Abstract
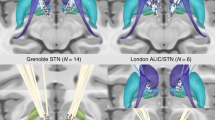
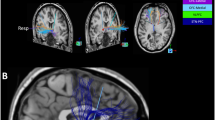
Neurosurgical interventions including deep brain stimulation (DBS) and capsulotomy have been demonstrated effective for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), although treatment-shared/-specific network mechanisms remain largely unclear. We retrospectively analyzed resting-state fMRI data from three cohorts: a cross-sectional dataset of 186 subjects (104 OCD and 82 healthy controls), and two longitudinal datasets of refractory patients receiving ventral capsule/ventral striatum DBS (14 OCD) and anterior capsulotomy (27 OCD). We developed a machine learning model predictive of OCD symptoms (indexed by the Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale, Y-BOCS) based on functional connectivity profiles and used graphic measures of network communication to characterize treatment-induced profile changes. We applied a linear model on 2 levels treatments (DBS or capsulotomy) and outcome to identify whether pre-surgical network communication was associated with differential treatment outcomes. We identified 54 functional connectivities within fronto-subcortical networks significantly predictive of Y-BOCS score in patients across 3 independent cohorts, and observed a coexisting pattern of downregulated cortico-subcortical and upregulated cortico-cortical network communication commonly shared by DBS and capsulotomy. Furthermore, increased cortico-cortical communication at ventrolateral and centrolateral prefrontal cortices induced by DBS and capsulotomy contributed to improvement of mood and anxiety symptoms, respectively (p < 0.05). Importantly, pretreatment communication of ventrolateral and centrolateral prefrontal cortices were differentially predictive of mood and anxiety improvements by DBS and capsulotomy (effect sizes = 0.45 and 0.41, respectively). These findings unravel treatment-shared and treatment-specific network characteristics induced by DBS and capsulotomy, which may facilitate the search of potential evidence-based markers for optimally selecting among treatment options for a patient.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, et al. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989;46:1006–11.
Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32:50–5.
Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol, Neurosurg, Psychiatry. 1960;23:56–62.
Pauls DL, Abramovitch A, Rauch SL, Geller DA. Obsessive-compulsive disorder: an integrative genetic and neurobiological perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15:410–24.
Robbins TW, Vaghi MM, Banca P. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Puzzles and Prospects. Neuron. 2019;102:27–47.
Stein DJ, Costa DLC, Lochner C, Miguel EC, Reddy YCJ, Shavitt RG, et al. Obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5:52.
Nuttin B, Cosyns P, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J, Meyerson B. Electrical stimulation in anterior limbs of internal capsules in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Lancet. 1999;354:1526.
Mallet L, Polosan M, Jaafari N, Baup N, Welter ML, Fontaine D, et al. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N. Engl J Med. 2008;359:2121–34.
Dougherty DD, Baer L, Cosgrove GR, Cassem EH, Price BH, Nierenberg AA, et al. Prospective long-term follow-up of 44 patients who received cingulotomy for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:269–75.
Ruck C, Karlsson A, Steele JD, Edman G, Meyerson BA, Ericson K, et al. Capsulotomy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: long-term follow-up of 25 patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:914–21.
Davidson B, Hamani C, Rabin JS, Goubran M, Meng Y, Huang Y, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound capsulotomy for refractory obsessive compulsive disorder and major depressive disorder: clinical and imaging results from two phase I trials. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25:1946–57.
Goodman WK, Foote KD, Greenberg BD, Ricciuti N, Bauer R, Ward H, et al. Deep brain stimulation for intractable obsessive compulsive disorder: pilot study using a blinded, staggered-onset design. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:535–42.
Denys D, Mantione M, Figee M, van den Munckhof P, Koerselman F, Westenberg H, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:1061–8.
Greenberg BD, Gabriels LA, Malone DA Jr, Rezai AR, Friehs GM, Okun MS, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral internal capsule/ventral striatum for obsessive-compulsive disorder: worldwide experience. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:64–79.
Denys D, Graat I, Mocking R, de Koning P, Vulink N, Figee M, et al. Efficacy of Deep Brain Stimulation of the Ventral Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule for Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Clinical Cohort of 70 Patients. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177:265–71.
Lopes AC, Greenberg BD, Canteras MM, Batistuzzo MC, Hoexter MQ, Gentil AF, et al. Gamma ventral capsulotomy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71:1066–76.
Rasmussen SA, Noren G, Greenberg BD, Marsland R, McLaughlin NC, Malloy PJ, et al. Gamma Ventral Capsulotomy in Intractable Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84:355–64.
Graat I, Mocking R, Figee M, Vulink N, de Koning P, Ooms P, et al. Long-term Outcome of Deep Brain Stimulation of the Ventral Part of the Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule in a Cohort of 50 Patients With Treatment-Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;90:714–20.
