Abstract
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a life-threatening critical syndrome resulting largely from the accumulation of and the inability to clear pulmonary edema. Protectin DX, an endogenously produced lipid mediator, is believed to exert anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution effects. Protectin DX (5 µg/kg) was injected i.v. 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) administration, and alveolar fluid clearance was measured in live rats (n = 8). In primary rat ATII epithelial cells, protectin DX (3.605 × 10−3 mg/l) was added to the culture medium with LPS for 6 h. Protectin DX improved alveolar fluid clearance (9.65 ± 1.60 vs. 15.85 ± 1.49, p < 0.0001) and decreased pulmonary edema and lung injury in LPS-induced lung injury in rats. Protectin DX markedly regulated alveolar fluid clearance by upregulating sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase protein expression levels in vivo and in vitro. Protectin DX also increased the activity of Na, K-ATPase and upregulated P-Akt via inhibiting Nedd4–2 in vivo. In addition, protectin DX enhanced the subcellular distribution of sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase, which were specifically localized to the apical and basal membranes of primary rat ATII cells. Furthermore, BOC-2, Rp-cAMP, and LY294002 blocked the increased alveolar fluid clearance in response to protectin DX. Protectin DX stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through a mechanism partly dependent on alveolar epithelial sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase activation via the ALX/PI3K/Nedd4–2 signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a devastating clinical syndrome characterized by alveolar epithelial injury that leads to non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, which floods alveolar spaces with protein-rich fluid1,2. Although our understanding of the pathophysiological changes associated with ARDS has improved, this condition cannot be effectively managed, and its mortality remains at ~40%2. It has been reported that alveolar fluid clearance is impaired in the majority of ARDS patients3. Hence, the timely and effective removal of excess alveolar edema fluid is important for obtaining better clinical outcomes4.
Alveolar fluid clearance relies on active ion transport, which leads to an osmotic gradient that drives the fluid from the alveolar space back into the interstitium and eventually into the blood circulation5. The mechanism of alveolar fluid clearance is its active Na+ transport across the alveolar epithelium via apical alveolar sodium channels6 and basolateral Na, K-ATPases7. Although therapies such as A2B adenosine receptor agonists8, angiotensin9, triiodo-L-thyronine10, and estradiol11 have shown promising clinical effects in animal models, they have failed to translate positively in human studies12. We previously reported that an intravenous β-agonist (salbutamol) decreased extravascular lung water in ARDS patients13,14. However, we found that the side effects of salbutamol, such as tachycardia, arrhythmia, and lactic acidosis, significantly increased the 28-day mortality rate in a multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial15. Therefore, new therapeutic agents need to be identified.
Protectins are novel lipid mediators of anti-inflammation and resolution16. Protectin DX is an isomer of protectin D117 and is believed to exert anti-inflammatory properties, including the inhibition of neutrophil activation and the regulation of inflammatory cytokines. Protectin DX is produced by an apparent double lipoxygenase-mediated reaction in murine peritonitis exudates and human leukocyte suspensions or by incubating soybean 15-lipoxygenase with DHA17,18. The mean concentration of protectin DX in human blood is below 25 pg/ml19. The protectin DX level is ~60 pg/106 cells in C57BL/6 macrophages20, 30 pg/g in the skeletal muscle of mice, and 100 pg/g in the liver21. A recent study demonstrated that protectin DX could block neutrophil infiltration in murine peritonitis by 20–25% at a dose of 1 ng/mouse18. It has been reported that protectin DX could alleviate insulin resistance by activating the myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis22. Previous data from our group suggested that posttreatment with 15-epi-16-parafluorophenoxy lipoxin A4 could attenuate LPS -induced acute lung injury in mice23. However, there are no studies that have addressed the effect of protectin DX on pulmonary edema.
The present study tested the hypothesis that the administration of protectin DX will increase alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-injured rat lungs. Our secondary hypothesis was that augmented alveolar fluid clearance would also be associated with the stimulation of ATII cell sodium channels, Na, K-ATPase, P-Akt and Nedd4–2 after treatment with protectin DX. Finally, as the receptors and downstream signaling pathways of protectin DX were under investigation, we determined the effects of an ALX receptor inhibitor (BOC-2), cAMP inhibitor (Rp-cAMP), cGMP inhibitor (Rp-cGMP), PI3K inhibitor (LY294002), and PKA inhibitor (H89) on alveolar fluid clearance in ARDS to gain a better understanding of the mechanisms.
Materials and methods
Materials
Protectin DX, LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor), and H89 (PKA inhibitor) were from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI). LPS (Escherichia coli serotype 055:B5) was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-α, myeloperoxidase, and cAMP ELISA kits were from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). BOC-2 (ALX inhibitor), Rp-cAMP (cAMP inhibitor), and Rp-cGMP (cGMP inhibitor) were obtained from Biomol-Enzo Life Sciences (Farmingdale, NY). Anti-Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA), and anti-sodium channel α, β, and γ antibodies were purchased from Biorbyt (Cambridge, Cambridgeshire). Anti-P-Akt, total Akt (T-Akt), and Nedd4–2 antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA).
Animal preparation
Specific pathogen-free adult male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250–300 g were obtained from Slac Laboratory Animal (Shanghai, China). The rats were housed under controlled temperature and humidity on a day–night cycle and had free access to food and water. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The study was approved by the Animal Studies Ethics Committee of Wenzhou Medical University.
