Abstract
Short telomere length is a risk factor for age-related disease, but it is also associated with reduced hippocampal volumes, age-related cognitive decline and psychiatric disorder risk. The current study explored whether telomere shortening might have an influence on cognitive function and psychiatric disorder pathophysiology, via its hypothesised effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. We modelled telomere shortening in human hippocampal progenitor cells in vitro using a serial passaging protocol that mimics the end-replication problem. Serially passaged progenitors demonstrated shorter telomeres (P ≤ 0.05), and reduced rates of cell proliferation (P ≤ 0.001), with no changes in the ability of cells to differentiate into neurons or glia. RNA-sequencing and gene-set enrichment analyses revealed an effect of cell ageing on gene networks related to neurogenesis, telomere maintenance, cell senescence and cytokine production. Downregulated transcripts in our model showed a significant overlap with genes regulating cognitive function (P ≤ 1 × 10−5), and risk for schizophrenia (P ≤ 1 × 10−10) and bipolar disorder (P ≤ 0.005). Collectively, our results suggest that telomere shortening could represent a mechanism that moderates the proliferative capacity of human hippocampal progenitors, which may subsequently impact on human cognitive function and psychiatric disorder pathophysiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder, have an average life expectancy approximately a decade lower than the rest of the population [1,2,3]. This statistic primarily reflects the higher prevalence of comorbid age-related diseases, including coronary artery disease, diabetes and dementia, which contribute to early mortality [3, 4]. Epidemiological findings such as these, have prompted researchers to consider whether faster ageing represents a core component to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders, or whether it represents the consequences of unhealthy lifestyles and stressful experiences, more common amongst those diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder [5, 6].
Telomere length is one biological marker which has been used to study rates of cell ageing amongst psychiatric disorder patients [7]. Telomeres are DNA repeat structures found at the ends of chromosomes, which in humans, comprise of a six-nucleotide repeat sequence (TTAGGG) [8]. Telomeres are vital for maintaining chromosomal stability [9] and have been shown to regulate a cell’s ability to replicate via mitosis [10]. Telomere length gets shorter with each somatic cell division due to the inability of DNA polymerase to fully replicate the 3′ end of the new DNA strand during DNA replication; a phenomenon known as the end-replication problem [11]. Furthermore, telomerase activity [12], oxidative stress [13], genetics [14] and specific environmental factors, such as stress and exercise [15], moderate telomere length and the rate at which it shortens. When a telomere reaches a critically short length, the cell stops dividing and reaches a state of cellular senescence, often referred to as the ‘Hayflick limit’ [16]. The Hayflick limit has been demonstrated in a variety of adult cell types in vitro, including fibroblasts [10], endothelial cells [17] and lymphocytes [18], whereby cells exhibit progressively shorter telomeres over increasing passages (or ‘population doublings’), a gradual reduction in their ability to proliferate, a reduced propensity to undergo programmed cell death, and a maladaptive proinflammatory phenotype [19]. The reduced replicative capacity of ageing cells is hypothesised to contribute to age-related tissue-level pathology in vivo; as old, damaged cells, can no longer be replaced with new, healthy cells [20].
In the context of psychiatry, meta-analyses reveal that, in general, psychiatric disorder patients exhibit shorter leukocyte telomere lengths relative to unaffected individuals of equivalent ages, which could contribute to the increased burden of age-related disease [21,22,23,24]. In addition to shorter telomere lengths, psychiatric disorder patients frequently exhibit neurological differences such as smaller hippocampi [25,26,27], and some studies have suggested a relationship between shortened telomere length and psychiatric disorder neuropathology [28,29,30,31].
The hippocampus is a brain structure important in cognition and mood regulation that is capable of adult neurogenesis due to the retainment of neural progenitors in the dentate gyrus; a specialised niche that allows progenitors to form new, functional neurons [32]. Most cross-sectional studies [29, 33,34,35], though not all [36,37,38], have reported positive associations between peripheral telomere length and hippocampal volume, or between peripheral telomerase activity and hippocampal volume [39]. Recent longitudinal data also support this relationship, demonstrating that greater leukocyte telomere shortening in elderly individuals is associated with a steeper loss in hippocampal volume [40]. Intriguingly, there is also a positive relationship between telomere length and cognitive performance [29, 31], and it has been hypothesised that telomere length contributes to this association by moderating the rate of adult neurogenesis [41]. This hypothesis is supported by various lines of evidence. First, chronological age and mood dysfunction is associated with both shorter telomere length in hippocampal tissue, and reduced rates of hippocampal neurogenesis [42,43,44,45,46]. Consequently, telomere shortening in proliferating neural cell populations might be driving tissue-level differences in telomere length observed in the hippocampus. Second, reduced rates of hippocampal neurogenesis correlate with poorer performance in the Morris water maze task [47], and in visual pattern discrimination tasks [48], indicative of cognitive dysfunction; as well as reduced swim time in the forced-swim test, indicative of depression-like behaviour [49]. Third, reductions in the expression of genes that regulate telomere length in the adult hippocampus in conditional knockout mouse models recapitulate age-related impairments to hippocampal neurogenesis, cognitive performance and behaviour, suggesting that telomere function is a key regulator of age-related changes to neurogenesis and cognition [50, 51]. Despite these insights, to-date, there have been no studies investigating the impact of telomere shortening on human hippocampal progenitor cells, nor its downstream relationship to cognition and psychiatric disease. This is largely due to the inaccessibility of the dentate gyrus; the fact that there are no validated peripheral biomarkers or neuroimaging tools to assess rates of hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo, in association with cognition and psychiatric conditions; and methodological challenges, like reliably immuno-staining post-mortem brain samples in large numbers [52].
The current study employed a systematic, multidisciplinary approach which aimed to model the effects of telomere shortening on human hippocampal neurogenesis, and subsequently its relationship to cognition and psychiatric disorder risk. First, we modelled telomere shortening using a serial passaging protocol that recapitulates the end-replication problem, in a human hippocampal progenitor cell line. We confirmed that reductions in telomere length were associated with lower levels of cell proliferation, without affecting the ability of cells to differentiate into neurons or glia. Second, complementary RNA-sequencing data revealed 3281 transcripts which change in association with telomere shortening. Of these, the 1594 downregulated genes strongly overlap with genes implicated in cognitive function and schizophrenia, and to a lesser extent bipolar disorder. Our work suggests that in addition to the established role of telomere length in age-related pathology, it may also play a role in psychiatric disorder neuropathophysiology via its effects on hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation.
