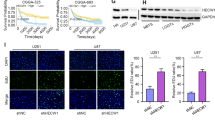
Abstract
Medulloblastoma (MB) is a prevalent malignant brain tumor among children, which can be classified into four primary molecular subgroups. Group 3 MB (G3-MB) is known to be highly aggressive and associated with a poor prognosis, necessitating the development of novel and effective therapeutic interventions. Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death induced by lipid peroxidation, has been identified as a natural tumor suppression mechanism in various cancers. Nevertheless, the potential role of ferroptosis in the treatment of G3-MB remains unexplored. In this study, we demonstrate that RNF126 acts as an anti-ferroptotic gene by interacting with ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1, also known as AIFM2) and ubiquitinating FSP1 at the 4KR-2 sites. Additionally, the deletion of RNF126 reduces the subcellular localization of FSP1 in the plasma membrane, resulting in an increase in the CoQ/CoQH2 ratio in G3-MB. The RNF126-FSP1-CoQ10 pathway plays a pivotal role in suppressing phospholipid peroxidation and ferroptosis both in vivo and in vitro. Clinically, RNF126 exhibited elevated expression in G3-MB and its overexpression was significantly associated with reduced patient survival. Our findings indicate that RNF126 regulates G3-MB sensitivity to ferroptosis by ubiquitinating FSP1, which provides new evidence for the potential G3-MB therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
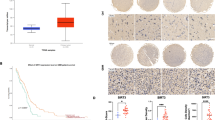
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Holgado BL, Guerreiro Stucklin A, Garzia L, Daniels C, Taylor MD. Tailoring medulloblastoma treatment through genomics: making a change, one subgroup at a time. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 2017;18:143–66.
Kuzan-Fischer CM, Guerreiro Stucklin AS, Taylor MD. Advances in genomics explain medulloblastoma behavior at the bedside. Neurosurgery. 2017;64:21–6.
Northcott PA, Robinson GW, Kratz CP, Mabbott DJ, Pomeroy SL, Clifford SC, et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5:11.
Thomas A, Noël G. Medulloblastoma: optimizing care with a multidisciplinary approach. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2019;12:335–47.
Wang J, Garancher A, Ramaswamy V, Wechsler-Reya RJ. Medulloblastoma: from molecular subgroups to molecular targeted therapies. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018;41:207–32.
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266–82.
Conrad M, Pratt DA. The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:1137–47.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171:273–85.
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31:107–25.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1180–91.
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang PH, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575:688–92.
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, Aldrovandi M, da Silva MC, Ingold I, et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature. 2019;575:693–8.
Mao C, Liu X, Zhang Y, Lei G, Yan Y, Lee H, et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature. 2021;593:586–90.
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:280–96.
Ubellacker JM, Tasdogan A, Ramesh V, Shen B, Mitchell EC, Martin-Sandoval MS, et al. Lymph protects metastasizing melanoma cells from ferroptosis. Nature. 2020;585:113–8.
Rodriguez R, Schreiber SL, Conrad M. Persister cancer cells: Iron addiction and vulnerability to ferroptosis. Mol cell. 2022;82:728–40.
Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijón M, Kennedy PD, Johnson JK, et al. CD8(+) T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;569:270–4.
Deng L, Meng T, Chen L, Wei W, Wang P. The role of ubiquitination in tumorigenesis and targeted drug discovery. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:11.
Yang L, Chen X, Yang Q, Chen J, Huang Q, Yao L, et al. Broad spectrum deubiquitinase inhibition induces both apoptosis and ferroptosis in cancer cells. Front Oncol. 2020;10:949.
Kamikubo K, Kato H, Kioka H, Yamazaki S, Tsukamoto O, Nishida Y, et al. A molecular triage process mediated by RING finger protein 126 and BCL2-associated athanogene 6 regulates degradation of G(0)/G(1) switch gene 2. J Biol Chem. 2019;294:14562–73.
