Abstract
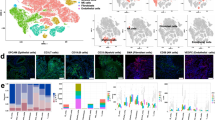
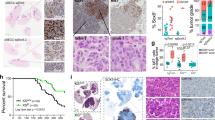
Metastasis predicts poor prognosis in cancer patients. It has been recognized that specific tumor microenvironment defines cancer cell metastasis, whereas the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here we show that Galectin-7 is a crucial mediator of metastasis associated with immunosuppression. In a syngeneic mouse squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) model of NR-S1M cells, we isolated metastasized NR-S1M cells from lymph nodes in tumor-bearing mice and established metastatic NR-S1M cells in in vitro culture. RNA-seq analysis revealed that interferon gene signature was markedly downregulated in metastatic NR-S1M cells compared with parental cells, and in vivo NR-S1M tumors heterogeneously developed focal immunosuppressive areas featured by deficiency of anti-tumor immune cells. Spatial transcriptome analysis (Visium) for the NR-S1M tumors revealed that various pro-metastatic genes were significantly upregulated in immunosuppressive areas when compared to immunocompetent areas. Notably, Galectin-7 was identified as a novel metastasis-driving factor. Galectin-7 expression was induced during tumorigenesis particularly in the microenvironment of immunosuppression, and extracellularly released at later stage of tumor progression. Deletion of Galectin-7 in NR-S1M cells significantly suppressed lymph node and lung metastasis without affecting primary tumor growth. Therefore, Galectin-7 is a crucial mediator of tumor metastasis of SCC, which is educated in the immune-suppressed tumor areas, and may be a potential target of cancer immunotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660.
Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:449–58.
Arnold M, Ferlay J, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Soerjomataram I. Global burden of oesophageal and gastric cancer by histology and subsite in 2018. Gut. 2020;69:1564.
Mody MD, Rocco JW, Yom SS, Haddad RI, Saba NF. Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:2289–99.
Wenig BM. Squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: dysplasia and select variants. Mod Pathol. 2017;30:S112–S118.
van Hagen P, Hulshof MCCM, van Lanschot JJB, Steyerberg EW, Henegouwen MIVB, Wijnhoven BPL, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2074–84.
Cramer JD, Burtness B, Le QT, Ferris RL. The changing therapeutic landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:669–83.
Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–37.
Lawson DA, Kessenbrock K, Davis RT, Pervolarakis N, Werb Z. Tumour heterogeneity and metastasis at single-cell resolution. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:1349–60.
Talmadge JE, Fidler IJ. AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5649–69.
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR, Weinberg RA. Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell. 2017;168:670–91.
Gonzalez H, Hagerling C, Werb Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: from tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018;32:1267–84.
Janssen LME, Ramsay EE, Logsdon CD, Overwijk WW. The immune system in cancer metastasis: friend or foe? J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:79.
Rahma OE, Hodi FS. The intersection between tumor angiogenesis and immune suppression. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:5449–57.
Terry S, Buart S, Chouaib S. Hypoxic stress-induced tumor and immune plasticity, suppression, and impact on tumor heterogeneity. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1625.
Johannes L, Jacob R, Leffler H. Galectins at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2018;131:jcs208884.
Yang R-Y, Rabinovich GA, Liu F-T. Galectins: structure, function and therapeutic potential. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008;10:e17.
Si Y, Yao Y, Jaramillo Ayala G, Li X, Han Q, Zhang W, et al. Human galectin-16 has a pseudo ligand binding site and plays a role in regulating c-Rel-mediated lymphocyte activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2021;1865:129755.
Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Flint T, Gromov P, Kruse TA, Honoré B, et al. Cloning, expression, and chromosome mapping of human Galectin-7 (∗). J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5823–9.
Magnaldo T, Bernerd F, Darmon M. Galectin-7, a human 14-kDa S-lectin, specifically expressed in keratinocytes and sensitive to retinoic acid. Dev Biol. 1995;168:259–71.
Magnaldo T, Fowlis D, Darmon M. Galectin-7, a marker of all types of stratified epithelia. Differentiation. 1998;63:159–68.
Saussez S, Kiss R. Galectin-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:686–97.