Materials and methods
Human hippocampal progenitor cell line
An existing multipotent human foetal hippocampal progenitor cell line, HPCOA07/03 (ReNeuron, UK), was used to model human hippocampal neurogenesis in vitro, as used previously by our team [53,54,55,56]. These cells proliferate in the presence of growth factors, and upon their removal, differentiate into PROX-1 positive neurons, and glia. For further details on the cell line and culture conditions for proliferating and differentiating cells, see Supplementary information, S1, S2.
Modelling telomere shortening via the ‘end replication problem’
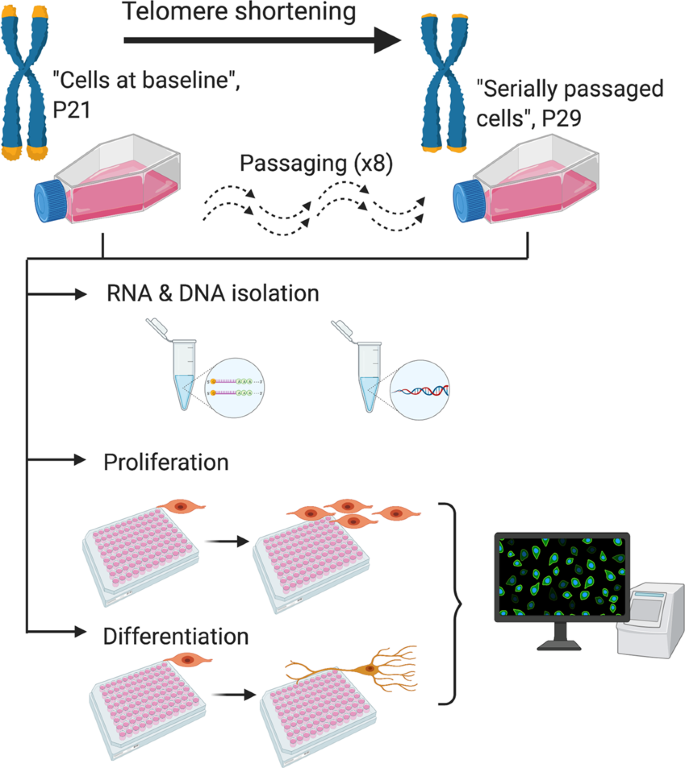
As in other in vitro systems [17, 18, 57], we modelled telomere shortening by serially passaging cells. Serial passaging allows cell populations to double numerous times, and facilitates telomere shortening resulting from the end-replication problem (the incomplete synthesis of chromosome ends during DNA replication).
Our experimental protocol utilised four cryovials corresponding to four subcultures of cells (biological replicates), which were revived in separate T25 flasks and grown in proliferating medium. Once confluent, the cells were passaged onto a T75 flask under the same conditions, see Supplementary information, S1. ‘Cells at baseline’ in our model corresponded to those utilised at the start of our study, which had undergone fewer cell divisions and which have a lower passage number (P21). Subsets of cells were then, either isolated and pelleted for DNA and RNA extraction (telomere length assessment and RNA-sequencing); seeded onto two 96-well plates for proliferation and differentiation assays (immunocytochemistry); or seeded onto a new T75 flask for subsequent serial passaging, see Fig. 1. Passaging occurred once cells were 80–90% confluent (~48 h), as confirmed by cell count. At each passage, cells were reseeded at a density of 2 × 106 cells/T75 flask to ensure an approximately consistent number of population doublings across biological replicates. ‘Serially passaged cells’ in our model corresponded to a subset of P21 cells that underwent eight subsequent passages (P29), where again we isolated DNA and RNA, or submitted cells to a final proliferation or differentiation assay, Fig. 1.
Proliferation and differentiation assays (immunocytochemistry)
To compare differences in cell marker levels between cells at baseline and serially passaged cells, we performed immunocytochemistry using an established 3-day proliferation protocol performed on 96-well plates, where we assayed the proliferation markers BrdU and Ki67, and the apoptosis marker caspase-3 (CC3). We also assessed differentiation as part of a 7-day protocol, where we assayed neuronal markers, doublecortin (DCX) and microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2), the astrocyte marker, S100β and apoptotic marker, CC3. See Supplementary information, S3–S5 for further details.
Nucleic acid extraction
Approximately 50% of the cell suspension obtained during passaging was pelleted and stored at −80 °C at the beginning (passage 21; cells at baseline) and end of experiments (passage 29; serially passaged cells). DNA and RNA were extracted using the Qiagen AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), see Supplementary information, S6, for further details.
Telomere length measurements
Relative telomere length was quantified using DNA samples and a modified version of the quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction protocol described by Cawthon [58], as used by our lab previously [5, 7, 14, 29], see Supplementary information, S7, for further details.
RNA-sequencing
Library preparation and RNA-sequencing was performed at The Genomic Centre, King’s College London. Briefly, total RNA samples were submitted to a DNAse treatment using the DNA-free™ DNA Removal Kit (Invitrogen, California, USA). Subsequently, 300 ng of total RNA from each sample was submitted for ribosomal RNA depletion using the NEBNext rRNA Depletion kit (New England Biolabs, Massachusetts, USA), and RNA-Seq libraries were constructed using the NEBNext Ultra II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina. The samples were sequenced in a HiSeq 4000 sequencing system (Illumina). Raw reads were downloaded and processed using a systematic approach, see Supplementary information, S8. Differential expression analysis was performed to compare cells at baseline versus serially passaged cells (N = 4 biological replicates per condition) using the Wald test in DESeq2, controlling for biological replicates. Log2 fold-changes were shrunk using apeglm [59], and the false discovery rate (FDR) correction was used to control for multiple comparisons. Gene expression differences were considered significant if PFDR < 0.05.
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment
To understand which biological mechanisms were being affected in our cell model in association with telomere shortening, we separately entered genes (PFDR < 0.05) showing an increase in expression, and those showing a decrease in expression, into FUMA [60]. The GENE2FUNC tool performs a gene-set enrichment analysis, where gene sets were defined by The Molecular Signatures Database. We included all transcripts surviving DESeq2’s internal filtering criteria as our background list (i.e. all genes expressed in the samples). Multiple testing correction was performed using the FDR method, and GO terms were considered significant if PFDR < 0.05.