Rats were randomized into ten groups (n = 8): control group, LPS group, LPS + alcohol group (alcohol was used as the solvent for protectin DX, 50 µl/kg), PDX group, LPS + PDX group, LPS + PDX + BOC-2 group, LPS + PDX + RP-cAMP group, LPS + PDX + RP-cGMP group, LPS + PDX + H89 group, and LPS + PDX + LY294002 group (PDX = protectin DX). The LPS-induced lung injury model was created by injecting 14 mg/kg LPS into the caudal vein. For the protectin DX group and the control group, the rats received protectin DX (5 µg/kg) or an equivalent volume of saline via the caudal vein. For the LPS + PDX group and the LPS + alcohol group, the rats received protectin DX or alcohol (50 µl/kg) via the caudal vein 8 h after LPS administration. For the LPS + PDX + BOC-2 group, LPS + PDX + RP-cAMP group, LPS + PDX + RP-cGMP group, LPS + PDX + H89 group, and LPS + PDX + LY294002 group, the rats received protectin DX with BOC-2 (600 ng/kg), RP-cAMP (5 mg/kg), RP-cGMP (5.5 mg/kg), H89 (10 mg/kg), or LY294002 (3 mg/kg) via the caudal vein 8 h after LPS administration. Before a tracheotomy tube was placed, the rats were anesthetized with an i.p. injection of 5% chloral hydrate (7 ml/kg). Subsequently, the rats were killed after 60 min of sustained mechanical ventilation, and their lungs were harvested.
Pathological studies
The right lower lung lobes were harvested, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h, embedded in paraffin, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for light microscopy analysis. A semi-quantitative scoring system was adopted to evaluate lung injury, which included alveolar congestion, alveolar hemorrhage, neutrophil infiltration, or aggregation in the airspace or vessel wall, and alveolar wall/hyaline membrane thickness and inflammatory cell infiltration. The grading scale for the light microscopy pathologic findings was as follows: 0 = no injury; 1 = slight injury (25%); 2 = moderate injury (50%); 3 = severe injury (75%); and 4 = very severe injury (almost 100%). The results were graded from 0 to 4 for each item, as described previously27,28. The four variables were summed to represent the lung injury score (total score: 0–16).
Part of the right lung from individual rats was homogenized and centrifuged, and the levels of myeloperoxidase, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-10 in the resulting tissue supernatants were determined using myeloperoxidase, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-10 ELISA kits.
Transmission electron microscopy
Tissue blocks were incubated overnight in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (350 mOsm, pH 7.4) and postfixed for 2 h in osmium tetroxide (1% osmium tetroxide in 0.125 sodium cacodylate buffer; 400 mOsm, pH 7.4). The samples were then subjected to stepwise dehydration in increasing concentrations of ethanol (50–100%), rinsed with propylene oxide, and embedded in araldite. The tissue blocks were then cut into ultra-thin sections (50–70 nm) and contrast stained with saturated uranyl acetate and bismuth subnitrate. The sections were examined at an accelerating voltage of 60 kV using a Zeiss EM 10C transmission electron microscope (HITACHI, H-7500, Abcamm, Japan). Micrographs of a carbon grating replica were taken for calibration.
Measurement of alveolar fluid clearance in live rats
Alveolar fluid clearance was measured in live rats as previously described10 with some modifications. The clearance is expressed as a percentage of the total instilled volume that was cleared after 60 min. The alveolar fluid clearance was determined by Evans blue-tagged albumin concentration changes; this method has been clearly described by our laboratory24.
For the alveolar instillate, a 5% albumin instillate solution was prepared by dissolving 50 mg/ml BSA in modified lactated Ringer’s solution: 137 mM NaCl, 4.67 mM KCl, 1.82 mM CaCl2·2H2O, 1.25 mM MgSO4·7H2O, 5.55 mM dextrose, and 12 mM HEPES. The pH was adjusted to 7.4 at 37 °C. The albumin solution was labeled with 0.15 mg/ml Evans blue. Briefly, after anesthesia with 5% chloral hydrate (7 ml/kg), a polyethylene endotracheal tube was inserted via tracheotomy. The rats were ventilated with a constant volume ventilator (model HX-300 Animal Ventilator; Taimeng Company of Chengdu, China) with an inspired oxygen fraction of 100%, a respiratory rate of 45–50 breaths/min and a 4.5 ± 0.2 ml tidal volume; the positive end-expiratory pressure was maintained at 2–3 cm H2O during the baseline period. After tracheotomy, the rats were allowed to stabilize for 10 min. The animals were then placed in the left lateral decubitus position, and instillation tubing (16G epidural catheter) was gently passed through the tracheotomy tube into the left lung. A total of 1.5 ml (5 ml/kg) of the instillate solution was instilled at a rate of 0.08 ml/min using a syringe pump. After the instillation was complete, 0.2 ml of air was injected to clear the instillation catheter of liquid. The instillate remaining in the syringe was collected as the initial sample. After instillation, the catheter was left in place for 60 min. The final alveolar sample was collected via the instillation catheter. The concentrations of Evans blue-labeled albumin in the instilled and aspirated solutions were measured by a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 621 nm. The alveolar fluid clearance was calculated using the following equation: alveolar fluid clearance = (1−C0/C1), where C0 is the protein concentration of the instillate before instillation, and C1 is the protein concentration of the sample obtained at the end of 60 min of mechanical ventilation.