Voon V, Droux F, Morris L, Chabardes S, Bougerol T, David O, et al. Decisional impulsivity and the associative-limbic subthalamic nucleus in obsessive-compulsive disorder: stimulation and connectivity. Brain. 2017;140:442–56.
Dougherty DD, Brennan BP, Stewart SE, Wilhelm S, Widge AS, Rauch SL. Neuroscientifically informed formulation and treatment planning for patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:1081–7.
Cagnan H, Denison T, McIntyre C, Brown P. Emerging technologies for improved deep brain stimulation. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:1024–33.
Kohl S, Schonherr DM, Luigjes J, Denys D, Mueller UJ, Lenartz D, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive compulsive disorder: a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14:214.
Herrington TM, Cheng JJ, Eskandar EN. Mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 2016;115:19–38.
Chen X, Zhang C, Li Y, Huang P, Lv Q, Yu W, et al. Functional Connectivity-Based Modelling Simulates Subject-Specific Network Spreading Effects of Focal Brain Stimulation. Neurosci Bull. 2018;34:921–38.
Lv Q, Lv Q, Yin D, Zhang C, Sun B, Voon V, et al. Neuroanatomical substrates and predictors of response to capsulotomy in intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2021;6:29–38.
Yin D, Zhang C, Lv Q, Chen X, Zeljic K, Gong H, et al. Dissociable frontostriatal connectivity: mechanism and predictor of the clinical efficacy of capsulotomy in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84:926–36.
Hoexter MQ. Are we ready for individualized target planning of ablative procedures in intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder? Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84:e85–7.
Baldermann JC, Melzer C, Zapf A, Kohl S, Timmermann L, Tittgemeyer M, et al. Connectivity profile predictive of effective deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:735–43.
Li N, Baldermann JC, Kibleur A, Treu S, Akram H, Elias GJB, et al. A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3364.
Abi-Dargham A, Horga G. The search for imaging biomarkers in psychiatric disorders. Nat Med. 2016;22:1248–55.
Zhan Y, Wei J, Liang J, Xu X, He R, Robbins TW, et al. Diagnostic classification for human autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder based on machine learning from a primate genetic model. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178:65–76.
Figee M, Luigjes J, Smolders R, Valencia-Alfonso CE, van Wingen G, de Kwaasteniet B, et al. Deep brain stimulation restores frontostriatal network activity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16:386–7.
Wang Z, Zeljic K, Jiang Q, Gu Y, Wang W, Wang Z. Dynamic network communication in the human functional connectome predicts perceptual variability in visual illusion. Cereb Cortex. 2018;28:48–62.
Lv Q, Yang L, Li G, Wang Z, Shen Z, Yu W, et al. Large-scale persistent network reconfiguration induced by ketamine in anesthetized monkeys: relevance to mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79:765–75.
Lv Q, Wang Z, Zhang C, Fan Q, Zhao Q, Zeljic K, et al. Divergent structural responses to pharmacological interventions in orbitofronto-striato-thalamic and premotor circuits in obsessive-compulsive disorder. EBioMedicine. 2017;22:242–8.
Zhang C, Kim SG, Li J, Zhang Y, Lv Q, Zeljic K, et al. Anterior limb of the internal capsule tractography: relationship with capsulotomy outcomes in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;92:637.
Behzadi Y, Restom K, Liau J, Liu TT. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. Neuroimage. 2007;37:90–101.
Bezgin G, Vakorin VA, van Opstal AJ, McIntosh AR, Bakker R. Hundreds of brain maps in one atlas: registering coordinate-independent primate neuro-anatomical data to a standard brain. Neuroimage. 2012;62:67–76.
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, et al. Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron. 2002;33:341–55.
Zalesky A, Fornito A, Bullmore ET. Network-based statistic: identifying differences in brain networks. Neuroimage. 2010;53:1197–207.
Moody TD, Morfini F, Cheng G, Sheen C, Tadayonnejad R, Reggente N, et al. Mechanisms of cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder involve robust and extensive increases in brain network connectivity. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1230.
Lee JJ, Kim HJ, Ceko M, Park BY, Lee SA, Park H, et al. A neuroimaging biomarker for sustained experimental and clinical pain. Nat Med. 2021;27:174–82.
McGrath CL, Kelley ME, Holtzheimer PE, Dunlop BW, Craighead WE, Franco AR, et al. Toward a neuroimaging treatment selection biomarker for major depressive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:821–9.
Norman LJ, Mannella KA, Yang H, Angstadt M, Abelson JL, Himle JA, et al. Treatment-Specific Associations Between Brain Activation and Symptom Reduction in OCD Following CBT: A Randomized fMRI Trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178:39–47.