Gene-set enrichment analysis
We tested for a genetic overlap between upregulated and downregulated genes affected in our cell ageing model and those implicated in major depressive disorder [61], bipolar disorder [62], schizophrenia [63] and general cognitive function [64], using MAGMA [65] and publicly available GWAS summary statistics, see Supplementary Information, S9.
Foetal brain samples
We performed a complementary experiment using foetal brain samples in order to clarify whether telomere shortening occurs in the human brain during early development in accordance with gestational age, and therefore, whether our cell model could also be recapitulating a neurodevelopmental cell process. Brain tissue was obtained frozen and had not been dissected into regions. Half of the brain tissue from each individual foetus was homogenised for subsequent genomic DNA extraction, which was performed by standard phenol-chloroform procedures as described previously [66]. Sample sex was determined via PCR amplification [66]. In total, DNA was available from 37 females and 48 males (n = 85). Gestational ages were estimated using foot and knee to heel length measurements. Gestational ages ranged from 75–161 days, with a mean gestational age of 107.96 (S.D. = 16.12). Telomere length was quantified as above, and as described in Supplementary Information S7. The human embryonic and foetal material was provided by the Joint MRC/Wellcome Human Developmental Biology Resource (www.hdbr.org). Ethical approval for the HDBR was granted by the Royal Free Hospital research ethics committee under reference 18/NE/0290.
Statistical analyses
Differences in telomere length between the baseline condition and serially passaged cells was determined using a two-tailed independent-samples t-test. Similarly, differences in the expression of cell markers were determined using two-tailed independent-samples t-tests, followed by a Bonferroni correction to account for the total number of markers assayed in either the proliferating or differentiating cell conditions. To test the effect of gestational age on telomere length in the foetal brain, we ran a linear regression with relative telomere length as the outcome variable, sex as a covariate and gestational age (days) as the independent variable. Data normality was confirmed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. RNA-sequencing and downstream analyses were performed as described above.
Figure generation
Figures were created using Prism7 (GraphPad, San Diego USA), the EnhancedVolcano package in R [67] and BioRender (Toronto, Canada).
Results
(i) Hippocampal progenitor cells demonstrate telomere shortening in response to serial passaging and the end-replication problem
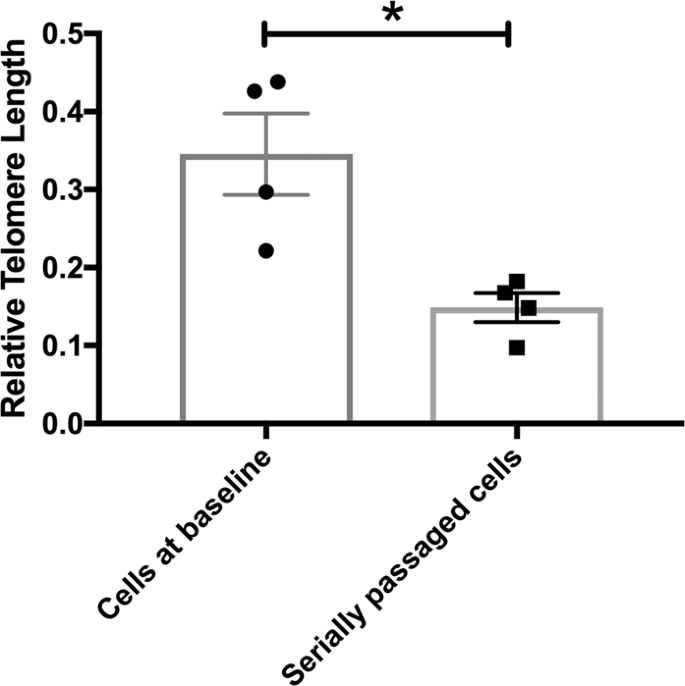
We compared relative telomere length in cells at baseline (P21) and in cells which had undergone serial passaging (P29). An independent samples t-test confirmed shorter telomere length in the serially passaged cells relative to cells at baseline (t(6) = 3.542, P = 0.012), Fig. 2.
This bar chart shows the relative telomere length in cells at baseline (P21) and serially passaged cells (P29). There is a significant reduction in telomere length in serially passaged cells relative to cells at baseline. Group differences were detected using an independent samples t-test. Significant differences were considered when P ≤ 0.05, indicated by *.
To complement this finding, we confirmed that telomere shortening was likely being driven by the end-replication problem, as opposed to changes to the telomerase enzyme (another critical telomere regulator) during passaging. hTERT codes for the catalytic subunit of the telomerase enzyme and is tightly controlled, and closely associated with enzyme activity [68]. We performed a quantitative PCR to assess differences in the expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in cells at baseline and serially passaged cells, and found consistently low levels of hTERT expression (relative to the reference gene, Vimentin), which did not differ between groups (t(6) = 1.151, P = 0.294); see Supplementary information, S10.
(ii) Serially passaged hippocampal progenitor cells exhibit decreased cell proliferation
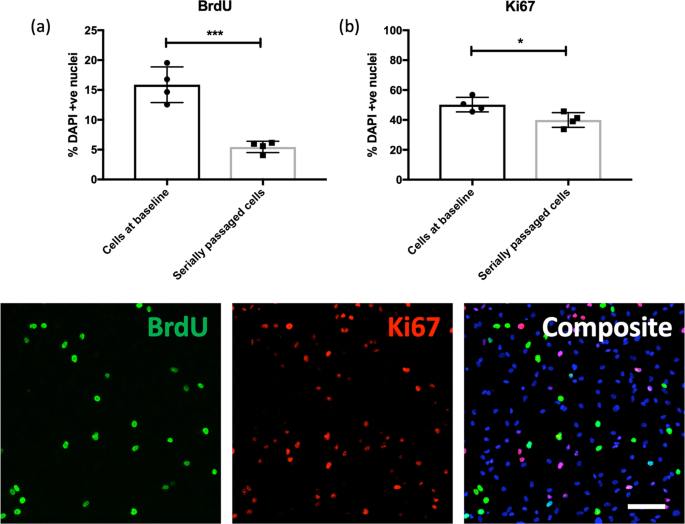
Cells demonstrated a significant reduction in proliferation in association with telomere shortening, Fig. 3. Serially passaged cells exhibited significantly lower levels of proliferation relative to baseline cells, as marked using BrdU staining (two-sample t-test, t(6) = 6.663, P = 0.0006), a difference which remained significant after correcting for the number of cell markers tested (P ≤ 0.05). This difference was also supported by quantification of the proliferation marker Ki67 (two-sample t-test, t(6) = 2.959, P = 0.025). We also observed a lower percentage of serially passaged cells stained with CC3 (indicative of lower rates of cell death), relative to cells at baseline (two-sample t-test, t(6) = 2.481, P = 0.047), however this effect did not survive multiple testing correction (P > 0.05); representative CC3 staining is shown in Fig. 4.