Primary rat ATII cells isolation, culture, and treatment
Primary rat ATII cells were isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats (250–300 g) via the elastase digestion of lung tissue and then differentially adhered to IgG-coated plates as described by Dobbs et al.25. The purity of ATII cells was assessed by using a modified Papanicolaou stain and looking for the presence of dark blue inclusions. Cell viability was assessed by trypan blue exclusion assays (>95%). ATII cells were seeded onto plastic culture dishes at 1 × 106/cm2 and cultured in 5% CO2 and 95% air in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin after isolation. For all experiments, cells were subcultured in six-well plates and maintained until subconfluence (80%); then, the cells were serum deprived for 24 h before adding LPS (1 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of protectin DX (3.605 × 10−3 mg/l).
Western blotting for sodium channels, Na, K-ATPase, P-Akt, and Nedd4-2
Proteins were extracted using RIPA lysis buffer (50 mM Tris [pH 7.4], 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100,1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium-dodecyl sulfonate, sodium orthovanadate, sodium fluoride, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, leupeptin) and phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride. The samples were ultrasonicated three times for 5 s and then spun at 12,000 × g/min for 30 min. The protein concentrations of the supernatants were determined by using a bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL). Proteins were separated on 10% sodium-dodecyl sulfonate polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. After blocking with 5% nonfat dried milk in TBS containing 0.05% Tween-20, the membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C with the following primary antibodies: sodium channel α, β, and γ (1:500, 1:700, 1:800); Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 (1:500, 1:1000); β-actin (internal control, 1:500); Akt (1: 1000); P-Akt (1:2000), and Nedd4–2 (1:1000); then, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary Ab (1:000; Santa Cruz Company) at room temperature for 1.5 h. The protein bands were detected by electrochemiluminescence (ECL) and visualized by using a UVP gel imaging system (Upland, CA). The band intensities were analyzed by using AlphaEaseFC (version 4.0).
Confocal imaging
ATII cells were treated with saline, LPS (1 µg/ml), LPS + alcohol (the same volume of protectin DX), LPS + PDX (3.605 × 10−3 mg/l), or protectin DX for 6 h before being fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and blocked with PBS containing 10% donkey serum for 30 min. The cells were then incubated in a 1:50 dilution of monoclonal mouse anti-Na, K-ATPase α1 and goat anti-sodium channel α antibodies at 4 °C for 48 h, followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor donkey anti-goat and donkey anti-mouse IgG antibodies (1:100 and 1:300; Jackson) at room temperature for 2 h. Cell images were acquired with a confocal laser-scanning microscope (Leica) and analyzed by using Image-Pro plus 6.3 software (Media Cybernetics, Crofton, MA).
Measurement of Na, K-ATPase activity in rat lung tissues
The hydrolytic activity of Na, K-ATPase was measured as ouabain-sensitive ATP hydrolysis under maximal velocity conditions by measuring the release of inorganic phosphate from ATP, as previously described26. Briefly, rat lung tissues were digested, subjected to centrifugal sedimentation, lysed, and homogenized. A minimal ATP enzyme test kit (Jian Cheng Company, Nanjing, China) was used to assay Na, K-ATPase activity according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Measurement of cAMP concentrations
Lung samples were treated with isobutyryl methylxanthine (Sigma) to inhibit phosphodiesterases; then, the samples were homogenized in ice-cold 1 M TCA and centrifuged at 2500 × g to precipitate the particulate material. The cAMP content in the supernatant was measured via ELISA according to the manufacturer’s instructions (R&D Systems).
Blinding method
The present study used randomized, blinded methods. The randomization list of animals was computer generated by a statistician using SAS/STAT software. Blinding was accomplished by the separation of function: a treatment administrator was responsible for dispensation and administration to the animal models. Others extracted the lung tissue for the pathological analyses, transmission electron microscopy, alveolar fluid clearance measurement, and western blotting.
Statistical analysis
The data represent the mean ± SD. There were no missing, lost, or excluded data. Based on previous experience, no a priori power calculation was conducted; all data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. All tests were two-sided, and significance was determined at the p < 0.05 level. Statistical analyses were performed using Prism 6.0 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA).
Results
Protectin DX protected lung tissues from LPS-induced acute lung injury in vivo
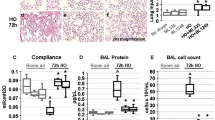
First, we evaluated the effect of protectin DX (5 µg/kg) on LPS (14 mg/kg)-induced acute lung injury. The control group presented normal pulmonary histology (Fig. 1a, b). Compared with those in the control group, the lung tissues in the LPS group were markedly damaged; these tissues had interstitial edema, hemorrhage, and inflammatory cell infiltration as evidenced by increases in lung injury scores (Fig. 1c). All of the morphologic changes were less pronounced in the LPS + PDX group. Protectin DX significantly reduced the LPS-induced pathologic changes as evidenced by decreases in the lung injury scores. There was no significant difference between the control and protectin DX groups (Fig. 1c).
Protectin DX (5 µg/kg) was injected into the caudal veins of Sprague-Dawley rats 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) stimulation; the rats were then ventilated for 60 min, and the effects of protectin DX were assessed (a, b) in hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections (original magnification ×100, ×400). Lung injury scores (c) were recorded from 0 (no damage) to 16 (maximum damage) according to the criteria described in the “Materials and methods”. Myeloperoxidase (d), TNF-α (e), IL-1 (f), and IL-10 (g) expression levels in lung tissues were measured by ELISA to quantitatively determine the resolution of infiltrated cells. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX, MPO myeloperoxidase. Alcohol was the solvent for protectin DX. **p < 0.01 versus the control group; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group; ‡p < 0.05, ‡‡p < 0.01 versus the LPS + alcohol group
In addition, the concentrations of myeloperoxidase, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-10 in the lung tissue homogenate were significantly higher in the LPS group than in the control group and were lower in the protectin DX treatment group than in the LPS group (Fig. 1d–g).
