Abstract
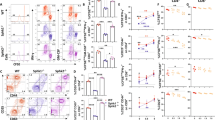
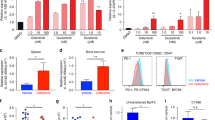
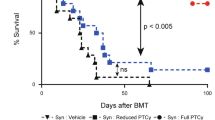
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is an effective immunotherapy for various hematologic malignancies, predominantly through potent graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect. However, the mortality after allo-HCT is because of relapse of primary malignancy and followed by graft-vs-host-disease (GVHD) as a major cause of transplant-related mortality. Hence, strategies to limit GVHD while preserving the GVL effect are highly desirable. Ceramide, which serves a central role in sphingolipid metabolism, is generated by ceramide synthases (CerS1–6). In this study, we found that genetic or pharmacologic targeting of CerS6 prevented and reversed chronic GVHD (cGVHD). Furthermore, specific inhibition of CerS6 with ST1072 significantly ameliorated acute GVHD (aGVHD) while preserving the GVL effect, which differed from FTY720 that attenuated aGVHD but impaired GVL activity. At the cellular level, blockade of CerS6 restrained donor T cells from migrating into GVHD target organs and preferentially reduced activation of donor CD4 T cells. At the molecular level, CerS6 was required for optimal TCR signaling, CD3/PKCθ co-localization, and subsequent N-RAS activation and ERK signaling, especially on CD4+ T cells. The current study provides rationale and means for targeting CerS6 to control GVHD and leukemia relapse, which would enhance the efficacy of allo-HCT as an immunotherapy for hematologic malignancies in the clinic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data in this research are available.
References
Zeiser R, Blazar BR. Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease - Biologic process, prevention, and therapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2167–79.
Srinivasan M, Flynn R, Price A, Ranger A, Browning JL, Taylor PA, et al. Donor B-cell alloantibody deposition and germinal center formation are required for the development of murine chronic GVHD and bronchiolitis obliterans. Blood. 2012;119:1570–80.
Flynn R, Du J, Veenstra RG, Reichenbach DK, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Taylor PA, et al. Increased T follicular helper cells and germinal center B cells are required for cGVHD and bronchiolitis obliterans. Blood. 2014;123:3988–98.
Daenthanasanmak A, Iamsawat S, Chakraborty P, Nguyen HD, Bastian D, Liu C, et al. Targeting Sirt-1 controls GVHD by inhibiting T-cell allo-response and promoting Treg stability in mice. Blood. 2019;133:266–79.
Olson MF, Marais R. Ras protein signalling. Semin Immunol. 2000;12:63–73.
Ehrhardt A, David MD, Ehrhardt GR, Schrader JW. Distinct mechanisms determine the patterns of differential activation of H-Ras, N-Ras, K-Ras 4B, and M-Ras by receptors for growth factors or antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:6311–23.
Mor A, Campi G, Du G, Zheng Y, Foster DA, Dustin ML, et al. The lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 receptor costimulates plasma membrane Ras via phospholipase D2. Nat cell Biol. 2007;9:713–9.
Iborra S, Soto M, Stark-Aroeira L, Castellano E, Alarcon B, Alonso C, et al. H-ras and N-ras are dispensable for T-cell development and activation but critical for protective Th1 immunity. Blood. 2011;117:5102–11.
Kunkel GT, Maceyka M, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:688–702.
Schneider G, Sellers ZP, Bujko K, Kakar SS, Kucia M, Ratajczak MZ. Novel pleiotropic effects of bioactive phospholipids in human lung cancer metastasis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:58247–63.
Taylor PA, Ehrhardt MJ, Lees CJ, Tolar J, Weigel BJ, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, et al. Insights into the mechanism of FTY720 and compatibility with regulatory T cells for the inhibition of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Blood. 2007;110:3480–8.
Rotolo JA, Stancevic B, Lu SX, Zhang J, Suh D, King CG, et al. Cytolytic T cells induce ceramide-rich platforms in target cell membranes to initiate graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2009;114:3693–706.
Sofi MH, Heinrichs J, Dany M, Nguyen H, Dai M, Bastian D, et al. Ceramide synthesis regulates T cell activity and GVHD development. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e91701–16.
