M, et al. Feasibility and safety of targeted focal microwave ablation of the index tumor in patients with low to intermediate risk prostate cancer: Results of the FOSTINE trial. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0252040.
Oderda M, Marquis A, Calleris G, D'Agate D, Faletti R, Gatti M, et al. Safety and feasibility of transperineal targeted microwave ablation for low- to intermediate-risk prostate cancer. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022;46:3–7.
Chiu PK-F, Chan C-H, Yee C-H, Lau S-Y, Teoh JY-C, Wong H-F, et al. Transperineal Targeted Microwave Ablation (TMA) of localized prostate cancer guided by MRI-Ultrasound fusion and organ-based tracking: a pilot study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022;79:243. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00577-8.
Villers A, Puech P, Flamand V, Haber G-P, Desai MM, Crouzet S, et al. Partial prostatectomy for anterior cancer: short-term oncologic and functional outcomes. Eur Urol. 2017;72:333–42.
Kaouk JH, Ferguson EL, Beksac AT, Zeinab MA, Kaviani A, Weight C, et al. Single-port robotic transvesical partial prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer: initial series and description of technique. Eur Urol. 2022;82:551–8.
Aydin AM, Gage K, Dhillon J, Cheriyan SK, Poch MA, Manley BJ, et al. Focal bipolar radiofrequency ablation for localized prostate cancer: Safety and feasibility. Int J Urol J Jpn Urol Assoc. 2020;27:882–9.
Orczyk C, Barratt D, Brew-Graves C, Peng Hu Y, Freeman A, McCartan N, et al. Prostate Radiofrequency Focal Ablation (ProRAFT) trial: a prospective development study evaluating a bipolar radio frequency device to treat prostate cancer. J Urol. 2021;205:1090–9.
Frandon J, Bey E, Hamard A, Mohammad H, Gonzalez S, Greffier J, et al. Early results of unilateral prostatic artery embolization as a focal therapy in patients with prostate cancer under active surveillance: cancer prostate embolisation, a pilot study. J Vasc Inter Radio. 2021;32:247–55.
Ahn H, Hwang SI, Kim TM, Lee HJ, Choe G, Hong SK, et al. Diagnostic value of multiparametric MRI in detecting residual or recurrent prostate cancer after high-intensity focused ultrasound. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022;26:360–6.
Muller BG, van den Bos W, Brausi M, Futterer JJ, Ghai S, Pinto PA, et al. Follow-up modalities in focal therapy for prostate cancer: results from a Delphi consensus project. World J Urol. 2015;33:1503–9.
Postema AW, De Reijke TM, Ukimura O, Van den Bos W, Azzouzi AR, Barret E, et al. Standardization of definitions in focal therapy of prostate cancer: report from a Delphi consensus project. World J Urol. 2016;34:1373–82.
Donaldson IA, Alonzi R, Barratt D, Barret E, Berge V, Bott S, et al. Focal therapy: patients, interventions, and outcomes—a report from a consensus meeting. Eur Urol. 2015;67:771–7.
Lebastchi AH, George AK, Polascik TJ, Coleman J, de la Rosette J, Turkbey B, et al. Platinum priority-prostate cancer standardized nomenclature and surveillance methodologies after focal therapy and partial gland ablation for localized prostate cancer: an international multidisciplinary consensus. Eur Urol. 2020;78:371–78.
Van Den Bos W, Muller BG, Ahmed H, Bangma CH, Barret E, Crouzet S, et al. Focal therapy in prostate cancer: international multidisciplinary consensus on trial design. Eur Urol. 2014;65:1078–83.
Bianco FJ, Scardino PT, Eastham JA. Radical prostatectomy: Long-term cancer control and recovery of sexual and urinary function (“trifecta”). Urology. 2005;66:83–94.
Patel VR, Sivaraman A, Coelho RF, Chauhan S, Palmer KJ, Orvieto MA, et al. Pentafecta: a new concept for reporting outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2011;59:702–7.
Reijnen C, Brunenberg EJL, Kerkmeijer LGW. Advancing the treatment of localized prostate cancer with MR-guided radiotherapy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023;26:50–52.
Wang F, Li Z, Feng X, Yang D, Lin M. Advances in PSMA-targeted therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022;25:11–26.
Barkin J. High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). Can J Urol. 2011;18:5634–43.
Gage AA, Baust J. Mechanisms of tissue injury in cryosurgery. Cryobiology. 1998;37:171–86.
Kimm SY, Tarin TV, Monette S, Srimathveeravalli G, Gerber D, Durack JC, et al. Nonthermal ablation by using intravascular oxygen radical generation with WST11: dynamic tissue effects and implications for focal therapy. Radiology. 2016;281:109–18.
Davalos RV, Mir LM, Rubinsky B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33:223–31.
Lee T, Mendhiratta N, Sperling D, Lepor H. Focal laser ablation for localized prostate cancer: principles, clinical trials, and our initial experience. Rev Urol. 2014;16:55–66.
Cosset JM, Cathelineau X, Wakil G, Pierrat N, Quenzer O, Prapotnich D, et al. Focal brachytherapy for selected low-risk prostate cancers: a pilot study. Brachytherapy. 2013;12:331–7.
Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency tumor ablation: principles and techniques. Eur J Ultrasound. 2001;13:129–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN and AA were responsible for interpreting data, editing and revise the tables, write the paper. DC, CHY, KZ, DP, PC and RC were responsible for interpreting data, editing summary tables, and editing the manuscript. DC and JYCT were responsible for designing the review protocol, coordinate the group and supervise the project. GRR, ED, GMP, GC, DF, CB, CG and VDS were responsible for collecting and reviewing journal articles, editing summary tables. SS, VG, CFN provided feedback on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
As this is a systematic review, institutional review board or patient consent were not required. As for all systematic reviews, the patients presented in this systematic review have been previously reported.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nicoletti, R., Alberti, A., Castellani, D. et al. Functional outcomes and safety of focal therapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review on results and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs). Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00698-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00698-8
This article is cited by
-
Best of 2023 in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2024)
-
Health-related quality of life following salvage radical prostatectomy for recurrent prostate cancer after radiotherapy or focal therapy
World Journal of Urology (2024)