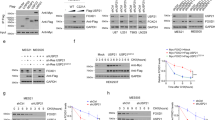
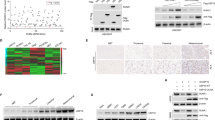
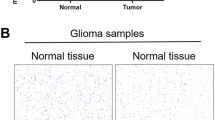
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive primary brain tumor as one of the deadliest cancers. The TGF-β signaling acts as an oncogenic factor in GBM, and plays vital roles in development of GBM. SMAD7 is a major inhibitor of TGF-β signaling, while the deubiquitination of SMAD7 has been poorly studied in GBM. Here, we found USP2 as a new prominent candidate that could regulate SMAD7 stability. USP2 was lost in GBM, leading to the poor prognosis in patients. Moreover, aberrant DNA methylation mediated by DNMT3A induced the low expression of USP2 in GBM. USP2 depletion induced TGF-β signaling and progression of GBM. In contrast, overexpressed USP2 suppressed TGF-β signaling and GBM development. Specifically, USP2 interacted with SMAD7 and prevented SMAD7 ubiquitination. USP2 directly cleaved Lys27- and Lys48-linked poly-ubiquitin chains of SMAD7, and Lys27-linked poly-ubiquitin chains of SMAD7 K185 mediated the recruitment of SMAD7 to HERC3, which regulated Lys63-linked poly-ubiquitination of SMAD7. Moreover, we demonstrated that the DNMT3A inhibitor SGI-1027 induced USP2, suppressed TGF-β signaling and GBM development. Thus, USP2 repressed development of GBM by inhibition TGF-β signaling pathway via the deubiquitination of SMAD7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tu Y, Chen Z, Zhao P, Sun G, Bao Z, Chao H, et al. Smoothened promotes glioblastoma radiation resistance via activating USP3-mediated claspin deubiquitination. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:1749–62.
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66.
Dixit D, Prager BC, Gimple RC, Poh HX, Wang Y, Wu Q, et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDF2 maintains oncogene expression and is a targetable dependency in glioblastoma stem cells. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:480–99.
Jiang T, Nam DH, Ram Z, Poon WS, Wang J, Boldbaatar D, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of adult diffuse gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2021;499:60–72.
Sanai N, Li J, Boerner J, Stark K, Wu J, Kim S, et al. Phase 0 trial of AZD1775 in first-recurrence glioblastoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:3820–8.
Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA, et al. TGF-beta receptor inhibitors target the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:655–68.
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Gu S, Xu Y, Liu T, Li H, et al. ALK phosphorylates SMAD4 on tyrosine to disable TGF-beta tumour suppressor functions. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21:179–89.
Song B, Park SH, Zhao JC, Fong KW, Li S, Lee Y, et al. Targeting FOXA1-mediated repression of TGF-beta signaling suppresses castration-resistant prostate cancer progression. J Clin Investig. 2019;129:569–82.
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Moren A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R, et al. Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature. 1997;389:631–5.
Zhang Z, Fan Y, Xie F, Zhou H, Jin K, Shao L, et al. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor OTUD1 deubiquitinates SMAD7. Nat Commun. 2017;8:2116.
Yan X, Liu Z, Chen Y. Regulation of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2009;41:263–72.
Wiesner S, Ogunjimi AA, Wang HR, Rotin D, Sicheri F, Wrana JL, et al. Autoinhibition of the HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 through its C2 domain. Cell. 2007;130:651–62.
Zhang S, Fei T, Zhang L, Zhang R, Chen F, Ning Y, et al. Smad7 antagonizes transforming growth factor beta signaling in the nucleus by interfering with functional Smad-DNA complex formation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:4488–99.
Qu Q, Mao Y, Xiao G, Fei X, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. USP2 promotes cell migration and invasion in triple negative breast cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:5415–23.
He J, Lee HJ, Saha S, Ruan D, Guo H, Chan CH. Inhibition of USP2 eliminates cancer stem cells and enhances TNBC responsiveness to chemotherapy. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:285.
Zhang J, Liu S, Li Q, Shi Y, Wu Y, Liu F, et al. The deubiquitylase USP2 maintains ErbB2 abundance via counteracting endocytic degradation and represents a therapeutic target in ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:2710–25.
Niederlander C, Walsh JJ, Episkopou V, Jones CM. Arkadia enhances nodal-related signalling to induce mesendoderm. Nature. 2001;410:830–4.
Koinuma D, Shinozaki M, Komuro A, Goto K, Saitoh M, Hanyu A, et al. Arkadia amplifies TGF-beta superfamily signalling through degradation of Smad7. EMBO J. 2003;22:6458–70.