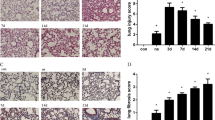
Finally, we examined the effects of protectin DX on the ultrastructure of lung tissues. The lamellar bodies, which is the most significant diagnostic characteristic of ATII cells, were severely vacuolated in the LPS group compared with those in the control group; however, the lamellar bodies recovered from this pathological change in the protectin DX treatment group (Fig. 2a). As shown in Fig. 2b, the control group had a normal air–blood barrier. In contrast, the air–blood barrier in the LPS group was damaged and had broken epithelial bridges and capillary walls in the tissues. For the treatment group, protectin DX significantly improved the LPS-induced damage to the air–blood barrier.
Protectin DX (5 µg/kg) was injected into the caudal veins of Sprague-Dawley rats 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) stimulation; the rats were then ventilated for 60 min, and the effects of protectin DX were assessed by electron microscope photomicrographs of the lung tissues from rats. The lamellar bodies in the LPS group were severely vacuolated compared with those in the control group; however, the lamellar body damage was recovered in the protectin DX treatment group (a). The control group presented a normal air–blood barrier. In contrast, the air–blood barrier in the LPS group was damaged and had broken epithelial bridges and capillary walls in the tissues. In the treatment group, protectin DX significantly improved the damage to the air–blood barrier induced by LPS (b). lb lamellar body, bc blood capillary, ac air capillary, ep epithelial bridge, en endothelial cell, ecm extracellular matrix of the capillary wall, cn cell nucleus, er erythrocyte. After intratracheal instillation of a 5% albumin solution containing Evans blue-labeled albumin (5 ml/kg) through a tracheostomy to the left lung, alveolar fluid clearance was measured over 60 min in ventilated animals (c). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX. Alcohol was the solvent for protectin DX. **p < 0.01 versus the control group; ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group; ‡‡p < 0.01 versus the LPS + alcohol group
Protectin DX upregulated alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-induced acute lung injury in vivo
Next, we examined the effect of protectin DX (5 µg/kg) on alveolar fluid clearance in LPS (14 mg/kg)-induced acute lung injury in vivo. Of the protectin DX concentrations (1.5, 2.5, 5, and 7.5 μg/kg), 1.5 µg/kg protectin DX could not improve the LPS-induced alveolar fluid clearance reduction. The 2.5 μg/kg protectin DX dose improved the LPS-induced alveolar fluid clearance reduction, and the maximal effect was achieved at the 5 μg/kg dose; the effects of protectin DX were similar for the 5 μg/kg and 7.5 μg/kg doses. Therefore, protectin DX at a concentration of 5 µg/kg or vehicle alone was injected into the caudal vein 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) administration, and alveolar fluid clearance was determined after 60 min. As expected, alveolar fluid clearance in the LPS group was lower than that in the control group (9.65 ± 1.60 vs. 19.23 ± 1.20), whereas protectin DX increased alveolar fluid clearance after LPS-induced acute lung injury (15.85 ± 1.49 vs. 9.65 ± 1.60). However, there was no significant difference between the control and protectin DX groups (Fig. 2c).
Protectin DX upregulated sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase in LPS-induced acute lung injury in vivo
The protein expression levels of the sodium channel α and γ subunits and Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 subunits, but not the β subunit, were higher in the LPS + PDX group than in the LPS group (14 mg/kg) in rat lung tissue homogenates (Fig. 3a–e). In addition, LPS markedly reduced the Na, K-ATPase activity compared with that in the control group, whereas protectin DX (5 µg/kg) increased Na, K-ATPase activity 8 h after LPS-induced acute lung injury (Fig. 3f).
Protectin DX (5 µg/kg) was injected into the caudal veins of Sprague-Dawley rats 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) stimulation; the rats were ventilated for 60 min, and the right lung tissues were harvested to measure the protein expression levels of the sodium channel α, β, and γ subunits (a, b, c) and Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 subunits (d, e) by western blotting. In addition, the Na, K-ATPase activity in the lung tissue homogenates was detected by kits (f). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX. Alcohol was the solvent for protectin DX. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus the control group; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group; ‡p < 0.05, ‡‡p < 0.01 versus the LPS + alcohol group
Protectin DX promoted alveolar fluid clearance through activating the ALX/cAMP/PI3K pathway in vivo
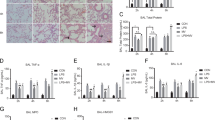
To further investigate the ALX/cAMP/PI3K-dependent actions of protectin DX (5 µg/kg) in vivo, we first measured cAMP concentrations in the lung tissues. We found that cAMP concentrations were lower in the LPS group (14 mg/kg) than in the control group, and protectin DX treatment increased cAMP concentrations in LPS-treated lungs (Fig. 4a). In addition, cAMP concentrations were lower in the LPS + PDX + BOC-2 and LPS + PDX + LY294002 groups than in the LPS + PDX group (Fig. 4b). Protein expression levels of Ser473-phosphorylated Akt in rat lung tissue homogenates were measured by western blotting. The protein levels of phosphorylated Akt were markedly lower in the LPS group than in the control group and considerably higher in the LPS + PDX group than in the LPS group. BOC-2 (600 ng/kg) and LY294002 (3 mg/kg) markedly suppressed the protectin DX-induced increases in P-Akt protein levels (Fig. 4c).