Sewgobind NV, Albers S, Pieters RJ. Functions and inhibition of Galectin-7, an emerging target in cellular pathophysiology. Biomolecules. 2021;11:1720.
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1997;389:300–5.
Advedissian T, Deshayes F, Viguier M. Galectin-7 in epithelial homeostasis and carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2760.
Kaur M, Kaur T, Kamboj SS, Singh J. Roles of Galectin-7 in cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17:455–61.
St-Pierre Y, Campion CG, Grosset A-A. A distinctive role for galectin-7 in cancer? Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012;17:438–50.
Zhu X, Ding M, Yu M-L, Feng M-X, Tan L-J, Zhao F-K. Identification of galectin-7 as a potential biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by proteomic analysis. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:290–290.
Zhu H, Wu T-C, Chen W-Q, Zhou L-J, Wu Y, Zeng L, et al. Roles of galectin-7 and S100A9 in cervical squamous carcinoma: clinicopathological and in vitro evidence. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:1051–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27764.
Zhu H, Pei H-P, Zeng S, Chen J, Shen L-F, Zhong M-Z, et al. Profiling protein markers associated with the sensitivity to concurrent chemoradiotherapy in human cervical carcinoma. J Proteome Res. 2009;8:3969–76.
Tsai CJ, Sulman EP, Eifel PJ, Jhingran A, Allen PK, Deavers MT, et al. Galectin-7 levels predict radiation response in squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Gynecologic Oncol. 2013;131:645–9.
Guo J-P, Li X-G. Galectin-7 promotes the invasiveness of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via activation of ERK and JNK signaling. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:1919–24.
Mesquita JA, Queiroz LMG, Silveira ÉJD, Gordon-Nunez MA, Godoy GP, Nonaka CFW, et al. Association of immunoexpression of the galectins-3 and -7 with histopathological and clinical parameters in oral squamous cell carcinoma in young patients. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016;273:237–43.
Alves PM, Godoy GP, Gomes DQ, Medeiros AMC, de Souza LB, da Silveira EJD, et al. Significance of galectins-1, -3, -4 and -7 in the progression of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Pathol Res Pract. 2011;207:236–40.
Saussez S, Cludts S, Capouillez A, Mortuaire G, Smetana K, Kaltner H, et al. Identification of matrix metalloproteinase-9 as an independent prognostic marker in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer with opposite correlations to adhesion/growth-regulatory galectins-1 and -7. Int J Oncol. 2009;34:433–9.
Saussez S, Cucu D-R, Decaestecker C, Chevalier D, Kaltner H, André S, et al. Galectin 7 (p53-Induced Gene 1): a new prognostic predictor of recurrence and survival in stage IV hypopharyngeal cancer. Ann Surgical Oncol. 2006;13:999–1009.
Chen Y-S, Chang C-W, Tsay Y-G, Huang L-Y, Wu Y-C, Cheng L-H, et al. HSP40 co-chaperone protein Tid1 suppresses metastasis of head and neck cancer by inhibiting Galectin-7-TCF3-MMP9 axis signaling. Theranostics. 2018;8:3841–55.
Demers M, Rose AAN, Grosset A-A, Biron-Pain K, Gaboury L, Siegel PM, et al. Overexpression of galectin-7, a myoepithelial cell marker, enhances spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:3023–31.
Gozgit JM, Vasbinder MM, Abo RP, Kunii K, Kuplast-Barr KG, Gui B, et al. PARP7 negatively regulates the type I interferon response in cancer cells and its inhibition triggers antitumor immunity. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:1214.e1210.
Owen KL, Gearing LJ, Zanker DJ, Brockwell NK, Khoo WH, Roden DL, et al. Prostate cancer cell-intrinsic interferon signaling regulates dormancy and metastatic outgrowth in bone. EMBO Rep. 2020;21:e50162. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202050162.
Hirakawa S, Kodama S, Kunstfeld R, Kajiya K, Brown LF, Detmar M. VEGF-A induces tumor and sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis. J Exp Med. 2005;201:1089–99.
Richardson AM, Havel LS, Koyen AE, Konen JM, Shupe J, Wiles WGT, et al. Vimentin is required for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via heterotypic tumor cell-cancer-associated fibroblast interactions during collective invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:420–32.