Benini M, Fortuni S, Condò I, Alfedi G, Malisan F, Toschi N, et al. E3 ligase RNF126 directly ubiquitinates frataxin, promoting its degradation: identification of a potential therapeutic target for Friedreich ataxia. Cell Rep. 2017;18:2007–17.
Castro IH, Ferrari A, Herrera MG, Noguera ME, Maso L, Benini M, et al. Biophysical characterisation of the recombinant human frataxin precursor. FEBS Open Bio. 2018;8:390–405.
Yoshino S, Hara T, Nakaoka HJ, Kanamori A, Murakami Y, Seiki M, et al. The ERK signaling target RNF126 regulates anoikis resistance in cancer cells by changing the mitochondrial metabolic flux. Cell Discov. 2016;2:16019.
Huang CY, Lee FL, Peng SF, Lin KH, Chen RJ, Ho TJ, et al. HSF1 phosphorylation by ERK/GSK3 suppresses RNF126 to sustain IGF-IIR expression for hypertension-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:979–89.
Kim SY, Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Kim CH. Non-thermal plasma induces antileukemic effect through mTOR ubiquitination. Cells. 2020;9:595.
Zhi X, Zhao D, Wang Z, Zhou Z, Wang C, Chen W, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF126 promotes cancer cell proliferation by targeting the tumor suppressor p21 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Cancer Res. 2013;73:385–94.
Rodrigo-Brenni MC, Gutierrez E, Hegde RS. Cytosolic quality control of mislocalized proteins requires RNF126 recruitment to Bag6. Mol cell. 2014;55:227–37.
Ishida N, Nakagawa T, Iemura SI, Yasui A, Shima H, Katoh Y, et al. Ubiquitylation of Ku80 by RNF126 promotes completion of nonhomologous end joining-mediated DNA repair. Mol Cell Biol. 2017;37:e00347–16.
Migita K, Matsumoto S, Wakatsuki K, Kunishige T, Nakade H, Miyao S, et al. RNF126 as a marker of prognosis and proliferation of gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:1367–74.
Wang L, Wang X, Zhao Y, Niu W, Ma G, Yin W, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF126 regulates the progression of tongue cancer. Cancer Med. 2016;5:2043–7.
Rees MG, Seashore-Ludlow B, Cheah JH, Adams DJ, Price EV, Gill S, et al. Correlating chemical sensitivity and basal gene expression reveals mechanism of action. Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12:109–16.
Ivanov DP, Coyle B, Walker DA, Grabowska AM. In vitro models of medulloblastoma: choosing the right tool for the job. J Biotechnol. 2016;236:10–25.
Seibt TM, Proneth B, Conrad M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:144–52.
Sato H, Shiiya A, Kimata M, Maebara K, Tamba M, Sakakura Y, et al. Redox imbalance in cystine/glutamate transporter-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:37423–9.
Lo M, Ling V, Low C, Wang YZ, Gout PW. Potential use of the anti-inflammatory drug, sulfasalazine, for targeted therapy of pancreatic cancer. Curr Oncol. 2010;17:9–16.
Sehm T, Fan Z, Ghoochani A, Rauh M, Engelhorn T, Minakaki G, et al. Sulfasalazine impacts on ferroptotic cell death and alleviates the tumor microenvironment and glioma-induced brain edema. Oncotarget. 2016;7:36021–33.
Robe PA, Bentires-Alj M, Bonif M, Rogister B, Deprez M, Haddada H, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of the nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor sulfasalazine in human glioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5595–603.
Young O, Crotty T, O’Connell R, O’Sullivan J, Curran AJ. Levels of oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation in thyroid neoplasia. Head Neck. 2010;32:750–6.
Feng H, Stockwell BR. Unsolved mysteries: how does lipid peroxidation cause ferroptosis? PLoS Biol. 2018;16:e2006203.
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S, Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 2017;547:453–7.