Bar charts (top) show the percentage of BrdU (a) and Ki67 (b) -positive cells relative to the percentage of DAPI stained nuclei (y-axis), in cells at baseline and serially passaged cells (x-axis). Each datapoint represents one biological replicate (N = 4). * represents an uncorrected P ≤ 0.05, and *** represents an uncorrected P ≤ 0.001. Each of the images (below) are representative of a field of immuno-stained cells, taken using a ×10 objective with the CellInsight High Content Screening Platform. Each composite image includes the nuclear marker DAPI in blue. Scale bar = 100 μm.
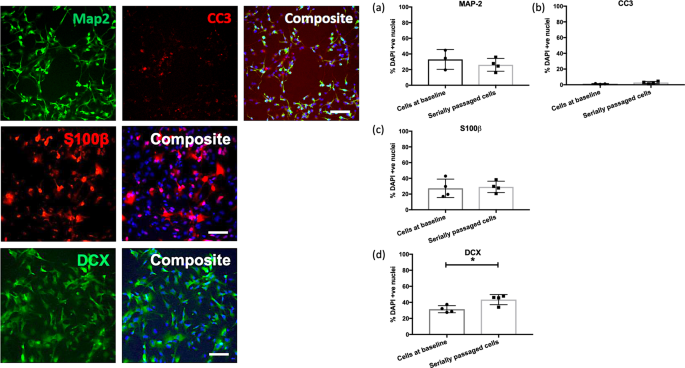
The bar charts (right) show the percentage of MAP-2 (a), CC3 (b), S100β (c) and DCX (d) -positive cells relative to the percentage of DAPI stained nuclei (y-axis), in cells at baseline and serially passaged cells (x-axis). Each datapoint represents one biological replicate (N = 4). * represents an uncorrected P ≤ 0.05. Each of the images (left) are representative of a field of immuno-stained cells, taken using a ×10 objective with the CellInsight High Content Screening Platform. Each composite image includes the nuclear marker DAPI in blue. Scale bar = 100 μm.
(iii) Serially passaged hippocampal progenitor cells do not show differences in their rate of cell differentiation
We observed no differences (P > 0.05) in markers pertaining to glial cells (S100β), cell death (CC3) or more mature neurons (MAP-2), between cells at baseline and serially passaged cells. There was a small increase in the number of doublecortin-positive neurons observed in serially passaged cells (two-sample t(6) = 3.097, P = 0.021), though this difference did not survive multiple testing correction (P > 0.05), Fig. 4.
(iv) Cell ageing is associated with vast transcriptional changes related to neurogenic processes, cellular senescence and inflammation
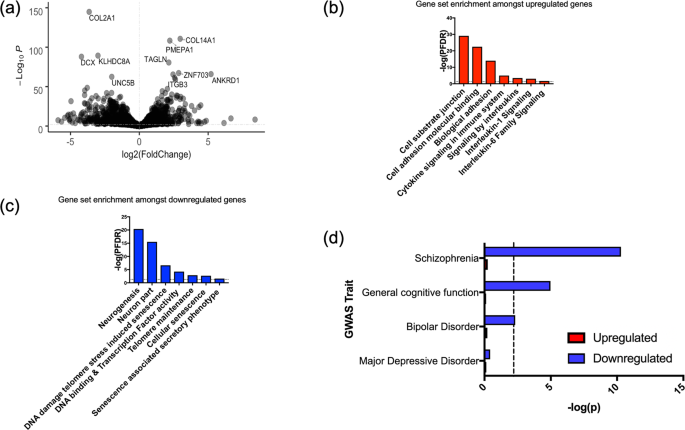
We identified 3281 transcripts which were differentially expressed in serially passaged cells relative to cells at baseline (PFDR < 0.05), Fig. 5a. We found that 1687 genes were upregulated in serially passaged cells, and these genes were associated with cell adhesion. Enrichment amongst canonical pathways revealed an over-representation of genes related to inflammation and cytokine signalling, Fig. 5b. In agreement with previous work relating to the senescence associated secretory phenotype, amongst the upregulated transcripts we observed increased expression of the cytokine regulator, Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NFKB1) and increased interleukin-6 (IL6) levels (PFDR < 0.05) [19]. See Supplementary Datasets for full results.
a A volcano plot summarising the RNA-sequencing results, where log2(Fold change) is shown on the x-axis, and the strength of the association given by −Log10(P), is shown on the y-axis. b Examples of gene sets which significantly overlap with the upregulated genes in our cell model. All gene sets represent those which surpassed a false discovery rate correction, PFDR < 0.05, in our enrichment analysis, as marked by the dashed line. c Examples of gene sets which significantly overlap with the downregulated genes in our cell model. d A bar plot showing the genetic overlap between various traits as assayed by GWAS (y-axis) and genes either upregulated or downregulated in association with cell ageing. The strength of the association is shown on the y-axis (−log(p)). The dashed line represents the threshold of significance (corrected for the number of tests).
1594 genes were also downregulated in serially passaged cells. These genes were broadly associated with neurogenesis and nervous system development. Furthermore, enrichment amongst canonical pathways revealed an over-representation of genes related to telomeres, and cell senescence, Fig. 5c. Note that the downregulated gene expression changes were also enriched for genes affecting cell proliferation (GO_REGULATION_OF_CELL_POPULATION_PROLIFERATION, adj P = 0.00244125; see Supplementary dataset), which supports our cell staining data.
(v) Genes downregulated in association with cell ageing overlap with those implicated in cognitive performance, schizophrenia and bipolar disorder risk
We found a significant overlap between genes which were downregulated in serially passaged cells (PFDR < 0.05) and those implicated in: schizophrenia (β = 0.207, SE = 0.032, P = 5.105 × 10−11); bipolar disorder (β = 0.071, SE = 0.027, P = 0.005); and general cognitive function (β = 0.138, SE = 0.037, P = 1.057 × 10−5), based on GWAS results, Fig. 5d.