Tang Y, Reissig S, Glasmacher E, Regen T, Wanke F, Nikolaev A, et al. Alternative splice forms of CYLD mediate ubiquitination of SMAD7 to prevent tgfb signaling and promote colitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:692–707. e7
Zhao Y, Thornton AM, Kinney MC, Ma CA, Spinner JJ, Fuss IJ, et al. The deubiquitinase CYLD targets Smad7 protein to regulate transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling and the development of regulatory T cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:40520–30.
Wang Q, Hu B, Hu X, Kim H, Squatrito M, Scarpace L, et al. Tumor evolution of glioma-intrinsic gene expression subtypes associates with immunological changes in the microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:152.
Bhat KPL, Balasubramaniyan V, Vaillant B, Ezhilarasan R, Hummelink K, Hollingsworth F, et al. Mesenchymal differentiation mediated by NF-kappaB promotes radiation resistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:331–46.
Heyn H, Esteller M. DNA methylation profiling in the clinic: applications and challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:679–92.
Wang Q, Cai J, Fang C, Yang C, Zhou J, Tan Y, et al. Mesenchymal glioblastoma constitutes a major ceRNA signature in the TGF-beta pathway. Theranostics. 2018;8:4733–49.
Li H, Li J, Chen L, Qi S, Yu S, Weng Z, et al. HERC3-mediated SMAD7 ubiquitination degradation promotes autophagy-induced EMT and chemoresistance in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:3602–16.
Yin Q, Han T, Fang B, Zhang G, Zhang C, Roberts ER, et al. K27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF by ITCH engages cytokine response to maintain MEK-ERK signaling. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1870.
Wu X, Lei C, Xia T, Zhong X, Yang Q, Shu HB. Regulation of TRIF-mediated innate immune response by K27-linked polyubiquitination and deubiquitination. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4115.
Chai RC, Chang YZ, Chang X, Pang B, An SY, Zhang KN, et al. YTHDF2 facilitates UBXN1 mRNA decay by recognizing METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification to activate NF-kappaB and promote the malignant progression of glioma. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:109.
Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocana A, Penuelas S, Arias A, et al. High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:147–60.
Tong L, Shen S, Huang Q, Fu J, Wang T, Pan L, et al. Proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad7 is critical for lung cancer metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:1795–806.
Park SH, Jung EH, Kim GY, Kim BC, Lim JH, Woo CH. Itch E3 ubiquitin ligase positively regulates TGF-beta signaling to EMT via Smad7 ubiquitination. Mol Cells. 2015;38:20–5.
Izzi L, Attisano L. Regulation of the TGFbeta signalling pathway by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Oncogene. 2004;23:2071–8.
De Boeck M, ten Dijke P. Key role for ubiquitin protein modification in TGFbeta signal transduction. UPS J Med Sci. 2012;117:153–65.
Imamura T, Oshima Y, Hikita A. Regulation of TGF-beta family signalling by ubiquitination and deubiquitination. J Biochem. 2013;154:481–9.
Song Y, Jiang Y, Tao D, Wang Z, Wang R, Wang M, et al. NFAT2-HDAC1 signaling contributes to the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2020;22:46–57.
Behnan J, Finocchiaro G, Hanna G. The landscape of the mesenchymal signature in brain tumours. Brain. 2019;142:847–66.
Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–28.
Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:143–53.
Xu TH, Liu M, Zhou XE, Liang G, Zhao G, Xu HE, et al. Structure of nucleosome-bound DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B. Nature. 2020;586:151–5.
Gu X, Gong H, Shen L, Gu Q. MicroRNA-129-5p inhibits human glioma cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest by directly targeting DNMT3A. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:2834–47.
Kit Leng Lui S, Iyengar PV, Jaynes P, Isa Z, Pang B, Tan TZ, et al. USP26 regulates TGF-beta signaling by deubiquitinating and stabilizing SMAD7. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:797–808.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82120108018 and 81972153), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M701495), Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD, Grant No. JX10231803), and Gusu School, Nanjing Medical University (GSKY202201010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJ designed the experiments. YT, LX, and JX performed the experiments. ZB, WT, YY, and GS analyzed the data. ZM and HC collected samples. YY and NL supervised the study. YT wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, Y., Xu, L., Xu, J. et al. Loss of deubiquitylase USP2 triggers development of glioblastoma via TGF-β signaling. Oncogene 41, 2597–2608 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02275-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02275-0
This article is cited by
-
O-GlcNAcylation of melanophilin enhances radiation resistance in glioblastoma via suppressing TRIM21 mediated ubiquitination
Oncogene (2024)
-
USP2 Promotes the Proliferation and Inflammation of Fibroblast-Like Synovial Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through Deubiquitination of TRAF2
Biochemical Genetics (2024)
-
USP32 deubiquitinase: cellular functions, regulatory mechanisms, and potential as a cancer therapy target
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
USP10 deubiquitinates RUNX1 and promotes proneural-to-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Ubiquitinomics revealed disease- and stage-specific patterns relevant for the 3PM approach in human sigmoid colon cancers
EPMA Journal (2023)