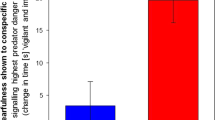
Abstract
Adverse experiences early in life are associated with the development of psychiatric illnesses. The hippocampus is likely to play pivotal role in generating these effects: it undergoes significant development during childhood and is extremely reactive to stress. In rodent models, stress in the pre-pubertal period impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) and behaviours which rely on this process. In normal adult animals, environmental enrichment (EE) is a potent promoter of AHN and hippocampal function. Whether exposure to EE during adolescence can restore normal hippocampal function and AHN following pre-pubertal stress (PPS) is unknown. We investigated EE as a treatment for reduced AHN and hippocampal function following PPS in a rodent model. Stress was administered between post-natal days (PND) 25–27, EE from PND 35 to early adulthood, when behavioural testing and assessment of AHN took place. PPS enhanced fear reactions to a conditioned stimulus (CS) following a trace fear protocol and reduced the survival of 4-week-old adult-born neurons throughout the adult hippocampus. Furthermore, we show that fewer adult-born neurons were active during recall of the CS stimulus following PPS. All effects were reversed by EE. Our results demonstrate lasting effects of PPS on the hippocampus and highlight the utility of EE during adolescence for restoring normal hippocampal function. EE during adolescence is a promising method of enhancing impaired hippocampal function resulting from early life stress, and due to multiple benefits (low cost, few side effects, widespread availability) should be more thoroughly explored as a treatment option in human sufferers of childhood adversity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teicher MH, Samson JA, Anderson CM, Ohashi K. The effects of childhood maltreatment on brain structure, function and connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17:652–6.
de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F. Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:463–75.
Calem M, Bromis K, McGuire P, Morgan C, Kempton MJ. Meta-analysis of associations between childhood adversity and hippocampus and amygdala volume in non-clinical and general population samples. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;14:471–9.
Paquola C, Bennett MR, Lagopoulos J. Understanding heterogeneity in grey matter research of adults with childhood maltreatment—a meta-analysis and review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;69:299–312.
Lambert HK, Sheridan MA, Sambrook KA, Rosen ML, Askren MK, McLaughlin KA. Hippocampal contribution to context encoding across development is disrupted following early-life adversity. J Neurosci. 2017;37:1925–34.
Bolton JL, Molet J, Ivy A, Baram TZ. New insights into early-life stress and behavioural outcomes. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017;14:133–9.
Brydges NM, Wood ER, Holmes MC, Hall J. Prepubertal stress and hippocampal function: sex-specific effects. Hippocampus. 2014;24:684–92.
Brydges NM, Moon A, Rule L, Watkin H, Thomas KL, Hall J. Sex specific effects of prepubertal stress on hippocampal neurogenesis and behaviour. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0322-4.
Brydges NM, Seckl J, Torrance HS, Holmes MC, Evans KL, Hall J. Juvenile stress produces long-lasting changes in hippocampal DISC1, GSK3 beta and NRG1 expression. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:854–5.
Tiwari A, Gonzalez A. Biological alterations affecting risk of adult psychopathology following childhood trauma: a review of sex differences. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018;66:69–79.
van Erp TGM, Hibar DP, Rasmussen JM, Glahn DC, Pearlson GD, Andreassen OA, et al. Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2028 individuals with schizophrenia and 2540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:547–53.
Samuels BA, Leonardo ED, Hen R. Hippocampal subfields and major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:210–1.
Yun S, Reynolds RP, Masiulis I, Eisch AJ. Re-evaluating the link between neuropsychiatric disorders and dysregulated adult neurogenesis. Nat Med. 2016;22:1239–47.
Anacker C, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility—linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:335–46.
Ming GL, Song HJ. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron. 2011;70:687–702.
Kang EC, Wen ZX, Song HJ, Christian KM, Ming GL. Adult neurogenesis and psychiatric disorders. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8:1–27.
Toda T, Parylak SL, Linker SB, Gage FH. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:67–87.
Allen KM, Fung SJ, Weickert CS. Cell proliferation is reduced in the hippocampus in schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016;50:473–80.
Boldrini M, Hen R, Underwood MD, Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, Mann JJ, et al. Hippocampal angiogenesis and progenitor cell proliferation are increased with antidepressant use in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72:562–71.
Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2197, 2012). Lancet. 2014;384:582.
Sahay A, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1110–5.
Kempermann G. Environmental enrichment, new neurons and the neurobiology of individuality. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019;20:235–45.
Ilin Y, Richter-Levin G. Enriched environment experience overcomes learning deficits and depressive-like behavior induced by juvenile stress. Plos ONE. 2009;4:e4329.
Morley-Fletcher S, Rea M, Maccari S, Laviola G. Environmental enrichment during adolescence reverses the effects of prenatal stress on play behaviour and HPA axis reactivity in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:3367–74.
Zubedat S, Aga-Mizrachi S, Cymerblit-Sabba A, Ritter A, Nachmani M, Avital A. Methylphenidate and environmental enrichment ameliorate the deleterious effects of prenatal stress on attention functioning. Stress. 2015;18:280–8.
Francis DD, Diorio J, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ. Environmental enrichment reverses the effects of maternal separation on stress reactivity. J Neurosci. 2002;22:7840–3.
Vivinetto AL, Suarez MM, Rivarola MA. Neurobiological effects of neonatal maternal separation and post-weaning environmental enrichment. Behav Brain Res. 2013;240:110–8.
Ardi Z, Richter-Levin A, Xu L, Cao X, Volkmer H, Stork O, et al. The role of the GABAA receptor alpha 1 subunit in the ventral hippocampus in stress resilience. Sci Rep. 2019;9:13513.
Hueston CM, Cryan JF, Nolan YM. Stress and adolescent hippocampal neurogenesis: diet and exercise as cognitive modulators. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2017.48.
Dresler M, Sandberg A, Ohla K, Bublitz C, Trenado C, Mroczko-Wasowicz A, et al. Non pharmacological cognitive enhancement. Neuropharmacology. 2013;64:529–43.
McDonald MW, Hayward KS, Rosbergen ICM, Jeffers MS, Corbett D. Is environmental enrichment ready for clinical application in human post-stroke rehabilitation? Front Behav Neurosci. 2018;12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00135.
Brydges NM. Pre-pubertal stress and brain development in rodents. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2016;7:8–14.
Jacobson-Pick S, Richter-Levin G. Differential impact of juvenile stress and corticosterone in juvenility and in adulthood, in male and female rats. Behav Brain Res. 2010;214:268–76.
Kempermann G, Gast D, Kronenberg G, Yamaguchi M, Gage FH. Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development. 2003;130:391–9.
Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG. Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 2003;467:1–10.
Ambrogini P, Lattanzi D, Ciuffoli S, Agostini D, Bertini L, Stocchi V, et al. Morpho-functional characterization of neuronal cells at different stages of maturation in granule cell layer of adult rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 2004;1017:21–31.
Detert JA, Kampa ND, Moyer JR. Differential effects of training intertrial interval on acquisition of trace and long-delay fear conditioning in rats. Behav Neurosci. 2008;122:1318–27.
Paxinos G, Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 6th edn. New York, USA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2007.
Noori HR, Fornal CA. The appropriateness of unbiased optical fractionators to assess cell proliferation in the adult hippocampus. Front Neurosci. 2011;5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2011.00140.
Kim EJ, Pellman B, Kim JJ. Stress effects on the hippocampus: a critical review. Learn Mem. 2015;22:411–6.
Riem MME, Alink LRA, Out D, Van Ijzendoorn MH, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ. Beating the brain about abuse: empirical and meta-analytic studies of the association between maltreatment and hippocampal volume across childhood and adolescence. Dev Psychopathol. 2015;27:507–20.
Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Vermetten E, Southwick SM, McGlashan T, Staib LH, et al. Neural correlates of declarative memory for emotionally valenced words in women with posttraumatic stress disorder related to early childhood sexual abuse. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:879–89.
van Rooij SJH, Stevens JS, Ely TD, Fani N, Smith AK, Kerley KA, et al. Childhood trauma and COMT genotype interact to increase hippocampal activation in resilient individuals. Front Psychiatry. 2016;7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00156.
Richter A, Kramer B, Diekhof EK, Gruber O. Resilience to adversity is associated with increased activity and connectivity in the VTA and hippocampus. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;23:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101920.
Derks NAV, Krugers HJ, Hoogenraad CC, Joels M, Sarabdjitsingh RA. Effects of early life stress on rodent hippocampal synaptic plasticity: a systematic review. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017;14:155–66.