To ensure this result was not being inflated by the relatively large size of our gene set (n = 1594), or by an overrepresentation of genes related to tissue type, we performed a sensitivity analysis. From the transcripts surpassing our multiple testing threshold, we selected 500 which exhibited the highest fold change. In addition, when mapping SNPs to genes, we removed any genes which were not expressed in our cell line from the genomic annotation. When repeating gene-set enrichment analysis, we confirmed that downregulated transcripts remained significantly associated with each trait (P ≤ 0.01). We found no significant overlap between downregulated genes and those implicated in major depressive disorder, nor between upregulated genes and any of our traits.
(vi) Telomere shortening may not occur during early neurodevelopment
Previous evidence suggests that telomere shortening and reduced rates of hippocampal neurogenesis are specific to the adult brain [42,43,44], but schizophrenia risk and cognitive function are also known to be affected by prenatal neurodevelopmental factors [69]. We performed a complementary experiment in order to clarify whether telomere shortening occurs in the human brain during early development in accordance with gestational age, and therefore, whether our cell model could also be recapitulating a neurodevelopmental cell process. To determine whether telomere shortening occurs in the developing brain, we assessed telomere length in foetal brain samples collected from various post-conception days (75–161 days), which is a measure that positively correlates with the number of cell divisions [70]. We did not find a significant correlation between telomere length and post-conception days (β = −0.003 [95% CI: −0.328 to 0.322], P = 0.985), nor an effect of sex (β = −0.001 [−0.011 to 0.009], P = 0.887), see Supplementary information, S11. This suggests that the effect we observe in our study, is unlikely to occur in early neurodevelopment, further supporting the specificity of this process to the postnatal brain.
Discussion
Our study used serial passaging, an established method for modelling telomere shortening via the end replication problem, in human hippocampal progenitor cells. Serially passaged cells demonstrated reduced rates of cell proliferation, as determined by BrdU and Ki67 immunostaining. Telomere shortening was further accompanied by changes to 3281 transcripts, whereby downregulated genes overlapped with those implicated in cognition, schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
The findings presented here support previous research performed in other cell model systems that reveal an intricate relationship between telomere length and cell replicative capacity related to the end-replication problem [17, 18, 57]. Our gene expression data further demonstrates an enrichment of transcript changes related to cell senescence, the senescence associated secretory phenotype, and interleukin-6 signalling. This is in agreement with previous research [19], and validates that our model is capturing meaningful biological changes related to telomere shortening and cell ageing. It also suggests that the decreased proliferation (marked by BrdU) and the nominally decreased cell death (marked by CC3; uncorrected P < 0.05) we observed in serially passaged progenitors, likely relates to early signs of cell senescence, i.e. a reduced number of new, healthy cells, and an accumulation of mitotically old, unhealthy cells that instead of apoptosing, demonstrate a proinflammatory phenotype.
In the context of neurogenesis, our findings extend prior work in animals and post-mortem brain which have shown a significant decline in markers of cell proliferation in the hippocampus in association with age [71, 72], by raising the possibility that telomere shortening is one potentially important age-related cellular mechanism. In contrast to some work [43, 51], we did not observe a robust effect of telomere shortening on rates of neuronal differentiation, as marked by doublecortin and MAP-2 in our cell staining data. However, amongst proliferating cells there was a strong downregulation of doublecortin at the transcript level in association with telomere shortening (Fig. 5a), which might suggest that there are very early, transient reductions in the rates of differentiation, which were not observable after the 7-day differentiation protocol used in our model.
Genetic and association studies have inferred a causal relationship between telomere length and cognition [31], but no study to-date, has demonstrated a cellular mechanism. Our work supports these findings and demonstrates that telomere shortening is associated with reduced hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation alongside changes to the expression of genes regulating general cognitive function. Our cell model and the gene-set enrichment results raise the possibility of a relationship between telomere shortening in human hippocampal progenitors and schizophrenia and bipolar disorder risk. Both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder share a common aetiology [73], and patients frequently exhibit smaller hippocampal volumes [25,26,27] and general cognitive deficits relating to attention, working memory, verbal learning and memory and executive functions [74]. In the context of our results, it is possible that telomere-induced reductions in hippocampal neurogenesis represent one mechanism that contributes to cognitive dysfunction amongst these patients. This notion is also supported by a study using mice, which demonstrates that a maternal infection results in offspring with schizophrenia-like behaviours, reduced rates of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and neural progenitors with both shorter telomere length and reduced telomerase activity [75]. Interestingly, an environmental intervention (increased exercise) was able to normalise both abnormal cell phenotypes and behaviour in this model [75].
Our results add to the work of others (e.g. [75, 76]), and collectively, they raise the possibility that environmental factors with the potential to prevent premature telomere shortening may also have positive influences on hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive function. Intriguingly, environmental interventions shown to reduce the rate of cognitive ageing [77], including exercise and energy restriction, have positive effects on both peripheral telomere length in humans [15, 78, 79] and hippocampal neurogenesis in animal models [80, 81]. Furthermore, diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, have been associated with both increased rates of hippocampal neurogenesis and longer telomeres [32, 82, 83], as have some drugs, such as resveratrol and lithium [14, 84,85,86]. This warrants further study in order to determine whether environmental, dietary and pharmacological interventions could be useful in systematically targeting premature cell ageing and reduced hippocampal neurogenesis.