Protectin DX (5 µg/kg) and BOC-2 (ALX receptor inhibitor, 600 ng/kg), LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor, 3 mg/kg), Rp-cAMP (5 mg/kg), Rp-cGMP (5.5 mg/kg) or H89 (10 mg/kg) were co-injected into the caudal veins of Sprague-Dawley rats 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) stimulation; then, intratracheal instillation of a 5% albumin solution containing Evans blue-labeled albumin (5 ml/kg) through a tracheostomy to the left lung was performed to measure alveolar fluid clearance (e), and right lung tissues were harvested to measure cAMP concentrations by using ELISA kits (a, b) and phosphorylated Akt (c) and Nedd4-2 (d) protein expression levels by western blotting. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX. Alcohol was the solvent for protectin DX. **p < 0.01 versus the control group; ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group; ‡p < 0.05, ‡‡p < 0.01 versus the LPS + PDX group
Nedd4–2, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, is critical for the negative control of Na+ transport. The protein levels of Nedd4–2 were significantly higher in the LPS group than in the control group and significantly lower in the protectin DX treatment group than in the LPS group (Fig. 4d). Finally, we co-administered protectin DX (5 µg/kg) and BOC-2 (600 ng/kg), Rp-cAMP (5 mg/kg), Rp-cGMP (5.5 mg/kg), LY294002 (3 mg/kg), or H89 (10 mg/kg) to rats via the caudal vein 8 h after LPS (14 mg/kg) administration, and alveolar fluid clearance was determined after 60 min. Alveolar fluid clearance was lower in the LPS + PDX + BOC-2 (11.94 ± 1.56), LPS + PDX + Rp-cAMP (11.90 ± 1.36), and LPS + PDX + LY294002 groups (10.81 ± 1.49) than in the LPS + PDX group (15.85 ± 1.49), and there were no significant changes in the LPS + PDX + Rp-cGMP and LPS + PDX + H89 groups (Fig. 4e). The beneficial effects of protectin DX on pulmonary histology were abrogated by treatment with BOC-2, Rp-cAMP, and LY294002 (Supplementary Figure).
Dose- and time-dependent protectin DX regulation of Na, K-ATPase α1 expression in primary ATII cells
Different concentrations of protectin DX, including 3.605 × 10−4, 3.605 × 10−3, 18.025 × 10−3, and 3.605 × 10−1 mg/l, were incubated with primary ATII cells. As shown in Fig. 5a, the expression level of the Na, K-ATPase α1 subunit was increased dose-dependently, and the 3.605 × 10−3 mg/l concentration produced the maximum effect. In subsequent experiments, the sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase expression levels in ATII cells were assessed using 3.605 × 10−3 mg/l protectin DX. The expression level of the Na, K-ATPase α1 subunit in primary ATII cells was significantly increased at 6 h (Fig. 5b).
The dose- and time-dependent changes in Na, K-ATPase protein expression levels in primary ATII cells stimulated with LPS (1 µg/ml) were determined by western blotting. Cells were incubated for 6 h with different concentrations of protectin DX, including 3.605 × 10−4, 3.605 × 10−3, 18.025 × 10−3, and 3.605 × 10−1 mg/l, to measure Na, K-ATPase α1 subunit protein expression levels (a). Moreover, ATII cells were incubated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 1, 2, 4, and 6 h to detect Na, K-ATPase α1 subunit protein expression levels (b). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus the control group; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group
Protectin DX increased the sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase expression levels in primary rat ATII cells
In vitro, rat primary ATII alveolar epithelial cells were incubated with protectin DX (3.605 × 10−3 mg/l) in the presence or absence of LPS (1 µg/ml) for 6 h at 37 °C. Protectin DX increased sodium channel α (Fig. 6a) and Na, K-ATPase α1 (Fig. 6b) expression according to confocal laser-scanning microscopy. The protein expression levels of the sodium channel α and γ subunits and Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 subunits, but not the sodium channel β subunit, were higher in the LPS + PDX group than in the LPS group (Fig. 6c, d).
Rat primary ATII cells were treated with protectin DX (3.605 × 10−3 mg/l) in the presence or absence of LPS (1 µg/ml) for 6 h. After incubation, the cells were harvested and sonicated. Sodium channel α (a) and Na, K-ATPase α1 (b) subunit protein expression levels in the cell lysates were detected by confocal laser-scanning microscopy using a specific Abs (original magnification ×400). In addition, sodium channel α, β, and γ subunit (c) and Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 subunit (d) protein expression levels in the cell lysates were detected by western blotting. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 8. PDX protectin DX. Alcohol was the solvent for protectin DX. **p < 0.01 versus the control group; †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 versus the LPS group; ‡p < 0.05, ‡‡p < 0.01 versus the LPS + alcohol group
Discussion
In the present study, we provided evidence of the pro-resolution actions of protectin DX in acute lung injury. Treatment with protectin DX improved alveolar fluid clearance and decreased pulmonary edema and lung injury in rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury. Protectin DX markedly regulated alveolar fluid clearance via upregulating sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase protein expression in vivo and in vitro. Protectin DX also increased the activity of Na, K-ATPase in vivo. In addition, protectin DX enhanced the subcellular distribution of sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase, which were specifically localized to the apical and basal membranes of primary rat ATII cells. Furthermore, BOC-2, Rp-cAMP, and LY294002 blocked the increase in alveolar fluid clearance in response to protectin DX. The results above indicated that protectin DX increased sodium channel and Na, K-ATPase expression to promote alveolar fluid clearance via the ALX/cAMP/Nedd4–2 signaling pathway.
