Abstract
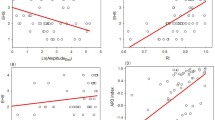
This randomized crossover and placebo-controlled trial evaluated the effects of daily use of sildenafil citrate (SIL, 1-month 50 mg twice daily) on penile and systemic endothelial microvascular function in hypertensive patients presenting with erectile dysfunction. The effects of SIL on arterial pressure were evaluated using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). Fifty patients diagnosed with primary arterial hypertension and erectile dysfunction (aged 57.4 ± 5.6 years), recruited in a tertiary public hospital, were treated with SIL (50 mg twice daily) or placebo (PLA) for two 30-day periods with a 30-day washout between them. Laser speckle contrast imaging coupled with acetylcholine skin iontophoresis was used to evaluate penile and systemic (forearm) cutaneous microvascular reactivity. SIL treatment increased penile basal microvascular flow (P = 0.002) and maximal endothelial-dependent peak response to skin iontophoresis of acetylcholine (ACh, P = 0.006). The area under the curve of microvascular vasodilation induced by ACh was also significantly increased (P = 0.02). Lastly, SIL treatment did not modify systemic microvascular reactivity. Twenty-four-hour ABPM (P = 0.0002) and daytime (P = 0.002) and nighttime (P = 0.001) mean diastolic blood pressure values were significantly reduced after SIL treatment. The scores of the Simplified International Index of Erectile Function (P < 0.0001) and the number of patients with positive responses to Sexual Encounter Profile question 3 (P < 0.0001) also increased after SIL treatment. Penile endothelium-dependent microvascular reactivity improved after continuous use of sildenafil in hypertensive patients with erectile dysfunction; the treatment also reduced blood pressure, suggesting that, in addition to improving erectile function, daily use of sildenafil could improve blood pressure control.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 June 2020
The original HTML version of this Article was updated shortly after publication in order to change all the figures from colour to black & white as per the authors’ request.
References
Solomon H, Man JW, Jackson G. Erectile dysfunction and the cardiovascular patient: endothelial dysfunction is the common denominator. Heart. 2003;89:251–3.
Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Goodman PJ, Probstfield JL, Moinpour CM, Coltman CA. Erectile dysfunction and subsequent cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2005;294:2996–3002.
Fonseca V, Jawa A. Endothelial and erectile dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, and the metabolic syndrome: common pathways and treatments? Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:13M–18M.
Kloner RA, Jarow JP. Erectile dysfunction and sildenafil citrate and cardiologists. Am J Cardiol. 1999;83:576–82. A577
Bortolotti A, Parazzini F, Colli E, Landoni M. The epidemiology of erectile dysfunction and its risk factors. Int J Androl. 1997;20:323–34.
Burchardt M, Burchardt T, Baer L, Kiss AJ, Pawar RV, Shabsigh A, et al. Hypertension is associated with severe erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 2000;164:1188–91.
Chrysant SG. Effectiveness and safety of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors in patients with cardiovascular disease and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2013;15:475–83.
Kloner RA, Brown M, Prisant LM, Collins M. Effect of sildenafil in patients with erectile dysfunction taking antihypertensive therapy. Sildenafil Study Group. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14:70–73.
Bohm M, Burkart M, Baumann G. Sildenafil is well tolerated by erectile dysfunction patients taking antihypertensive medications, including those on multidrug regimens. Curr Drug Saf. 2007;2:5–8.
Nehra A, Jackson G, Miner M, Billups KL, Burnett AL, Buvat J, et al. The Princeton III Consensus recommendations for the management of erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:766–78.
Oliver JJ, Melville VP, Webb DJ. Effect of regular phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition in hypertension. Hypertension. 2006;48:622–7.
Vardi Y, Dayan L, Apple B, Gruenwald I, Ofer Y, Jacob G. Penile and systemic endothelial function in men with and without erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol. 2009;55:979–85.
Vardi Y, Appel B, Ofer Y, Greunwald I, Dayan L, Jacob G. Effect of chronic sildenafil treatment on penile endothelial function: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study. J Urol. 2009;182:2850–5.
Wilkinson IB, Webb DJ. Venous occlusion plethysmography in cardiovascular research: methodology and clinical applications. Br J Clin Pharm. 2001;52:631–46.
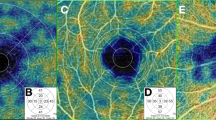
Verri V, Brandao A, Tibirica E. The evaluation of penile microvascular endothelial function using laser speckle contrast imaging in healthy volunteers. Microvasc Res. 2015;99:96–101.
Verri V, Brandao AA, Tibirica E. Penile microvascular endothelial function in hypertensive patients: effects of acute type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51:e6601.
Eardley I, Ellis P, Boolell M, Wulff M. Onset and duration of action of sildenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Br J Clin Pharm. 2002;53(Suppl 1):61S–65S.
Sullivan KM, Dean A, Soe MM. OpenEpi: a web-based epidemiologic and statistical calculator for public health. Public Health Rep. 2009;124:471–4.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1997;49:822–30.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Pena BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26.
Javaroni V, Queiroz-Miguez M, Abreu-Casanova M, Oigman W, Neves MF. Brachial flow-mediated dilation correlates with vardenafil response in hypertensive men with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2011;78:368–74.
Malachias MV. 7th Brazilian guideline of arterial hypertension: presentation. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2016;107:0.
Roustit M, Millet C, Blaise S, Dufournet B, Cracowski JL. Excellent reproducibility of laser speckle contrast imaging to assess skin microvascular reactivity. Microvasc Res. 2010;80:505–11.
