Abstract
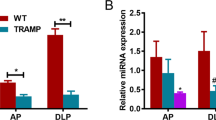
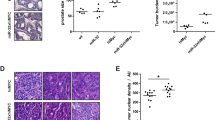
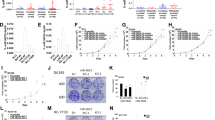
Although miR-7 suppresses the initiation and progression in cancers, little is known about its role in prostate cancer, especially in transgenic mouse models. In present study, we found that expression of miR-7, regulated by p53, was lower in prostate cancer tissues, and miR-7 overexpression significantly mitigated prostate cancer cells growth both in vitro, in organoids and in vivo regardless of p53 status. After we generated miR-7 overexpression transgenic mice and miR-7+/TRAMP mice, we found that transgenic overexpression of miR-7 in mice is safe and miR-7+/TRAMP mice have a preferred overall survival. Moreover, in vivo treatment of miR-7 inhibited subcutaneous tumour growth in mice and prolonged the survival of mice harboring prostate cancer lung metastasis when co-injection with PD-1 antibody. In addition, miR-7 downregulated glycolysis of prostate cancer cells by inhibiting several key pathways including HIF-1α, and subsequently remodeled acidic tumour microenvironment, PanKLa level and T cell infiltration. In summary, our findings highlighted a promising target for development of miRNA-based therapeutics for prostate cancer patients regardless of p53 status.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33.
Culp MB, Soerjomataram I, Efstathiou JA, Bray F, Jemal A. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2020;77:38–52.
Sehrawat A, Gao L, Wang Y, Bankhead A 3rd, McWeeney SK, King CJ, et al. LSD1 activates a lethal prostate cancer gene network independently of its demethylase function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E4179–E4188.
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004;432:231–5.
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S. MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharm. 2011;3:83–92.
Lin CL, Ying TH, Yang SF, Wang SW, Cheng SP, Lee JJ, et al. Transcriptional suppression of miR-7 by MTA2 induces Sp1-mediated klk10 expression and metastasis of cervical cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;20:699–710.
Pan CM, Chan KH, Chen CH, Jan CI, Liu MC, Lin CM, et al. MicroRNA-7 targets T-Box 2 to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Lett. 2020;493:133–42.
Gao Y, Liu J, Huan J, Che F. Downregulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0000735 boosts prostate cancer sensitivity to docetaxel via sponging miR-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:334.
Qi Z, Xu Z, Zhang L, Zou Y, Li J, Yan W, et al. Overcoming resistance to immune checkpoint therapy in PTEN-null prostate cancer by intermittent anti-PI3Kα/β/δ treatment. Nat Commun. 2022;13:182.
Li Z, Peng Y, Li J, Chen Z, Chen F, Tu J, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine regulates glycolysis of cancer cells through PDK4. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2578.
Wang C, Li Y, Yan S, Wang H, Shao X, Xiao M, et al. Interactome analysis reveals that lncRNA HULC promotes aerobic glycolysis through LDHA and PKM2. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3162.
Ren R, Guo J, Shi J, Tian Y, Li M, Kang H. PKM2 regulates angiogenesis of VR-EPCs through modulating glycolysis, mitochondrial fission, and fusion. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:6204–17.
Zhang T, Niu X, Liao L, Cho EA, Yang H. The contributions of HIF-target genes to tumor growth in RCC. PLoS One. 2013;8:e80544.
Westra J, Brouwer E, van Roosmalen IA, Doornbos-van der Meer B, van Leeuwen MA, Posthumus MD, et al. Expression and regulation of HIF-1alpha in macrophages under inflammatory conditions; significant reduction of VEGF by CaMKII inhibitor. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:61.
George AL, Rajoria S, Suriano R, Mittleman A, Tiwari RK. Hypoxia and estrogen are functionally equivalent in breast cancer-endothelial cell interdependence. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:80.
Lee KS, Kim SR, Park SJ, Min KH, Lee KY, Choe YH, et al. Mast cells can mediate vascular permeability through regulation of the PI3K-HIF-1alpha-VEGF axis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:787–97.
Riganti C, Doublier S, Viarisio D, Miraglia E, Pescarmona G, Ghigo D, et al. Artemisinin induces doxorubicin resistance in human colon cancer cells via calcium-dependent activation of HIF-1alpha and P-glycoprotein overexpression. Br J Pharm. 2009;156:1054–66.
Cardozo V, Vaamonde L, Parodi-Talice A, Zuluaga MJ, Agrati D, Portela M, et al. Multitarget neuroprotection by quercetin: Changes in gene expression in two perinatal asphyxia models. Neurochem Int. 2021;147:105064.
Wang J, Chen J, Sen S. MicroRNA as biomarkers and diagnostics. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231:25–30.
Sahraei M, Chaube B, Liu Y, Sun J, Kaplan A, Price NL, et al. Suppressing miR-21 activity in tumor-associated macrophages promotes an antitumor immune response. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:5518–36.
Ribas A, Dummer R, Puzanov I, VanderWalde A, Andtbacka RHI, Michielin O, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy promotes intratumoral T cell infiltration and improves Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Cell. 2017;170:1109–19. e1110
Bayraktar R, Ivan C, Bayraktar E, Kanlikilicer P, Kabil NN, Kahraman N, et al. Dual suppressive effect of miR-34a on the FOXM1/eEF2-kinase axis regulates triple-negative breast cancer growth and invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4225–41.