Acute lung injury is a critical illness characterized by the increased permeability of the alveolar–capillary barrier that results in impaired alveolar fluid clearance27. No specific therapy is currently available to modulate this inflammatory response28. It is widely accepted that the resolution of alveolar edema is crucial to patient survival4. Our data clearly demonstrate that protectin DX significantly improved the air–blood barrier and lamellar body structure damaged by LPS; in particular, protectin DX enhanced the rate of alveolar fluid clearance 8 h after LPS challenge, and no effects on alveolar fluid clearance in healthy rat lungs were observed. These results indicate that protectin DX plays an important role in the resolution of inflammation.
It is well known that active Na+ transport is the dominant ion transport mechanism involved in alveolar liquid clearance5. The cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the vectorial transport of Na+ from the alveoli to the interstitium have been reasonably well defined29. Sodium channels are the first constituent of the Na+ transport system, and they are expressed in both alveolar type II and type I cells30. Because they are unable to clear alveolar edema fluid, sodium channel α knockout mice die within 40 h after birth31. Previously, we found that specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), such as lipoxin and resolvin, could improve alveolar fluid clearance via regulating sodium channels, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), and aquaporin. In our study, protectin DX not only enhanced sodium channel α and γ subunit protein expression in lung tissue homogenates from LPS-induced acute lung injury rats, but also increased sodium channel α and γ subunit protein expression in primary ATII cells stimulated with LPS. Moreover, confocal laser-scanning microscopy results for primary ATII cells revealed identical outcomes. Consistent with our findings, similar results have shown that sodium channel upregulation increased pulmonary edema fluid reabsorption, and sodium channel downregulation delayed the reabsorption of fluid during pulmonary edema after thiourea-induced lung injury32. These findings thus suggest that protectin DX promotes alveolar fluid clearance through upregulating sodium channel expression.
Na+ enters the cell through amiloride-sensitive sodium channels or other cationic channels located at the apical surface, and it is expelled by Na, K-ATPase, located at the basolateral surface. It has been reported that the inhibition or loss of Na, K-ATPase could markedly decrease solute and fluid transport in alveoli7. Previous studies have shown that upregulation of sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase increased active Na+ transport, leading to an increase in the ability of the lungs to clear edema27,33. Impaired Na, K-ATPase function appears to be a hallmark of lung injury, even in a preclinical stage27,34. In our study, we demonstrated that protectin DX not only increased Na, K-ATPase α1 and β1 expression levels in rat lung tissues and primary ATII cells after LPS challenge, but also upregulated Na, K-ATPase activity in vivo; these results were indicated by western blotting and confocal laser-scanning microscopy analyses. Together, the lung tissue and cell culture data indicate that protectin DX promotes alveolar fluid clearance through the essential mechanisms of both sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase.
SPMs derived from ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids orchestrate resolution in diverse acute inflammation settings35. Protectin DX is a member of the SPM family; the side effects of low-dose protectin DX were minor, but high-dose protectin DX may induce calcium ion influx. Currently, the receptors and downstream signaling pathways of protectin DX are under investigation. It is generally believed that SPMs exert their actions by interacting with G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with high affinity and stereospecificity36,37. Previously, two G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) of resolvin D1 were identified and validated using a GPCR/arrestin-coupled system; these GPCRs were OrphanGPR32 and ALX (the lipoxin A4 receptor, formyl-peptide receptor type 2 [FPR2], also called ALX)38. ALX was the first receptor cloned and identified as a GPCR for lipoxin and resolvin with demonstrated cell-type-specific signaling pathways39,40. In our study, protectin DX increased alveolar fluid clearance, but its beneficial effects were abrogated by an ALX antagonist (BOC-2) in vivo, suggesting that the protectin DX response is ALX-dependent.
cAMP and cGMP are important second messengers through which cells transduce extracellular signals into intracellular response pathways. Extracellular signals interact with GPCRs to activate adenylate cyclase and increase intracellular cAMP levels. A previous study showed that the LPS-induced immune response led to a decrease in intracellular cAMP levels. Another study showed that cAMP stimulation not only increased Na+ transport within 5 min, but also promoted Na, K-ATPase recruitment to the plasma membrane41,42. Extracellular signals also interact with GPCRs to activate guanylyl cyclases and increase intracellular cGMP levels. In this context, there is evidence for the substantial compartmentalization of the cAMP and cGMP signaling pathways in regulating alveolar fluid clearance. In accordance with previous data, intracellular cAMP levels were decreased after LPS stimulation, and protectin DX abrogated the decrease observed in the LPS group in vivo. As further proof, Rp-cAMP and Rp-cGMP were used in vivo; interestingly, we found that Rp-cAMP, but not Rp-cGMP, reduced alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-induced acute lung injury, indicating that protectin DX promoted alveolar fluid clearance by activating cAMP via ALX, but not cGMP.
It is well known that PI3K signals are implicated in regulating sodium channel trafficking and activity43. PI3K has been identified to regulate sodium channel-mediated alveolar fluid clearance by insulin44. In this context, our aim was to evaluate whether the role of protectin DX in the lungs is ALX/cAMP/PI3K-dependent. Our studies illustrated that intracellular cAMP levels were decreased after LPS stimulation, and protectin DX abrogated the decrease observed in the LPS group in vivo. Furthermore, we found that the protectin DX-induced increase in cAMP levels was blocked by BOC-2 and LY294002. Moreover, BOC-2 and LY294002 blocked the increased alveolar fluid clearance in the protectin DX treatment group. These results, taken together, indicate that the protectin DX response is ALX/cAMP/PI3K-dependent.