Mirescu C, Peters JD, Gould E. Early life experience alters response of adult neurogenesis to stress. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:841–6.
Korosi A, Naninck EFG, Oomen CA, Schouten M, Krugers H, Fitzsimons C, et al. Early-life stress mediated modulation of adult neurogenesis and behavior. Behav Brain Res. 2012;227:400–9.
Ortega-Martinez S. Influences of prenatal and postnatal stress on adult hippocampal neurogenesis: the double neurogenic niche hypothesis. Behav Brain Res. 2015;281:309–17.
Loi M, Koricka S, Lucassen PJ, Joels M. Age- and sex- dependent effects of early life stress on hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Endocrinol. 2014;5:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00013.
Oomen CA, Soeters H, Audureau N, Vermunt L, van Hasselt FN, Manders EMM, et al. Severe early life stress hampers spatial learning and neurogenesis, but improves hippocampal synaptic plasticity and emotional learning under high-stress conditions in adulthood. J Neurosci. 2010;30:6635–45.
Lajud N, Torner L. Early life stress and hippocampal neurogenesis in the neonate: sexual dimorphism, long term consequences and possible mediators. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015;8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00003.
Maren S. Overtraining does not mitigate contextual fear conditioning deficits produced by neurotoxic lesions of the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci. 1998;18:3088–97.
Drew MR, Huckleberry KA. Modulation of aversive memory by adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14:646–61.
Burman MA, Starr MJ, Gewirtz JC. Dissociable effects of hippocampus lesions on expression of fear and trace fear conditioning memories in rats. Hippocampus. 2006;16:103–13.
Burman MA, Simmons CA, Hughes M, Lei L. Developing and validating trace fear conditioning protocols in C57BL/6 mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2014;222:111–7.
Pierson JL, Pullins SE, Quinn JJ. Dorsal hippocampus infusions of CNQX into the dentate gyrus disrupt expression of trace fear conditioning. Hippocampus. 2015;25:779–85.
Clelland CD, Choi M, Romberg C, Clemenson GD, Fragniere A, Tyers P, et al. A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science. 2009;325:210–3.
Kochli DE, Thompson EC, Fricke EA, Postle AF, Quinn JJ. The amygdala is critical for trace, delay, and contextual fear conditioning. Learn Mem. 2015;22:92–100.
Loi M, Koricka S, Lucassen PJ, Joels M. Age- and sex-dependent effects of early life stress on hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Endocrinol. 2014;5:13.
Ming GL, Song HJ. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:223–50.
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature. 2002;415:1030–4.
Toni N, Schinder AF. Maturation and functional integration of new granule cells into the adult hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018903.
Gu Y, Arruda-Carvalho M, Wang J, Janoschka SR, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW, et al. Optical controlling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-born dentate granule cells. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:1700–6.
Denny CA, Burghardt NS, Schachter DM, Hen R, Drew MR. 4-to 6-week-old adult-born hippocampal neurons influence novelty-evoked exploration and contextual fear conditioning. Hippocampus. 2012;22:1188–201.
Menard JL, Champagne DL, Meaney MJP. Variations of maternal care differentially influence ‘fear’ reactivity and regional patterns of cFos immunoreactivity in response to the shock probe burying test. Neuroscience. 2004;129:297–308.
Troakes C, Ingram CD. Anxiety behaviour of the male rat on the elevated plus maze: associated regional increase in c-fos mRNA expression and modulation by early maternal separation. Stress. 2009;12:362–9.
Koehnle TJ, Rinaman L. Early experience alters limbic forebrain Fos responses to a stressful interoceptive stimulus in young adult rats. Physiol Behav. 2010;100:105–15.
Sanders BJ, Anticevic A. Maternal separation enhances neuronal activation and cardiovascular responses to acute stress in borderline hypertensive rats. Behav Brain Res. 2007;183:25–30.
Banqueri M, Mendez M, Arias JL. Why are maternally separated females inflexible? Brain activity pattern of COx and c-Fos. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018;155:30–41.
Kempermann G, Gage FH. Genetic determinants of adult hippocampal neurogenesis correlate with acquisition, but not probe trial performance, in the water maze task. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;16:129–36.