Bogucka K, Pompaiah M, Marini F, Binder H, Harms G, Kaulich M, et al. ERK3/MAPK6 controls IL-8 production and chemotaxis. Elife. 2020;9:e52511.
Li H-J, Ke F-Y, Lin C-C, Lu M-Y, Kuo Y-H, Wang Y-P, et al. ENO1 promotes lung cancer metastasis via HGFR and WNT signaling–driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2021;81:4094–109.
Wang J, Huang Y, Zhang J, Xing B, Xuan W, Wang H, et al. NRP-2 in tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018;418:176–84.
Liu X, Tan X, Liu P, Wu Y, Qian S, Zhang X. Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1) promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) metastasis by acting as a novel downstream target of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol Res. 2018;26:1123–31.
Huang W-C, Jang T-H, Tung S-L, Yen T-C, Chan S-H, Wang L-H. A novel miR-365-3p/EHF/keratin 16 axis promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis, cancer stemness and drug resistance via enhancing β5-integrin/c-met signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:89–89.
Albini A, Mirisola V, Pfeffer U. Metastasis signatures: genes regulating tumor–microenvironment interactions predict metastatic behavior. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:75–83.
Liu Y, Cao X. Immunosuppressive cells in tumor immune escape and metastasis. J Mol Med. 2016;94:509–22.
Campbell PJ, Yachida S, Mudie LJ, Stephens PJ, Pleasance ED, Stebbings LA, et al. The patterns and dynamics of genomic instability in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2010;467:1109–13.
Nguyen B, Fong C, Luthra A, Smith SA, DiNatale RG, Nandakumar S, et al. Genomic characterization of metastatic patterns from prospective clinical sequencing of 25,000 patients. Cell. 2022;185:563–75. e511
Saussez S, Lorfevre F, Lequeux T, Laurent G, Chantrain G, Vertongen F, et al. The determination of the levels of circulating galectin-1 and -3 in HNSCC patients could be used to monitor tumor progression and/or responses to therapy. Oral Oncol. 2008;44:86–93.
Labrie M, Vladoiu MC, Grosset A-A, Gaboury L, St-Pierre Y. Expression and functions of galectin-7 in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:7705–21.
Pham NTH, Létourneau M, Fortier M, Bégin G, Al-Abdul-Wahid MS, Pucci F, et al. Perturbing dimer interactions and allosteric communication modulates the immunosuppressive activity of human galectin-7. J Biol Chem. 2021;297:101308.
Pape M, Vissers PAJ, Beerepoot L, Van Berge Henegouwen MI, Lagarde S, Mook S, et al. Treatment patterns and overall survival for recurrent esophageal or gastroesophageal junctional cancer: a nationwide European population-based study. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:186.
Matsumoto G, Yajima N, Saito H, Nakagami H, Omi Y, Lee U, et al. Cold shock domain protein A (CSDA) overexpression inhibits tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in a mouse model of squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:539–47.
Nagasawa S, Kuze Y, Maeda I, Kojima Y, Motoyoshi A, Onishi T, et al. Genomic profiling reveals heterogeneous populations of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Commun Biol. 2021;4:438.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of our laboratories for technical assistance and helpful discussions.
Funding
KKuba is supported by the Kaken [20H03426, 20K21566, 22K19551] from Japanese Ministry of Science and the Naito Foundation. JA is supported by the Kaken [20K16153, 22K06907], SM is supported by the Kaken [20K09048], YI is supported by the Kaken [17H06179], and TY is supported by the Kaken [20K07285] from Japanese Ministry of Science. This research was also supported by AMED under Grant Number JP 21lm0203079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JA, YN, SM and KKuba conceived the study. JA, YN, SM, MH, KKemuriyama, TY, TE, YM, YI and KKuba conducted experiments and/or analyzed data. YK and YS conducted deep sequencing and analyzed the data. JA and KKuba wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
An, J., Nagaki, Y., Motoyama, S. et al. Identification of Galectin-7 as a crucial metastatic enhancer of squamous cell carcinoma associated with immunosuppression. Oncogene 41, 5319–5330 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02525-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02525-1