It is well accepted that Akt is one of the signaling cascades downstream of PI3K, which is believed to be a central signaling mediator with profound effects on several physiological events45,46. Our studies revealed that P-Akt (ser473) levels were decreased after LPS stimulation and that protectin DX reversed the decrease in P-Akt (ser473) levels; however, these beneficial effects were abrogated by BOC-2 and LY294002. The implication of our work is that protectin DX promoted alveolar fluid clearance via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Nedd4–2 has been shown to negatively regulate sodium channel expression in vitro and in vivo47,48. Recent studies using Nedd4-2-deficient mice have clearly demonstrated that Nedd4–2, which is co-expressed with sodium channels in lung epithelial cells and transports Na+, plays a crucial role in regulating sodium channel activity in the lungs49. Another study using Fisher rat thyroid cells proved that the heterogeneous regulation of α-, β-, and γ-sodium channel expression via the PI3K/Akt pathway was suppressed by Nedd4–245. Consistently, we also found that protectin DX inhibited the increase in Nedd4–2 protein expression levels induced by LPS, and the beneficial effect of protectin DX on reducing Nedd4–2 protein expression levels was abolished by BOC-2 and LY294002 in vivo.
Our study demonstrates that protectin DX alleviated pulmonary edema, enhanced alveolar fluid clearance, and attenuated lung injury partially through stimulating sodium channels and Na, K-ATPase via activating the ALX/PI3K/Nedd4–2 pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury without affecting normal lungs (Fig. 7). Thus, the use of protectin DX in critically ill patients with acute lung injury has the potential to augment lung edema clearance. Our findings reveal a novel mechanism for pulmonary edema fluid reabsorption, and protectin DX may be a new treatment option for the resolution of ARDS.
References
Ware, L. B. & Matthay, M. A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 1334–1349 (2000).
Rubenfeld, G. D. et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 1685–1693 (2005).
Ware, L. B. & Matthay, M. A. Alveolar fluid clearance is impaired in the majority of patients with acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163, 1376–1383 (2001).
Sznajder, J. I. Alveolar edema must be cleared for the acute respiratory distress syndrome patient to survive. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 163, 1293–1294 (2001).
Matthay, M. A., Folkesson, H. G. & Clerici, C. Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary edema. Physiol. Rev. 82, 569–600 (2002).
Matalon, S. & O’Brodovich, H. Sodium channels in alveolar epithelial cells: molecular characterization, biophysical properties, and physiological significance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 61, 627–661 (1999).
Sznajder, J. I., Factor, P. & Ingbar, D. H. Invited review: lung edema clearance: role of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. J. Appl. Physiol. 93, 1860–1866 (2002).
Eckle, T., Grenz, A., Laucher, S. & Eltzschig, H. K. A2B adenosine receptor signaling attenuates acute lung injury by enhancing alveolar fluid clearance in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 3301–3315 (2008).
Deng, J., Wang, D. X., Deng, W., Li, C. Y. & Tong, J. The effect of endogenous angiotensin II on alveolar fluid clearance in rats with acute lung injury. Can. Respir. J. 19, 311–318 (2012).
Bhargava, M. et al. Triiodo-L-thyronine rapidly stimulates alveolar fluid clearance in normal and hyperoxia-injured lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 178, 506–512 (2008).
Qi, D. et al. 17beta-estradiol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through PI3K/Akt/SGK1 mediated up-regulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in vivo and in vitro. Respir. Res. 15, 159 (2014).
Dushianthan, A., Grocott, M. P., Postle, A. D. & Cusack, R. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Postgrad. Med. J. 87, 612–622 (2011).
Perkins, G. D., McAuley, D. F., Thickett, D. R. & Gao, F. The beta-agonist lung injury trial (BALTI): a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 173, 281–287 (2006).
O’Kane, C. M. et al. Salbutamol up-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the alveolar space in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 37, 2242–2249 (2009).
Gao Smith, F. et al. Effect of intravenous beta-2 agonist treatment on clinical outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome (BALTI-2): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 379, 229–235 (2012).
Serhan, C. N. Resolvins and protectins: novel lipid mediators in anti-inflammation and resolution. Food Nutr. Res. 50, 68–78 (2006).
Chen, P. et al. Full characterization of PDX, a neuroprotectin/protectin D1 isomer, which inhibits blood platelet aggregation. FEBS Lett. 583, 3478–3484 (2009).
Serhan, C. N. et al. Anti-inflammatory actions of neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 and its natural stereoisomers: assignments of dihydroxy-containing docosatrienes. J. Immunol. 176, 1848–1859 (2006).
Mas, E., Croft, K. D., Zahra, P., Barden, A. & Mori, T. A. Resolvins D1, D2, and other mediators of self-limited resolution of inflammation in human blood following n-3 fatty acid supplementation. Clin. Chem. 58, 1476–1484 (2012).
Lee, S. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome deficiency protects against microbial sepsis via increased lipoxin B4 synthesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 196, 713–726 (2017).
Mitchell, P. L. et al. Treatment with a novel agent combining docosahexaenoate and metformin increases protectin DX and IL-6 production in skeletal muscle and reduces insulin resistance in obese diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 19, 313–319 (2017).
White, P. J. et al. Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Nat. Med. 20, 664–669 (2014).
Jin, S. W. et al. Posttreatment with aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 analog attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice: the role of heme oxygenase-1. Anesth. Analg. 104, 369–377 (2007).
