Abstract
Objective
Williams and Alagille syndromes are genetic disorders associated with pathologic arterial narrowing. We hypothesized that fetal idiopathic ductus arteriosus (DA) constriction may represent a prenatal manifestation of the arteriopathy associated with these syndromes.
Methods
Multi-institutional case series review of the pre- and postnatal medical records, echocardiograms, and genetic test results of fetuses presenting with idiopathic DA constriction.
Results
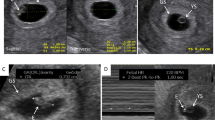
We identified four cases of idiopathic fetal DA constriction at 21–36 weeks of gestation. All had right ventricular hypertension, dilation, hypertrophy, and dysfunction and either DA constriction or absence. All demonstrated progressive peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis after birth. Three met clinical diagnostic criteria for Alagille syndrome; two tested had confirmatory JAG1 mutations. One also developed supravalvar aortic stenosis after birth and was positive for 7q11.23 deletion (Williams syndrome).
Conclusion
This is the first case series to suggest that idiopathic fetal DA constriction may be a prenatal manifestation of genetic arteriopathy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gewillig M, Brown SC, De Catte L, Debeer A, Eyskens B, Cossey V, et al. Premature foetal closure of the arterial duct: clinical presentations and outcome. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:1530–6.
Huhta JC, Moise KJ, Fisher DJ, Sharif DS, Wasserstrum N, Martin C. Detection and quantitation of constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus by Doppler echocardiography. Circulation. 1987;75:406–12.
Tulzer G, Gudmundsson S, Sharkey AM, Wood DC, Cohen AW, Huhta JC. Doppler echocardiography of fetal ductus arteriosus constriction versus increased right ventricular output. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;18:532–6.
Van den Veyver IB, Moise KJ Jr. Prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1993;48:493–502.
Moise KJ Jr. Effect of advancing gestational age on the frequency of fetal ductal constriction in association with maternal indomethacin use. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;168:1350–3.
Zielinsky P, Busato S. Prenatal effects of maternal consumption of polyphenol-rich foods in late pregnancy upon fetal ductus arteriosus. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo Today: Rev. 2013;99:256–74.
Hooper CW, Delaney C, Streeter T, Yarboro MT, Poole S, Brown N, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure constricts the mouse ductus arteriosus in utero. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;311:H572–81.
Shima Y, Ishikawa H, Matsumura Y, Yashiro K, Nakajima M, Migita M. Idiopathic severe constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus: a possible underestimated pathophysiology. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:237–40.
Luchese S, Manica JL, Zielinsky P. Intrauterine ductus arteriosus constriction: analysis of a historic cohort of 20 cases. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2003;81:405–10. 399-404
Lopes LM, Carrilho MC, Francisco RP, Lopes MA, Krebs VL, Zugaib M. Fetal ductus arteriosus constriction and closure: analysis of the causes and perinatal outcome related to 45 consecutive cases. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29:638–45.
Alagille D, Estrada A, Hadchouel M, Gautier M, Odievre M, Dommergues JP. Syndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts (Alagille syndrome or arteriohepatic dysplasia): review of 80 cases. J Pediatr. 1987;110:195–200.
Pober BR. Williams-Beuren syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:239–52.
Woolfenden AR, Albers GW, Steinberg GK, Hahn JS, Johnston DC, Farrell K. Moyamoya syndrome in children with Alagille syndrome: additional evidence of a vasculopathy. Pediatrics. 1999;103:505–8.
Rocha R, Soro I, Leitao A, Silva ML, Leao M. Moyamoya vascular pattern in Alagille syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2012;47:125–8.
McElhinney DB. Analysis of cardiovascular phenotype and genotype-phenotype correlation in individuals with a JAG1 mutation and/or Alagille syndrome. Circulation. 2002;106:2567–74.
Kamath BM, Spinner NB, Emerick KM, Chudley AE, Booth C, Piccoli DA, et al. Vascular anomalies in Alagille syndrome: a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Circulation. 2004;109:1354–8.
Merla G, Brunetti-Pierri N, Piccolo P, Micale L, Loviglio MN. Supravalvular aortic stenosis: elastin arteriopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012;5:692–6.
Manderfield LJ, High FA, Engleka KA, Liu F, Li L, Rentschler S, et al. Notch activation of Jagged1 contributes to the assembly of the arterial wall. Circulation. 2012;125:314–23.
Coceani F, Baragatti B. Mechanisms for ductus arteriosus closure. Semin Perinatol. 2012;36:92–7.
Feng X, Krebs LT, Gridley T. Patent ductus arteriosus in mice with smooth muscle-specific Jag1 deletion. Development. 2010;137:4191–9.
Dyamenahalli U, Smallhorn JF, Geva T, Fouron J-C, Cairns P, Jutras L, et al. Isolated ductus arteriosus aneurysm in the fetus and infant: a multi-institutional experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:262–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, S., Howley, L.W., Cuneo, B.F. et al. In-utero idiopathic ductal constriction: a prenatal manifestation of Alagille and Williams syndrome arteriopathy. J Perinatol 38, 1453–1456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-018-0221-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-018-0221-9
This article is cited by
-
Prenatal diagnosis of Williams-Beuren syndrome by ultrasound and chromosomal microarray analysis
Molecular Cytogenetics (2022)