Hangauer MJ, Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Bole D, Eaton JK, Matov A, et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature. 2017;551:247–50.
Smith CJ, McGlade CJ. The ubiquitin ligase RNF126 regulates the retrograde sorting of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Exp Cell Res. 2014;320:219–32.
Smith CJ, Berry DM, McGlade CJ. The E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF126 and Rabring7 regulate endosomal sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:1366–80.
Delker RK, Zhou Y, Strikoudis A, Stebbins CE, Papavasiliou FN. Solubility-based genetic screen identifies RING finger protein 126 as an E3 ligase for activation-induced cytidine deaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:1029–34.
Ge MK, Zhang N, Xia L, Zhang C, Dong SS, Li ZM, et al. FBXO22 degrades nuclear PTEN to promote tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1720.
d’Azzo A, Bongiovanni A, Nastasi T. E3 ubiquitin ligases as regulators of membrane protein trafficking and degradation. Traffic. 2005;6:429–41.
Yang WL, Wang J, Chan CH, Lee SW, Campos AD, Lamothe B, et al. The E3 ligase TRAF6 regulates Akt ubiquitination and activation. Science. 2009;325:1134–8.
Seykora JT, Myat MM, Allen LA, Ravetch JV, Aderem A. Molecular determinants of the myristoyl-electrostatic switch of MARCKS. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:18797–802.
Zhang S, Gou S, Zhang Q, Yong X, Gan B, Jia D. FSP1 oxidizes NADPH to suppress ferroptosis. Cell Res. 2023;33:967–70.
Lv Y, Liang C, Sun Q, Zhu J, Xu H, Li X, et al. Structural insights into FSP1 catalysis and ferroptosis inhibition. Nat Commun. 2023;14:5933.
Tsuchida T, Zou J, Saitoh T, Kumar H, Abe T, Matsuura Y, et al. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity. 2010;33:765–76.
Meierhofer D, Wang X, Huang L, Kaiser P. Quantitative analysis of global ubiquitination in HeLa cells by mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:4566–76.
Xu P, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, Cheng D, Xie Y, Robert J, et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals the function of unconventional ubiquitin chains in proteasomal degradation. Cell. 2009;137:133–45.
Gong J, Liu Y, Wang W, He R, Xia Q, Chen L, et al. TRIM21-promoted FSP1 plasma membrane translocation confers ferroptosis resistance in human cancers. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2302318.
Liang Z, Yang J, Wang J, Tian S, Wang Q, Wang B, et al. Systematic analysis of MCM3 in pediatric medulloblastoma via multi-omics analysis. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:815260.
Zhang Y, Shi J, Liu X, Feng L, Gong Z, Koppula P, et al. BAP1 links metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:1181–92.
Yao H, Xie W, Dai Y, Liu Y, Gu W, Li J, et al. TRIM65 determines the fate of a novel subtype of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors via ubiquitination and degradation of TPIT. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24:1286–97.
Wang J, Sui Y, Li Q, Zhao Y, Dong X, Yang J, et al. Effective inhibition of MYC-amplified group 3 medulloblastoma by FACT-targeted curaxin drug CBL0137. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:1029.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants and personnel involved in the study. We thank Professor Yujie Tang (Department of Pathophysiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China) for providing the D283 and D458 cells.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFC2705002 to JM), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 8227102214 to JM) and Shanghai Leading Talent Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WX, JW, and ST performed the experiments, and prepared figures and tables. WX and JM co-wrote the manuscript. LC coordinated and oversaw the bioinformatics data analysis. LC, ST, JY, ZL, BW, YZ, QW, and FJ analyzed the data, collected samples or clinical data, and prepared figures. LC and JW guided the animal experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, W., Wang, J., Tian, S. et al. RNF126-mediated ubiquitination of FSP1 affects its subcellular localization and ferroptosis. Oncogene (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-02949-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-02949-x