Scheffel MJ, Helke K, Lu P, Bowers JS, Ogretmen B, Garrett-Mayer E, et al. Adoptive transfer of ceramide synthase 6 deficient splenocytes reduces the development of colitis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15552.
Schiffmann S, Hartmann D, Fuchs S, Birod K, Ferreiròs N, Schreiber Y, et al. Inhibitors of specific ceramide synthases. Biochimie. 2012;94:558–565.
Ebel P, Vom Dorp K, Petrasch-Parwez E, Zlomuzica A, Kinugawa K, Mariani J, et al. Inactivation of ceramide synthase 6 in mice results in an altered sphingolipid metabolism and behavioral abnormalities. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:21433–47.
Sofi MH, Wu Y, Schutt SD, Dai M, Daenthanasanmak A, Heinrichs Voss J, et al. Thioredoxin-1 confines T cell alloresponse and pathogenicity in graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Investig. 2019;129:2760–74.
Taylor SJ, Resnick RJ, Shalloway D. Nonradioactive determination of Ras-GTP levels using activated ras interaction assay. Methods Enzymol. 2001;333:333–42.
Bielawski J, Pierce JS, Snider J, Rembiesa B, Szulc ZM, Bielawska A. Sphingolipid analysis by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:46–59.
Schiffmann S, Hartmann D, Fuchs S, Birod K, Ferreiros N, Schreiber Y, et al. Inhibitors of specific ceramide synthases. Biochimie. 2012;94:558–65.
Schroeder MA, DiPersio JF. Mouse models of graft-versus-host disease: advances and limitations. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4:318–33.
Wu T, Young JS, Johnston H, Ni X, Deng R, Racine J, et al. Thymic damage, impaired negative selection, and development of chronic graft-versus-host disease caused by donor CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 2013;191:488–99.
Ryu J, Jhun J, Park MJ, Baek JA, Kim SY, Cho KH, et al. FTY720 ameliorates GvHD by blocking T lymphocyte migration to target organs and by skin fibrosis inhibition. J Transl Med. 2020;18:225.
Wysocki CA, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Blazar BR, Serody JS. Leukocyte migration and graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2005;105:4191–9.
Kremer KN, Kumar A, Hedin KE. G alpha i2 and ZAP-70 mediate RasGRP1 membrane localization and activation of SDF-1-induced T cell functions. J Immunol. 2011;187:3177–85.
Lynch SJ, Zavadil J, Pellicer A. In TCR-stimulated T-cells, N-ras regulates specific genes and signal transduction pathways. PloS One. 2014;8:e63193.
Zhang EY, Kong KF, Altman A. The yin and yang of protein kinase C-theta (PKCθ): a novel drug target for selective immunosuppression. Adv Pharm. 2013;66:267–312.
Monks CR, Kupfer H, Tamir I, Barlow A, Kupfer A. Selective modulation of protein kinase C-theta during T-cell activation. Nature. 1997;385:83–86.
Bi K, Tanaka Y, Coudronniere N, Sugie K, Hong S, van Stipdonk MJ, et al. Antigen-induced translocation of PKC-theta to membrane rafts is required for T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:556–63.
López-Huertas MR, Li J, Zafar A, Rodríguez-Mora S, García-Domínguez C, Mateos E, et al. PKCθ and HIV-1 transcriptional regulator tat co-exist at the LTR promoter in CD4(+) T cells. Front Immunol. 2016;7:69.
Byerly J, Halstead-Nussloch G, Ito K, Katsyv I, Irie HY. PRKCQ promotes oncogenic growth and anoikis resistance of a subset of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:95.
Martin PJ, Rizzo JD, Wingard JR, Ballen K, Curtin PT, Cutler C, et al. First- and second-line systemic treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease: recommendations of the American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant: J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:1150–63.
Martin PJ, Inamoto Y, Flowers ME, Carpenter PA. Secondary treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease: a critical review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant: J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:982–8.
Bastian D, Sui X, Nguyen HD, Wu Y, Schutt S, Tian L, et al. Interleukin-23 receptor signaling by interleukin-39 potentiates T cell pathogenicity in acute graft-versus-host disease. Am J Transplant. 2021;21:3538–49.
Wegner MS, Schiffmann S, Parnham MJ, Geisslinger G, Grosch S. The enigma of ceramide synthase regulation in mammalian cells. Prog lipid Res. 2016;63:93–119.