Roustit M, Cracowski JL. Assessment of endothelial and neurovascular function in human skin microcirculation. Trends Pharm Sci. 2013;34:373–84.
Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 1988.
Wallis RM, Corbin JD, Francis SH, Ellis P. Tissue distribution of phosphodiesterase families and the effects of sildenafil on tissue cyclic nucleotides, platelet function, and the contractile responses of trabeculae carneae and aortic rings in vitro. Am J Cardiol. Springer; Berlin Heidelberg. 1999;83:3C–12C.
Spieker LE, Flammer AJ, Luscher TF. The vascular endothelium in hypertension. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 2006: 249–83.
Simonsen U, Garcia-Sacristan A, Prieto D. Penile arteries and erection. J Vasc Res. 2002;39:283–303.
Prieto D. Physiological regulation of penile arteries and veins. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20:17–29.
Vaziri ND, Wang XQ. cGMP-mediated negative-feedback regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression by nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1999;34:1237–41.
Mahmud A, Hennessy M, Feely J. Effect of sildenafil on blood pressure and arterial wave reflection in treated hypertensive men. J Hum Hypertens. 2001;15:707–13.
Vlachopoulos C, Hirata K, O’Rourke MF. Effect of sildenafil on arterial stiffness and wave reflection. Vasc Med. 2003;8:243–8.
Collins R, Peto R, MacMahon S, Hebert P, Fiebach NH, Eberlein KA, et al. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Part 2, Short-term reductions in blood pressure: overview of randomised drug trials in their epidemiological context. Lancet. 1990;335:827–38.
Cholesterol, diastolic blood pressure, and stroke: 13,000 strokes in 450,000 people in 45 prospective cohorts. Prospective studies collaboration. Lancet. 1995;346:1647–53.
Elesber AA, Solomon H, Lennon RJ, Mathew V, Prasad A, Pumper G, et al. Coronary endothelial dysfunction is associated with erectile dysfunction and elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with early atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:824–31.
Ponholzer A, Temml C, Obermayr R, Wehrberger C, Madersbacher S. Is erectile dysfunction an indicator for increased risk of coronary heart disease and stroke? Eur Urol. 2005;48:512–8. discussion 517-8
Montorsi F, Briganti A, Salonia A, Rigatti P, Margonato A, Macchi A, et al. Erectile dysfunction prevalence, time of onset and association with risk factors in 300 consecutive patients with acute chest pain and angiographically documented coronary artery disease. Eur Urol. 2003;44:360–4. discussion 364-5
Kloner R. Erectile dysfunction and hypertension. Int J Impot Res. 2006;19:296.
Cordeiro AC, Mizzaci CC, Fernandes RM, Araujo-Junior AG, Cardoso PO, Dutra LV, et al. Simplified International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) and coronary artery disease in hypertensive patients. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2012;99:924–30.
Baumhakel M, Schlimmer N, Kratz M, Hackett G, Jackson G, Bohm M. Cardiovascular risk, drugs and erectile function-a systematic analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65:289–98.
Javaroni V, Neves MF. Erectile dysfunction and hypertension: impact on cardiovascular risk and treatment. Int J Hypertens. 2012;2012:627278.
Fogari R, Preti P, Derosa G, Marasi G, Zoppi A, Rinaldi A, et al. Effect of antihypertensive treatment with valsartan or atenolol on sexual activity and plasma testosterone in hypertensive men. Eur J Clin Pharm. 2002;58:177–80.
Fogari R, Zoppi A, Poletti L, Marasi G, Mugellini A, Corradi L. Sexual activity in hypertensive men treated with valsartan or carvedilol: a crossover study. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14:27–31.
Brixius K, Middeke M, Lichtenthal A, Jahn E, Schwinger RH. Nitric oxide, erectile dysfunction and beta-blocker treatment (MR NOED study): benefit of nebivolol versus metoprolol in hypertensive men. Clin Exp Pharm Physiol. 2007;34:327–31.
Wassertheil-Smoller S, Blaufox MD, Oberman A, Davis BR, Swencionis C, Knerr MO, et al. Effect of antihypertensives on sexual function and quality of life: the TAIM study. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114:613–20.
Viigimaa M, Doumas M, Vlachopoulos C, Anyfanti P, Wolf J, Narkiewicz K, et al. Hypertension and sexual dysfunction: time to act. J Hypertens. 2011;29:403–7.
Reffelmann T, Kloner RA. Pharmacotherapy of erectile dysfunction: focus on cardiovascular safety. Exp Opin Drug Saf. 2005;4:531–40.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Marcio Marinho Gonzalez for his excellent technical assistance.
Funding
CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, ET grant # 305234/2017-0), FAPERJ (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, ET grant # E-26/202.822/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VV and ET conceived and designed the study. VV and ET analyzed the data and interpreted the results of the experiments. ET drafted the manuscript. VV, AA and ET edited and revised the manuscript. All of the authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Part of the present work was presented during the 26th European Meeting on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Protection (2016), during the European Society of Cardiology Congress (2017) and during the 29th European Meeting on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Protection (2019).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verri, V., Nascimento, A.R., Brandao, A.A. et al. Effects of chronic type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibition on penile microvascular reactivity in hypertensive patients with erectile dysfunction: a randomized crossover placebo-controlled trial. J Hum Hypertens 35, 360–370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0343-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0343-3
This article is cited by
-
Conservative Non-surgical Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Current Urology Reports (2023)