Yang Y, Ishak Gabra MB, Hanse EA, Lowman XH, Tran TQ, Li H, et al. MiR-135 suppresses glycolysis and promotes pancreatic cancer cell adaptation to metabolic stress by targeting phosphofructokinase-1. Nat Commun. 2019;10:809.
Xiong L, Lin XM, Nie JH, Ye HS, Liu J. Resveratrol and its nanoparticle suppress doxorubicin/docetaxel-resistant anaplastic thyroid cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Nanotheranostics. 2021;5:143–54.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2017;16:203–22.
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2013;12:847–65.
Ottosen S, Parsley TB, Yang L, Zeh K, van Doorn LJ, van der Veer E, et al. In vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis C virus therapeutic targeting the human factor miR-122. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:599–608.
van Zandwijk N, Pavlakis N, Kao SC, Linton A, Boyer MJ, Clarke S, et al. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: a first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1386–96.
Li M, Pan M, You C, Zhao F, Wu D, Guo M, et al. MiR-7 reduces the BCSC subset by inhibiting XIST to modulate the miR-92b/Slug/ESA axis and inhibit tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22:26.
Zhu H, Gan X, Jiang X, Diao S, Wu H, Hu J. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:163.
Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Sharma S, Watabe M, Pai SK, et al. miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1434–44.
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J, Tian L. MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55:1852–62.
Chang YL, Zhou PJ, Wei L, Li W, Ji Z, Fang YX, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits the stemness of prostate cancer stem-like cells and tumorigenesis by repressing KLF4/PI3K/Akt/p21 pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:24017–31.
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324:1029–33.
Ward C, Langdon SP, Mullen P, Harris AL, Harrison DJ, Supuran CT, et al. New strategies for targeting the hypoxic tumour microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39:171–9.
Lequeux A, Noman MZ, Xiao M, Van Moer K, Hasmim M, Benoit A, et al. Targeting HIF-1 alpha transcriptional activity drives cytotoxic immune effector cells into melanoma and improves combination immunotherapy. Oncogene. 2021;40:4725–35.
Reid MA, Dai Z, Locasale JW. The impact of cellular metabolism on chromatin dynamics and epigenetics. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:1298–306.
Irizarry-Caro RA, McDaniel MM, Overcast GR, Jain VG, Troutman TD, Pasare C. TLR signaling adapter BCAP regulates inflammatory to reparatory macrophage transition by promoting histone lactylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:30628–38.
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C, Weng Y, et al. Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature. 2019;574:575–80.
Wu Z, Chen H, Luo W, Zhang H, Li G, Zeng F, et al. The landscape of immune cells infiltrating in prostate cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10:517637.
Bullock AN, Fersht AR. Rescuing the function of mutant p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:68–76.
Hu J, Cao J, Topatana W, Juengpanich S, Li S, Zhang B, et al. Targeting mutant p53 for cancer therapy: direct and indirect strategies. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:157.
Thapa D, Meng P, Bedolla RG, Reddick RL, Kumar AP, Ghosh R. NQO1 suppresses NF-κB-p300 interaction to regulate inflammatory mediators associated with prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5644–55.
Cheteh EH, Sarne V, Ceder S, Bianchi J, Augsten M, Rundqvist H, et al. Interleukin-6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts attenuates the p53 response to doxorubicin in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Disco. 2020;6:42.
Lin RW, Ho CJ, Chen HW, Pao YH, Chen LE, Yang MC, et al. P53 enhances apoptosis induced by doxorubicin only under conditions of severe DNA damage. Cell Cycle. 2018;17:2175–86.
Sun Y, Xia P, Zhang H, Liu B, Shi Y. P53 is required for Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via the TGF-beta signaling pathway in osteosarcoma-derived cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6:114–25.
Karthaus WR, Iaquinta PJ, Drost J, Gracanin A, van Boxtel R, Wongvipat J, et al. Identification of multipotent luminal progenitor cells in human prostate organoid cultures. Cell. 2014;159:163–75.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81872089, 81672551 and 82102799), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant number BK20210230), Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (grant number BE2019751), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent (grant number ZDRCA2016080), The Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Team (grant number CXTDA2017025), Doctor of Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Jiangsu Province (grant number JSSCBS20210138, JSSCBS20210088), The General Project of Medical Research of Jiangsu Health and Wellness Committee (grant number M2020049), Key R & D (Social Development) Projects of Jiangsu Province (BE2018629) Wuxi “Taihu Talents Program” Medical and Health High-level Talents Project, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars (No. 2019BYYFYYQ09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BX and MC conceived, designed, and supervised the study. Can Wang perform the experiments. WL, NS and CL analyzed and interpreted the data. QH provided patient samples. SC provided pathology expertise. Ninghan Feng provided material and technical support. ZY wrote the original draft of the manuscript. HG reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Li, W., Hu, Q. et al. Transgenic construction and functional miRNA analysis identify the role of miR-7 in prostate cancer suppression. Oncogene 41, 4645–4657 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02461-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02461-0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular panorama of therapy resistance in prostate cancer: a pre-clinical and bioinformatics analysis for clinical translation
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2024)