Wu Y, Schutt S, Paz K, Zhang M, Flynn RP, Bastian D, et al. MicroRNA-17-92 is required for T-cell and B-cell pathogenicity in chronic graft-versus-host disease in mice. Blood. 2018;131:1974–86.
Young JS, Wu T, Chen Y, Zhao D, Liu H, Yi T, et al. Donor B cells in transplants augment clonal expansion and survival of pathogenic CD4+ T cells that mediate autoimmune-like chronic graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2012;189:222–33.
Schiffmann S, Ferreiros N, Birod K, Eberle M, Schreiber Y, Pfeilschifter W, et al. Ceramide synthase 6 plays a critical role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2012;188:5723–33.
Schutt SD, Wu Y, Tang CH, Bastian D, Nguyen H, Sofi MH, et al. Inhibition of the IRE-1alpha/XBP-1 pathway prevents chronic GVHD and preserves the GVL effect in mice. Blood Adv. 2018;2:414–27.
Forcade E, Kim HT, Cutler C, Wang K, Alho AC, Nikiforow S, et al. Circulating T follicular helper cells with increased function during chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2016;127:2489–97.
Craft JE. Follicular helper T cells in immunity and systemic autoimmunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8:337–47.
Weinstein JS, Herman EI, Lainez B, Licona-Limon P, Esplugues E, Flavell R, et al. TFH cells progressively differentiate to regulate the germinal center response. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:1197–205.
Crotty S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity. 2014;41:529–42.
van Bergen CA, van Luxemburg-Heijs SA, de Wreede LC, Eefting M, von dem Borne PA, van Balen P, et al. Selective graft-versus-leukemia depends on magnitude and diversity of the alloreactive T cell response. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:517–29.
Zeiser R, Socie G, Blazar BR. Pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease: from intestinal microbiota alterations to donor T cell activation. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:191–207.
Soares-Silva M, Diniz FF, Gomes GN, Bahia D. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway: role in immune evasion by trypanosomatids. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:183.
Singh K, Deshpande P, Pryshchep S, Colmegna I, Liarski V, Weyand CM, et al. ERK-dependent T cell receptor threshold calibration in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2009;183:8258–67.
Muller G, Storz P, Bourteele S, Doppler H, Pfizenmaier K, Mischak H, et al. Regulation of Raf-1 kinase by TNF via its second messenger ceramide and cross-talk with mitogenic signalling. EMBO J. 1998;17:732–42.
Lu SX, Alpdogan O, Lin J, Balderas R, Campos-Gonzalez R, Wang X, et al. STAT-3 and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation are critical for T-cell alloactivation and graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2008;112:5254–8.
Acknowledgements
We would also like to thank the Flow Cytometry Core, Small Animal Imaging Core, Lipidomics Shared Resources and Cell & Molecular Imaging Facilities at Medical University of South Carolina for the assistance. This work is supported in part by SC SmartState Cancer Stem Cell Biology & Therapy Program and by R01 grants from the National Institutes of Health including AI118305 and HL140953 (X-ZY); CA214641, DE016572, P01 CA203628, and SC SmartState Endowment in Lipidomics and Drug Discovery (BO); and the DFG GRK2158 (HS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MHS, LT, and X-ZY participated in designing research studies, MHS, SS, IK, HC, YW, DB, TT, MFK, FCA, KJ, and XS participated in conducting experiments and acquiring data. MHS, LT, and XZY participated in analyzing and interpreting data and wrote the manuscript. AZ and HS provided ST1072 inhibitor. PJM provided deidentified patient plasma samples and related information and participated in clinical data analysis and interpretation. SM, JO, and BO participated in interpreting data and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofi, M.H., Tian, L., Schutt, S. et al. Ceramide synthase 6 impacts T-cell allogeneic response and graft-versus-host disease through regulating N-RAS/ERK pathway. Leukemia 36, 1907–1915 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-022-01581-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-022-01581-6
This article is cited by
-
Chronic oral exposure to low-concentration fumonisin B2 significantly exacerbates the inflammatory responses of allergies in mice via inhibition of IL-10 release by regulatory T cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue
Archives of Toxicology (2023)
-
S1P/S1PR1 signaling differentially regulates the allogeneic response of CD4 and CD8 T cells by modulating mitochondrial fission
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2022)