Creer DJ, Romberg C, Saksida LM, van Praag H, Bussey TJ. Running enhances spatial pattern separation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:2367–72.
Lee SW, Clemenson GD, Gage FH. New neurons in an aged brain. Behav Brain Res. 2012;227:497–507.
Naninck EFG, Hoeijmakers L, Kakava-Georgiadou N, Meesters A, Lazic SE, Lucassen PJ, et al. Chronic early life stress alters developmental and adult neurogenesis and impairs cognitive function in mice. Hippocampus. 2015;25:309–28.
Frick KM, Stearns NA, Pan J-Y, Berger-Sweeney J. Effects of environmental enrichment on spatial memory and neurochemistry in middle-aged mice. Learn Mem. 2003;10:187–98.
Ohline SM, Abraham WC. Environmental enrichment effects on synaptic and cellular physiology of hippocampal neurons. Neuropharmacology. 2019;145:3–12.
Fox C, Merali Z, Harrison C. Therapeutic and protective effect of environmental enrichment against psychogenic and neurogenic stress. Behav Brain Res. 2006;175:1–8.
Veena J, Srikumar BN, Raju TR, Rao BSS. Exposure to enriched environment restores the survival and differentiation of new born cells in the hippocampus and ameliorates depressive symptoms in chronically stressed rats. Neurosci Lett. 2009;455:178–82.
Olson AK, Eadie BD, Ernst C, Christie BR. Environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise massively increase neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus via dissociable pathways. Hippocampus. 2006;16:250–60.
Clemenson GD, Deng W, Gage FH. Environmental enrichment and neurogenesis: from mice to humans. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2015;4:56–62.
Barros W, David M, Souza A, Silva M, Matos R. Can the effects of environmental enrichment modulate BDNF expression in hippocampal plasticity? A systematic review of animal studies. Synapse. 2019;73. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.22103.
Snyder JS. Recalibrating the relevance of adult neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2019;42:164–78.
O’Leary JD, Hoban AE, Murphy A, O’Leary OF, Cryan JF, Nolan YM. Differential effects of adolescent and adult-initiated exercise on cognition and hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus. 2019;29:352–65.
O’Leary JD, Hoban AE, Cryan JF, O’Leary OF, Nolan YM. Differential effects of adolescent and adult-initiated voluntary exercise on context and cued fear conditioning. Neuropharmacology. 2019;145:49–58.
Koe AS, Ashokan A, Mitra R. Short environmental enrichment in adulthood reverses anxiety and basolateral amygdala hypertrophy induced by maternal separation. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2015.217.
Doreste-Mendez R, Rios-Ruiz EJ, Rivera-Lopez LL, Gutierrez A, Torres-Reveron A. Effects of environmental enrichment in maternally separated rats: age and sex-specific outcomes. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019;13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00198.
Cui MH, Yang Y, Yang JL, Zhang JC, Han HL, Ma WP, et al. Enriched environment experience overcomes the memory deficits and depressive-like behavior induced by early life stress. Neurosci Lett. 2006;404:208–12.
Kempermann G, Gage FH, Aigner L, Song HJ, Curtis MA, Thuret S, et al. Human adult neurogenesis: evidence and remaining questions. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:25–30.
Boldrini M, Fulmore CA, Tartt AN, Simeon LR, Pavlova I, Poposka V, et al. Human hippocampal neurogenesis persists throughout aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22:589.
Kempermann G, Krebs J, Fabel K. The contribution of failing adult hippocampal neurogenesis to psychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2008;21:290–5.
Ruan LH, Lau BWM, Wang JX, Huang LJ, Zhuge QC, Wang B, et al. Neurogenesis in neurological and psychiatric diseases and brain injury: from bench to bedside. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;115:116–37.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge support from the Cardiff University Neuroscience and Mental Health Research Institute and The Jane Hodge Foundation who provided NMB with fellowship funding during this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rule, L., Yang, J., Watkin, H. et al. Environmental enrichment rescues survival and function of adult-born neurons following early life stress. Mol Psychiatry 26, 1898–1908 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0718-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0718-4
This article is cited by
-
Early life adversity as a risk factor for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
Translational Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Overlapping brain correlates of superior cognition among children at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease and/or major depressive disorder
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
A Baldwin interpretation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis: from functional relevance to physiopathology
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)