Cho S, Hachmann JT, Balzekas I, In MH, Andres-Beck LG, Lee KH, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity modulates the BOLD activation induced by nucleus accumbens stimulation in the swine brain. Brain Behav. 2019;9:e01431.
Lozano AM, Lipsman N, Bergman H, Brown P, Chabardes S, Chang JW, et al. Deep brain stimulation: current challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:148–60.
Alstott J, Breakspear M, Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Sporns O. Modeling the impact of lesions in the human brain. Plos Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000408.
Horn A, Wenzel G, Irmen F, Huebl J, Li N, Neumann WJ, et al. Deep brain stimulation induced normalization of the human functional connectome in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2019;142:3129–43.
Kahan J, Urner M, Moran R, Flandin G, Marreiros A, Mancini L, et al. Resting state functional MRI in Parkinson’s disease: the impact of deep brain stimulation on ‘effective’ connectivity. Brain. 2014;137:1130–44.
O’Reilly JX, Croxson PL, Jbabdi S, Sallet J, Noonan MP, Mars RB, et al. Causal effect of disconnection lesions on interhemispheric functional connectivity in rhesus monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:13982–7.
Roland JL, Snyder AZ, Hacker CD, Mitra A, Shimony JS, Limbrick DD, et al. On the role of the corpus callosum in interhemispheric functional connectivity in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:13278–83.
van den Heuvel MP, Sporns O. A cross-disorder connectome landscape of brain dysconnectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019;20:435–46.
Joglekar MR, Mejias JF, Yang GR, Wang XJ. Inter-areal balanced amplification enhances signal propagation in a large-scale circuit model of the primate cortex. Neuron. 2018;98:222–34.
Misic B, Betzel RF, Nematzadeh A, Goni J, Griffa A, Hagmann P, et al. Cooperative and competitive spreading dynamics on the human connectome. Neuron. 2015;86:1518–29.
Tyagi H, Apergis-Schoute AM, Akram H, Foltynie T, Limousin P, Drummond LM, et al. A randomized trial directly comparing ventral capsule and anteromedial subthalamic nucleus stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: clinical and imaging evidence for dissociable effects. Biol psychiatry. 2019;85:726–34.
Malone DA Jr., Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Friehs GM, Eskandar EN, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:267–75.
Fridgeirsson EA, Figee M, Luigjes J, van den Munckhof P, Schuurman PR, van Wingen G, et al. Deep brain stimulation modulates directional limbic connectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain. 2020;143:1603–12.
Schoene-Bake JC, Parpaley Y, Weber B, Panksepp J, Hurwitz TA, Coenen VA. Tractographic analysis of historical lesion surgery for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:2553–63.
Irmen F, Horn A, Mosley P, Perry A, Petry-Schmelzer JN, Dafsari HS, et al. Left prefrontal connectivity links subthalamic stimulation with depressive symptoms. Ann Neurol. 2020;87:962–75.
Cocchi L, Zalesky A, Nott Z, Whybird G, Fitzgerald PB, Breakspear M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a focus on network mechanisms and state dependence. NeuroImage Clin. 2018;19:661–74.
Siddiqi SH, Taylor SF, Cooke D, Pascual-Leone A, George MS, Fox MD. Distinct symptom-specific treatment targets for circuit-based neuromodulation. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177:435–46.
Yan Y, Dahmani L, Ren J, Shen L, Peng X, Wang R, et al. Reconstructing lost BOLD signal in individual participants using deep machine learning. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5046.
Acknowledgements
We specially thank Jinqiang Peng for his support to the management of our database and computation resources, where all the imaging and clinical data were harmonized and analyzed. This work was supported by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2019B030335001), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFC1310400; No. 2018YFC1313803), Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Science (No. XDB32000000), grants from National Natural Science Foundation (81527901, 31771174), and Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2018SHZDZX05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XC, ZW (Zhen Wang), DD, VV, and ZW (Zheng Wang) contributed to the conception and design of the study. XC, QL (Qian Lv), QL (Qiming Lv), GvW, EAF, DD, and VV contributed to acquisition, post-processing and analysis of the data. XC and ZW (Zhen Wang) analyzed all or parts of the data. XC and ZW (Zheng Wang) drafted the text and prepared the figures with the help of VV. ZW (Zheng Wang) obtained the funding and supervised the study. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, Z., Lv, Q. et al. Common and differential connectivity profiles of deep brain stimulation and capsulotomy in refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 27, 1020–1030 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01358-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01358-w
This article is cited by
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of deep-brain stimulation of the internal capsule in a mouse model
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Landscape and future directions of machine learning applications in closed-loop brain stimulation
npj Digital Medicine (2023)
-
Dissecting Psychiatric Heterogeneity and Comorbidity with Core Region-Based Machine Learning
Neuroscience Bulletin (2023)