Abstract
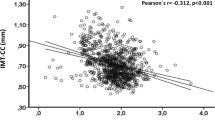
Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) can reflect the degree of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk in hemodialysis patients. Factors such as advanced age, male gender, family history, and smoking can increase the risk of CIMT. In hemodialysis (HD) patients, lower serum albumin level was found to be correlated with higher CIMT. This study aimed to evaluate the relation between CIMT and protein energy wasting (PEW) diagnosed according to the diagnostic criteria of International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM) expert panel in HD patients. This study involved 45 HD patients who were divided into two groups according to the diagnostic criteria for PEW proposed by the ISRNM expert panel including group with PEW (11 patients) and group without PEW (34 patients). Caloric intake was evaluated by food frequency questionnaire for 3 days. Subjective global assessment (SGA) and malnutrition inflammation score (MIS) were fulfilled. Anthropometric measurements, as well as body composition, was evaluated by electrical bioimpedance analysis. Doppler ultrasonography was used to assess CIMT that was significantly higher in patients with PEW (p = 0.030). CIMT had significant positive correlation to age, SGA, and MIS (p = 0.008, 0.002, and 0.003, respectively). Significant negative correlation was observed between CIMT and serum albumin. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that serum albumin was the only predictor of mean CIMT. In conclusion, CIMT seems to be related to malnutrition in HD patients. Low serum albumin was the only predictor of CIMT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Jager DJ, Grootendorst DC, Jager KJ, van Dijk PC, Tomas LM, Ansell D, et al. Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA. 2009;302:1782–9.
London GM, Drueke TB. Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997;51:1678–95.
London GM, Marchais SJ, Guerin AP. Arterial stiffness and function in end-stage renal disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2004;11:202–9.
Sarafidis PA, Georgianos PI, Karpetas A, Bikos A, Korelidou L, Tersi M, et al. Evaluation of a novel brachial cuff-based oscillometric method for estimating central systolic pressure in hemodialysis patients. Am J Nephrol. 2014;40:242–50.
Jankowska M, Cobo G, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P. Inflammation and protein-energy wasting in the uremic milieu. Contrib Nephrol. 2017;191:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479256. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Review. PMID: 28910791
Roumeliotis A, Roumeliotis S, Panagoutsos S, Theodoridis M, Argyriou C, Tavridou A, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular morbidity in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 and chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2019;41:131–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2019.1585372
Bossola M, Muscaritoli M, Tazza L, Panocchia N, Liberatori M, Giungi S, et al. Variables associated with reduced dietary intake in hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2005;15:244–52.
National Nutrition Institute (NNI). Food Composition Tables for Egypt. 2nd Edition, Cairo. National institute of nutrition. 2006.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kleiner M, Dunne E, Lee GH, Luft FC. A modified quantitative subjective global assessment of nutrition for dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 1999;14:1732–8.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD, Block G, Humphreys MH. A malnutrition-inflammation score is correlated with morbidity and mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:1251–63.
Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, Cano N, Chauveau P, Cuppari L, et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73, 391-8. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Erratum in: Kidney Int. 2008;74:393.
Carrero JJ, Thomas F, Nagy K, Arogundade F, Avesani CM, Chan M, et al. Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: a meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the international society of renal nutrition and metabolism. J Ren Nutr. 2018;28:380–92.
Ossareh S, Alaei A, Saedi D. Carotid intima-media thickness in maintenance hemodialysis patients: role of cardiovascular risk factor. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2011;5:169–74.
Stein JH, Douglas PS, Srinivasan SR, Bond MG, Tang R, Li S, et al. Distribution and cross-sectional age-related increases of carotid artery intima-media thickness in young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Stroke. 2004;35:2782–7.
Bots ML, Evans GW, Riley WA, Grobbee DE. Carotid intima-media thickness measurements in intervention studies: design options, progression rates, and sample size considerations: a point of view. Stroke 2003;34:2985–94.
Kuswardhani RT, Wiradharma KG, Kandarini Y, Widiana GR, Martadiani ED. Factors associated with carotid intima-media thickness in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Int J Gen Med. 2018;12:1–6. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S178276. eCollection 2019. Review
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Block G, Humphreys MH, Kopple JD. Reverse epidemiology of cardiovascular risk factors in maintenance dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2003;63:793–808.
Kato A, Takita T, Furuhashi M, Maruyama Y, Hishida A. Comparison of serum albumin, C-reactive protein and carotid atherosclerosis as predictors of 10-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2010;14:226–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542-4758.2009.00432.x. Epub 2010 Mar 24
Lowrie EG, Lew NL. Death risk in hemodialysis patients: the predictive value of commonly measured variables and an evaluation of death rate differences between facilities. Am J Kidney Dis. 1990;15:458–82.
Alves FC, Sun J, Qureshi AR, Dai L, Snaedal S, Bárány P, et al. The higher mortality associated with low serum albumin is dependent on systemic inflammation in end-stage kidney disease. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0190410 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190410. eCollection 2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The Institutional Research Board (IRB) of our institute approve study protocol.
Informed consent
Informed written consent was obtained from each participant in the study after assuring confidentiality.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, M., Nagy, E., AbdAlBary, M. et al. Relation of protein energy wasting to carotid intima media thickness in hemodialysis patients. J Hum Hypertens 35, 598–603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0376-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0376-7