Despite the promising evidence shown here, there are a number of limitations to our study which should be acknowledged. First, we are measuring changes to telomere length and its effect on hippocampal neurogenesis using a cell model system acquired from a single donor. It is possible that individuals from different genetic backgrounds respond differently to the effects of telomere shortening [14], and as such, future work utilising induced pluripotent stem cell models from a range of donors would be beneficial in validating and extending our work. In addition, our in vitro model may lack construct validity due to the absence of mature cells and established intercellular networks, which are known to interact with progenitor cells and affect their development [87]. Second, although our cell model demonstrated telomere shortening and signs of cellular senescence, the effect was modest, with some serially passaged cells continuing to proliferate [10]. It is likely that a longer culture protocol will provide greater insights into the progressive and longer-term consequences of telomere shortening in hippocampal cells, and this is an important future consideration. Third, the cell model attempts to investigate the relationship between telomere shortening and adult hippocampal neurogenesis, in order to better understand age-related changes to the brain. However, alongside changes in telomere length, there may also be independent changes to the cell (e.g. the epigenetic landscape [88]), so future work will also be needed to further differentiate the causative effects of telomere shortening (e.g. via TERT knockout), from other age-related cell changes. Furthermore, our model makes use of foetal-derived neural progenitors, which although studies suggest do recapitulate the functions of adult neural stem cells, they may not do so entirely [89]. Moreover, our work in foetal brain indicates that despite the importance of early neurodevelopmental factors in the aetiology of schizophrenia [69], telomere shortening does not appear to occur during early brain development. Consequently, further work will be needed to confirm at what stages in postnatal life telomere shortening impacts on hippocampal neurogenesis and becomes important in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disease.
This work extends our understanding of the age-related molecular mechanisms influencing hippocampal neurogenesis, and provides support that telomere shortening may be an important process associated with psychiatric disorders and cognitive function. It also raises the possibility that there is a multisystemic relationship, in which telomere shortening contributes not only to the heightened rates of age-related disease amongst psychiatric disorder patients, but its putative effects on hippocampal neurogenesis suggest it could also represent a mechanism important in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders themselves. Future work should consider whether leukocyte telomere length could act as a useful peripheral biomarker to estimate changes in the rates of hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo, and whether environmental interventions could be used to simultaneously prevent premature telomere shortening and promote hippocampal progenitor proliferation, as we age.
Funding and disclosure
Authors report no conflicts of interest. This work was funded by a Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship (MR/N014863/1) and a Psychiatry Research Trust Grant (grant reference: 92 Branthwaite) awarded to TRP, as well as by Medical Research Council funding (MR/N030087/1) awarded to ST. ABP is funded by a Rayne Foundation PhD studentship and by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Mental Health Biomedical Research Centre, South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care. The funding sources had no role in the study the design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report and in the decision to submit the article for publication. The human embryonic and foetal material was provided by the Joint MRC/Wellcome (MR/R006237/1) Human Developmental Biology Resource (www.hdbr.org).
References
Plana-Ripoll O, Pedersen CB, Agerbo E, Holtz Y, Erlangsen A, Canudas-Romo V, et al. A comprehensive analysis of mortality-related health metrics associated with mental disorders: a nationwide, register-based cohort study. Lancet. 2019;394:1827–35.
Laursen TM. Life expectancy among persons with schizophrenia or bipolar affective disorder. Schizophr Res. 2011;131:101–04.
Laursen TM, Musliner KL, Benros ME, Vestergaard M, Munk-Olsen T. Mortality and life expectancy in persons with severe unipolar depression. J Affect Disord. 2016;193:203–7.
Forty L, Ulanova A, Jones L, Jones I, Gordon-Smith K, Fraser C, et al. Comorbid medical illness in bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 2014;205:465–72.
Palmos AB, Breen G, Goodwin L, Frissa S, Hatch SL, Hotopf M, et al. Genetic risk for psychiatric disorders and telomere length. Front Genet. 2018;9:468.
Lou P, Chen P, Zhang P, Yu J, Wang Y, Chen N, et al. Effects of smoking, depression, and anxiety on mortality in COPD patients: a prospective study. Respir Care. 2014;59:54–61.
Vincent J, Hovatta I, Frissa S, Goodwin L, Hotopf M, Hatch SL, et al. Assessing the contributions of childhood maltreatment subtypes and depression case-control status on telomere length reveals a specific role of physical neglect. J Affect Disord. 2017;213:16–22.
Moyzis RK, Buckingham JM, Cram LS, Dani M, Deaven LL, Jones MD, et al. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1988;85:6622.
Preston RJ. Telomeres, telomerase and chromosome stability. Radiat Res. 1997;147:529–34.
Allsopp RC, Vaziri H, Patterson C, Goldstein S, Younglai EV, Futcher AB, et al. Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:10114–8.
Levy MZ, Allsopp RC, Futcher AB, Greider CW, Harley CB. Telomere end-replication problem and cell aging. J Mol Biol. 1992;225:951–60.
Chan SR, Blackburn EH. Telomeres and telomerase. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004;359:109–21.
Kurz DJ, Decary S, Hong Y, Trivier E, Akhmedov A, Erusalimsky JD. Chronic oxidative stress compromises telomere integrity and accelerates the onset of senescence in human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2417–26.
Coutts F, Palmos AB, Duarte RRR, de Jong S, Lewis CM, Dima D, et al. The polygenic nature of telomere length and the anti-ageing properties of lithium. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:757–65.
Puterman E, Weiss J, Lin J, Schilf S, Slusher AL, Johansen KL, et al. Aerobic exercise lengthens telomeres and reduces stress in family caregivers: a randomized controlled trial—Curt Richter Award Paper 2018. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018;98:245–52.
Shay JW, Wright WE. Hayflick, his limit, and cellular ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:72–6.
Yang J, Chang E, Cherry AM, Bangs CD, Oei Y, Bodnar A, et al. Human endothelial cell life extension by telomerase expression. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26141–8.
Chebel A, Bauwens S, Gerland LM, Belleville A, Urbanowicz I, de Climens AR, et al. Telomere uncapping during in vitro T-lymphocyte senescence. Aging Cell. 2009;8:52–64.
Ghosh K, Capell BC. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: critical effector in skin cancer and aging. J Investig Dermatol. 2016;136:2133–39.
Armanios M, Alder JK, Parry EM, Karim B, Strong MA, Greider CW. Short telomeres are sufficient to cause the degenerative defects associated with aging. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;85:823–32.
Darrow SM, Verhoeven JE, Révész D, Lindqvist D, BWJH Penninx, Delucchi KL, et al. The association between psychiatric disorders and telomere length: a meta-analysis involving 14,827 persons. Psychosom Med. 2016;78:776–87.
Huang YC, Wang LJ, Tseng PT, Hung CF, Lin PY. Leukocyte telomere length in patients with bipolar disorder: an updated meta-analysis and subgroup analysis by mood status. Psychiatry Res. 2018;270:41–49.
