Abstract
Background:
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is highly upregulated in human prostate carcinomas. Inhibition of FASN could arrest cell cycle and trigger apoptosis rapidly, implying the reliance of cancer cell survival on FASN. However, little is known about the effect of C75, a FASN inhibitor, and siFASN (that is, small interfering RNA targeted at FASN) on prostate cancer in living subjects.
Methods:
We used C75 and siFASN to mediate the endogenous fatty acid metabolism in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells stably expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase (HSV1-tk) and luciferase (luc) reporter genes, and assessed the effect of FASN blockade with different schedules of administration on tumor growth using noninvasive molecular imaging.
Results:
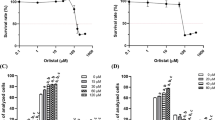
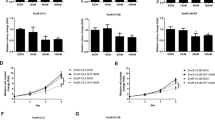
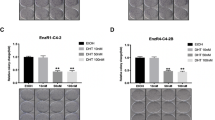
FASN blockade exhibited the proliferative inhibition and induced G1-phase cell cycle arrest of LNCaP cells. For in vivo studies, the tumor growth inhibition by C75 (total 120 mg kg−1; 30 mg kg−1 once a week or 15 mg kg−1 twice a week for 4 weeks) and siFASN (1.4 mg kg−1 every alternate day up to 16 days) treatments were 80% and 70%, respectively, compared with that of the control.
Conclusion:
The results suggest that C75 may be superior to siFASN in anticancer effect on prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuhajda FP . Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: new perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition 2000; 16: 202–208.
Menendez JA, Lupu R . Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 763–777.
Kuhajda FP, Jenner K, Wood FD, Hennigar RA, Jacobs LB, Dick JD et al. Fatty acid synthesis: a potential selective target for antineoplastic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 6379–6383.
Flavin R, Zadra G, Loda M . Metabolic alterations and targeted therapies in prostate cancer. J Pathol 2011; 223: 283–294.
Kuhajda FP . Fatty acid synthase and cancer: new application of an old pathway. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 5977–5980.
Funabashi H, Kawaguchi A, Tomoda H, mura S, Okuda S, Iwasaki S . Binding site of cerulenin in fatty acid synthetase. J Biochem 1989; 5: 751–755.
Lupu R, Menendez JA . Pharmacological inhibitors of fatty acid synthase (FASN)--catalyzed endogenous fatty acid biogenesis: a new family of anti-cancer agents? Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2006; 7: 483–493.
Kuhajda FP, Pizer ES, Li JN, Mani NS, Frehywot GL, Townsend CA . Synthesis and antitumor activity of an inhibitor of fatty acid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3450–3454.
Schrijver ED, Brusselmans K, Heyns W, Verhoeven G, Swinnen JV . RNA interference-mediated silencing of the fatty acid synthase gene attenuates growth and induces morphological changes and apoptosis of LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3799–3804.
Carvalho MA, Zecchin KG, Seguin F, Bastos DC, Agostini M, Rangel AL et al. Fatty acid synthase inhibition with orlistat promotes apoptosis and reduces cell growth and lymph node metastasis in a mouse melanoma model. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 2557–2565.
Orita H, Coulter J, Tully E, Kuhajda FP, Gabrielson E . Inhibiting fatty acid synthase for chemoprevention of chemically induced lung tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 2458–2464.
Chuang HY, Chang YF, Hwang JJ . Antitumor effect of orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, is via activation of caspase-3 on human colorectal carcinoma-bearing animal. Biomed Pharmacother 2011; 65: 286–292.
Chang YF, Lin YY, Wang HE, Liu RS, Pang F, Hwang JJ . Monitoring of tumor growth and metastasis potential in MDA-MB-435s/tk-luc human breast cancer xenografts. Nucl Instrum Meth A 2007; 571: 155–159.
Hochachka PW, Rupert JL, Goldenberg L, Gleave M, Kozlowski P . Going malignant: the hypoxia-cancer connection in the prostate. Bioessays 2002; 24: 749–757.
Nguyen PL, Ma J, Chavarro JE, Freedman ML, Lis R, Fedele G et al. Fatty acid synthase polymorphisms, tumor expression, body mass index, prostate cancer risk, and survival. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3958–3964.
Rossi S, Graner E, Febbo P, Weinstein L, Bhattacharya N, Onody T et al. Fatty acid synthase expression defines distinct molecular signatures in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2003; 1: 707–715.
Migita T, Ruiz S, Fornari A, Fiorentino M, Priolo C, Zadra G et al. Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic enzyme and candidate oncogene in prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009; 101: 519–532.
Jackowski S . Coordination of membrane phospholipid synthesis with the cell cycle. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 3858–3867.
Menendez JA, Vellon L, Colomer R, Lupu R . Pharmacological and small interference RNA-mediated inhibition of breast cancer-associated fatty acid synthase (oncogenic antigen-519) synergistically enhances Taxol (paclitaxel)-induced cytotoxicity. Int J Cancer 2005; 115: 19–35.
Loftus TM, Jaworsky DE, Frehywot GL, Townsend CA, Ronnett GV, Lane MD et al. Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors. Science 2000; 288: 2379–2381.
Massoud TF, Gambhir SS . Molecular imaging in living subjects: seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 545–580.
Vavere AL, Kridel SJ, Wheeler FB, Lewis JS . 1-11C-acetate as a PET radiopharmaceutical for imaging fatty acid synthase expression in prostate cancer. J Nucl Med 2008; 49: 327–334.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the grant 97-2314-B-010-046-MY3 from the National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan. We thank Molecular and Genetic Imaging Core (MAGIC) of the National Research Program for Genomic Medicine, Taiwan, for imaging services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HW., Chang, YF., Chuang, HY. et al. Targeted therapy with fatty acid synthase inhibitors in a human prostate carcinoma LNCaP/tk-luc-bearing animal model. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 15, 260–264 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.15
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.15
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transcending frontiers in prostate cancer: the role of oncometabolites on epigenetic regulation, CSCs, and tumor microenvironment to identify new therapeutic strategies
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2022)
-
A novel metabolic function of Myc in regulation of fatty acid synthesis in prostate cancer
Oncogene (2021)
-
SIK2 enhances synthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol in ovarian cancer cells and tumor growth through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Fatty Acid Inhibition Sensitizes Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Prostate Cancer to Radiotherapy via FASN/NF-κB Pathway
Scientific Reports (2019)