Wang, Q. et al. Lipoxin A(4) activates alveolar epithelial sodium channel, Na,K-ATPase, and increases alveolar fluid clearance. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 48, 610–618 (2013).
Leland, G. D., Mary, C. W. & Robert, G. Monoclonal antibodies specific to apical surfaces of rat alveolar type I cells bind to surfaces of cultured, but not freshly isolated, type II cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 970, 146–156 (1988).
Jiang, X., Ingbar, D. H. & O’Grady, S. M. Adrenergic regulation of ion transport across adult alveolar epithelial cells: effects on Cl- channel activation and transport function in cultures with an apical air interface. J. Membr. Biol. 181, 195–204 (2001).
Sartori, C. & Matthay, M. A. Alveolar epithelial fluid transport in acute lung injury: new insights. Eur. Respir. J. 20, 1299–1313 (2002).
Shyamsundar, M. et al. Keratinocyte growth factor promotes epithelial survival and resolution in a human model of lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 189, 1520–1529 (2014).
Berthiaume, Y. & Matthay, M. A. Alveolar edema fluid clearance and acute lung injury. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 159, 350–359 (2007).
Guidot, D. M. et al. Integrating acute lung injury and regulation of alveolar fluid clearance. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 291, L301–L306 (2006).
Hummler, E. et al. Early death due to defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 12, 325–328 (1996).
Morty, R. E., Eickelberg, O. & Seeger, W. Alveolar fluid clearance in acute lung injury: what have we learned from animal models and clinical studies? Intensive Care Med. 33, 1229–1240 (2007).
Smith, L. S., Zimmerman, J. J. & Martin, T. R. Mechanisms of acute respiratory distress syndrome in children and adults: a review and suggestions for future research. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 14, 631–643 (2013).
Guazzi, M., Phillips, S. A., Arena, R. & Lavie, C. J. Endothelial dysfunction and lung capillary injury in cardiovascular diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 57, 454–462 (2015).
Deng, B. et al. Maresin biosynthesis and identification of maresin 2, a new anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediator from human macrophages. PLoS ONE 9, e102362 (2014).
Serhan, C. N. Novel lipid mediators and resolution mechanisms in acute inflammation: to resolve or not? Am. J. Pathol. 177, 1576–1591 (2010).
Serhan, C. N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 510, 92–101 (2014).
Krishnamoorthy, S. et al. Resolvin D1 binds human phagocytes with evidence for proresolving receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 1660–1665 (2010).
Serhan, C. N., Chiang, N. & Van Dyke, T. E. Resolving inflammation: dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 349–361 (2008).
Chiang, N. et al. The lipoxin receptor ALX: potent ligand-specific and stereoselective actions in vivo. Pharmacol. Rev. 58, 463–487 (2006).
Thomas, C. P., Campbell, J. R., Wright, P. J. & Husted, R. F. cAMP-stimulated Na+ transport in H441 distal lung epithelial cells: role of PKA, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and sgk1. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 287, L843–L851 (2004).
Lecuona, E. et al. Myosin-Va restrains the trafficking of Na + /K + -ATPase-containing vesicles in alveolar epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 122, 3915–3922 (2009).
Soundararajan, R., Melters, D., Shih, I. C., Wang, J. & Pearce, D. Epithelial sodium channel regulated by differential composition of a signaling complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 7804–7809 (2009).
Deng, W., Li, C. Y., Tong, J., Zhang, W. & Wang, D. X. Regulation of ENaC-mediated alveolar fluid clearance by insulin via PI3K/Akt pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Respir. Res. 13, 29 (2012).
Lee, I. H., Dinudom, A., Sanchez-Perez, A., Kumar, S. & Cook, D. I. Akt mediates the effect of insulin on epithelial sodium channels by inhibiting Nedd4-2. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 29866–29873 (2007).
Mattes, C., Laube, M. & Thome, U. H. Rapid elevation of sodium transport through insulin is mediated by AKT in alveolar cells. Physiol. Rep. 2, e00269 (2014).
Snyder, P. M., Olson, D. R., Kabra, R., Zhou, R. & Steines, J. C. cAMP and serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulate the epithelial Na(+) channel through convergent phosphorylation of Nedd4-2. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 45753–45758 (2004).
Zhou, R. & Snyder, P. M. Nedd4-2 phosphorylation induces serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK) ubiquitination and degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 4518–4523 (2005).
Gille, T. et al. Hypoxia-induced inhibition of epithelial Na(+) channels in the lung. Role of Nedd4-2 and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 50, 526–537 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Hong-Xia Mei, Wang-Ning Shangguan, and Jun Li for technical assistance. This work was sponsored by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81571862, no. 81270132, and no. 81400059) and by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY13H150007, LY14H150011, and LY18H010005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. If you remix, transform, or build upon this article or a part thereof, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuo, XJ., Hao, Y., Cao, F. et al. Protectin DX increases alveolar fluid clearance in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Exp Mol Med 50, 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0075-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0075-4
This article is cited by
-
Protectin DX as a therapeutic strategy against frailty in mice
GeroScience (2023)
-
COVID-19 and cancer: start the resolution!
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2022)
-
Effects of maoto (ma-huang-tang) on host lipid mediator and transcriptome signature in influenza virus infection
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates pulmonary edema through the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) via the PI3K/Akt/Nedd4-2 pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury
Immunologic Research (2021)
-
PCTR1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammation and multiple organ damage via regulation of linoleic acid metabolism by promoting FADS1/FASDS2/ELOV2 expression and reducing PLA2 expression
Laboratory Investigation (2020)