Russo P, Prinzi G, Proietti S, Lamonaca P, Frustaci A, Boccia S, et al. Shorter telomere length in schizophrenia: evidence from a real-world population and meta-analysis of most recent literature. Schizophrenia Res. 2018;202:37–45.
Ridout KK, Ridout SJ, Price LH, Sen S, Tyrka AR. Depression and telomere length: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;191:237–47.
Velakoulis D, Pantelis C, McGorry PD, Dudgeon P, Brewer W, Cook M, et al. Hippocampal volume in first-episode psychoses and chronic schizophrenia: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:133–41.
Hibar DP, Westlye LT, van Erp TG, Rasmussen J, Leonardo CD, Faskowitz J, et al. Subcortical volumetric abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:1710–16.
Schmaal L, Veltman DJ, van Erp TG, Samann PG, Frodl T, Jahanshad N, et al. Subcortical brain alterations in major depressive disorder: findings from the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder working group. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:806–12.
Epel ES, Prather AA. Stress, telomeres, and psychopathology: toward a deeper understanding of a triad of early aging. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2018;14:371–97.
Powell TR, Dima D, Frangou S, Breen G. Telomere length and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacolog.y 2018;43:445–53.
Powell TR, De Jong S, Breen G, Lewis CM, Dima D. Telomere length as a predictor of emotional processing in the brain. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019;40:1750–59.
Hägg S, Zhan Y, Karlsson R, Gerritsen L, Ploner A, van der Lee SJ, et al. Short telomere length is associated with impaired cognitive performance in European ancestry cohorts. Translational. Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1100.
Stangl D, Thuret S. Impact of diet on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Genes Nutr. 2009;4:271–82.
King KS, Kozlitina J, Rosenberg RN, Peshock RM, McColl RW, Garcia CK. Effect of leukocyte telomere length on total and regional brain volumes in a large population-based cohort. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:1247–54.
Jacobs EG, Epel ES, Lin J, Blackburn EH, Rasgon NL. Relationship between leukocyte telomere length, telomerase activity, and hippocampal volume in early aging. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:921–23.
Grodstein F, van Oijen M, Irizarry MC, Rosas HD, Hyman BT, Growdon JH, et al. Shorter telomeres may mark early risk of dementia: preliminary analysis of 62 participants from the nurses’ health study. PloS ONE. 2008;3:e1590–e90.
Wikgren M, Karlsson T, Lind J, Nilbrink T, Hultdin J, Sleegers K, et al. Longer leukocyte telomere length is associated with smaller hippocampal volume among non-demented APOE ε3/ε3 subjects. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e34292.
Henje Blom E, Han LKM, Connolly CG, Ho TC, Lin J, LeWinn KZ, et al. Peripheral telomere length and hippocampal volume in adolescents with major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2015;5:e676–e76.
Shivakumar V, Kalmady SV, Rajasekaran A, Chhabra H, Anekal AC, Narayanaswamy JC, et al. Telomere length and its association with hippocampal gray matter volume in antipsychotic-naïve/free schizophrenia patients. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2018;282:11–7.
Wolkowitz OM, Mellon SH, Lindqvist D, Epel ES, Blackburn EH, Lin J, et al. PBMC telomerase activity, but not leukocyte telomere length, correlates with hippocampal volume in major depression. Psychiatry Res. 2015;232:58–64.
Staffaroni AM, Tosun D, Lin J, Elahi FM, Casaletto KB, Wynn MJ, et al. Telomere attrition is associated with declines in medial temporal lobe volume and white matter microstructure in functionally independent older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 2018;69:68–75.
Nilsonne G, Tamm S, Mansson KN, Akerstedt T, Lekander M. Leukocyte telomere length and hippocampus volume: a meta-analysis. F1000Res. 2015;4:1073.
Baek JH, Son H, Jeong YH, Park SW, Kim HJ. Chronological aging standard curves of telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number in twelve tissues of C57BL/6 male mouse. Cells. 2019;8:247.
Ferron SR, Marques-Torrejon MA, Mira H, Flores I, Taylor K, Blasco MA, et al. Telomere shortening in neural stem cells disrupts neuronal differentiation and neuritogenesis. J Neurosci. 2009;29:14394–407.
Lugert S, Basak O, Knuckles P, Haussler U, Fabel K, Gotz M, et al. Quiescent and active hippocampal neural stem cells with distinct morphologies respond selectively to physiological and pathological stimuli and aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:445–56.
Mathews KJ, Allen KM, Boerrigter D, Ball H, Shannon Weickert C, Double KL. Evidence for reduced neurogenesis in the aging human hippocampus despite stable stem cell markers. Aging Cell. 2017;16:1195–99.
Mamdani F, Rollins B, Morgan L, Myers RM, Barchas JD, Schatzberg AF, et al. Variable telomere length across post-mortem human brain regions and specific reduction in the hippocampus of major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2015;5:e636.
Drapeau E, Mayo W, Aurousseau C, Le Moal M, Piazza PV, Abrous DN. Spatial memory performances of aged rats in the water maze predict levels of hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:14385–90.
Sahay A, Wilson DA, Hen R. Pattern separation: a common function for new neurons in hippocampus and olfactory bulb. Neuron. 2011;70:582–8.
Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:2368–78.
Lobanova A, She R, Pieraut S, Clapp C, Maximov A, Denchi EL. Different requirements of functional telomeres in neural stem cells and terminally differentiated neurons. Genes Dev. 2017;31:639–47.
Zhou Q-G, Hu Y, Wu D-L, Zhu L-J, Chen C, Jin X, et al. Hippocampal telomerase is involved in the modulation of depressive behaviors. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12258–69.
Lee H, Thuret S. Adult human hippocampal neurogenesis: controversy and evidence. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24:521–22.
Smeeth DM, Kourouzidou I, Duarte RRR, Powell TR, Thuret S. Prolactin, Estradiol and testosterone differentially impact human hippocampal neurogenesis in an in vitro model. Neuroscience. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.12.021.
Powell TR, Murphy T, Lee SH, Duarte RRR, Lee HA, Smeeth D, et al. Inter-individual variation in genes governing human hippocampal progenitor differentiation in vitro is associated with hippocampal volume in adulthood. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15112.
Powell TR, Murphy T, Lee SH, Price J, Thuret S, Breen G. Transcriptomic profiling of human hippocampal progenitor cells treated with antidepressants and its application in drug repositioning. J Psychopharmacol. 2017;31:338–45.
Powell TR, Murphy T, de Jong S, Lee SH, Tansey KE, Hodgson K, et al. The genome-wide expression effects of escitalopram and its relationship to neurogenesis, hippocampal volume, and antidepressant response. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017;174:427–34.
Allsopp RC, Harley CB. Evidence for a critical telomere length in senescent human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1995;219:130–6.
Cawthon RM. Telomere length measurement by a novel monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR method. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:e21.
Zhu A, Ibrahim JG, Love MI. Heavy-tailed prior distributions for sequence count data: removing the noise and preserving large differences. Bioinforma. 2018;35:2084–92.
Watanabe K, Taskesen E, van Bochoven A, Posthuma D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1826.
Wray NR, Ripke S, Mattheisen M, Trzaskowski M, Byrne EM, Abdellaoui A, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat Genet. 2018;50:668–81.
Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, Ripke S, Trubetskoy V, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:793–803.
Pardinas AF, Holmans P, Pocklington AJ, Escott-Price V, Ripke S, Carrera N, et al. Common schizophrenia alleles are enriched in mutation-intolerant genes and in regions under strong background selection. Nat Genet. 2018;50:381–9.
Davies G, Lam M, Harris SE, Trampush JW, Luciano M, Hill WD, et al. Study of 300,486 individuals identifies 148 independent genetic loci influencing general cognitive function. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2098.
de Leeuw CA, Mooij JM, Heskes T, Posthuma D. MAGMA: generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015;11:e1004219.
Spiers H, Hannon E, Schalkwyk LC, Smith R, Wong CC, O’Donovan MC, et al. Methylomic trajectories across human fetal brain development. Genome Res. 2015;25:338–52.
Blighe K. R,S, Lewis M. EnhancedVolcano: Publication-ready volcano plots with enhanced colouring and labeling. 2020; R package version 1.6.0. https://github.com/kevinblighe/EnhancedVolcano.
Leao R, Apolonio JD, Lee D, Figueiredo A, Tabori U, Castelo-Branco P. Mechanisms of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) regulation: clinical impacts in cancer. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25:22.
Rapoport JL, Addington AM, Frangou S, Psych MR. The neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2005. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:434–49.
Samuelsen GB, Larsen KB, Bogdanovic N, Laursen H, Graem N, Larsen JF, et al. The changing number of cells in the human fetal forebrain and its subdivisions: a stereological analysis. Cereb Cortex. 2003;13:115–22.
Knoth R, Singec I, Ditter M, Pantazis G, Capetian P, Meyer RP, et al. Murine features of neurogenesis in the human hippocampus across the lifespan from 0 to 100 years. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e8809.
Kuhn HG, Toda T, Gage FH. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: a coming-of-age story. J Neurosci. 2018;38:10401–10.
Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C. Identification of risk loci with shared effects on five major psychiatric disorders: a genome-wide analysis. Lancet. 2013;381:1371–79.
Bowie CR, Harvey PD. Cognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006;2:531–6.
Wolf SA, Melnik A, Kempermann G. Physical exercise increases adult neurogenesis and telomerase activity, and improves behavioral deficits in a mouse model of schizophrenia. Brain, Behav, Immun. 2011;25:971–80.
Baruch-Eliyahu N, Rud V, Braiman A, Priel E. Telomerase increasing compound protects hippocampal neurons from amyloid beta toxicity by enhancing the expression of neurotrophins and plasticity related genes. Sci Rep. 2019;9:18118.
Kim C, Pinto AM, Bordoli C, Buckner LP, Kaplan PC, Del Arenal IM, et al. Energy restriction enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis-associated memory after four weeks in an adult human population with central obesity; a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2020;12:638.
Kark JD, Goldberger N, Kimura M, Sinnreich R, Aviv A. Energy intake and leukocyte telomere length in young adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:479–87.
Werner CM, Hecksteden A, Morsch A, Zundler J, Wegmann M, Kratzsch J, et al. Differential effects of endurance, interval, and resistance training on telomerase activity and telomere length in a randomized, controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:34–46.
van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH. Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci. 2005;25:8680–5.
Lee J, Seroogy KB, Mattson MP. Dietary restriction enhances neurotrophin expression and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. J Neurochem. 2002;80:539–47.
Farzaneh-Far R, Lin J, Epel ES, Harris WS, Blackburn EH, Whooley MA. Association of marine omega-3 fatty acid levels with telomeric aging in patients with coronary heart disease. JAMA. 2010;303:250–7.
Shen J, Gammon MD, Terry MB, Wang Q, Bradshaw P, Teitelbaum SL, et al. Telomere length, oxidative damage, antioxidants and breast cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:1637–43.
da Luz PL, Tanaka L, Brum PC, Dourado PMM, Favarato D, Krieger JE, et al. Red wine and equivalent oral pharmacological doses of resveratrol delay vascular aging but do not extend life span in rats. Atherosclerosis. 2012;224:136–42.
Kodali M, Parihar VK, Hattiangady B, Mishra V, Shuai B, Shetty AK. Resveratrol prevents age-related memory and mood dysfunction with increased hippocampal neurogenesis and microvasculature, and reduced glial activation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8075.
Chen G, Rajkowska G, Du F, Seraji-Bozorgzad N, Manji HK. Enhancement of hippocampal neurogenesis by lithium. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1729–34.
Mu Y, Lee SW, Gage FH. Signaling in adult neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20:416–23.
Horvath S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R115.
Kintner C. Neurogenesis in embryos and in adult neural stem cells. J Neurosci. 2002;22:639–43.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Nick Bray and Dr Araceli Rosa for their constructive feedback on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ABP, ST and TRP designed research; ABP, DMS, ECH, RRRD, ST and TRP carried out or led laboratory work; DFN contributed knowledge and critical input; ABP, RRRD and TRP analysed the data; ABP and TRP wrote the paper with the assistance of all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Palmos, A.B., Duarte, R.R.R., Smeeth, D.M. et al. Telomere length and human hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacol. 45, 2239–2247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00863-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00863-w
This article is cited by
-
Phenotypic aging mediates the association between blood cadmium and depression: a population-based study
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Exploring the Causal Relationship Between Telomere Biology and Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Epigenetic clocks in relapse after a first episode of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia (2022)
-
Lithium treatment and human hippocampal neurogenesis
Translational Psychiatry (2021)