Abstract
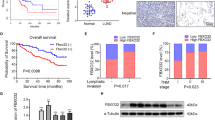
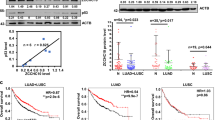
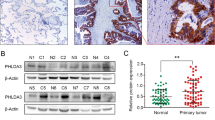
Chromosomal focal amplifications often cause an increase in gene copy number, contributing to the pathogenesis of cancer. PRR14 overexpression is associated with recurrent locus amplification in lung cancer, and it correlates with a poor prognosis. We show that increased PRR14 expression promoted and reduced PRR14 expression impeded lung cancer cell proliferation. Interestingly, PRR14 cells were markedly enlarged in size and exhibited an elevated activity of the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway, which was associated with a heightened sensitivity to the inhibitors of PI3K and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Biochemical analysis revealed that PRR14, as a proline-rich protein, binds to the Src homology 3 (SH3) domains of GRB2 resulting in PI3K activation. Significantly, two cancer patient-derived PRR14 mutants displayed considerably augmented GRB2-binding and an enhanced ability of promoting cell proliferation. Together with the in vivo data demonstrating a strong tumor-promoting activity of PRR14 and the mutants, our work uncovered this proline-rich protein as a novel activator of the PI3K pathway that promoted tumorigenesis in lung cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- DE:
-
Differentially expressed
- GRB2:
-
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LUSC:
-
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
- mTor:
-
mammalian target of rapamycin
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PRR14:
-
Proline-rich protein 14
- SCLC:
-
Small Cell Lung Cancer
- SH2:
-
Src Homology 2
- SH3:
-
Src Homology 3
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 5–29.
Group NM-AC.. Chemotherapy in addition to supportive care improves survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 16 randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4617–4625.
Cheng H, Shcherba M, Pendurti G, Liang Y, Piperdi B, Perez-Soler R . Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: potential for lung cancer treatment. Lung Cancer Manage 2014; 3: 67–75.
Klippel A, Escobedo MA, Wachowicz MS, Apell G, Brown TW, Giedlin MA et al. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is sufficient for cell cycle entry and promotes cellular changes characteristic of oncogenic transformation. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 5699–5711.
Frevert EU, Kahn BB . Differential effects of constitutively active phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase on glucose transport, glycogen synthase activity, and DNA synthesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 190–198.
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennstrom S, Warne PH, Downward J . Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J 1997; 16: 2783–2793.
Kennedy SG, Wagner AJ, Conzen SD, Jordan J, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN et al. The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway delivers an anti-apoptotic signal. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 701–713.
Castellano E, Downward J . RAS interaction with PI3K: more than just another effector pathway. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 261–274.
Chang HW, Aoki M, Fruman D, Auger KR, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN et al. Transformation of chicken cells by the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Science 1997; 276: 1848–1850.
Jimenez C, Jones DR, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Leonardo E, Wennstrom S et al. Identification and characterization of a new oncogene derived from the regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. EMBO J 1998; 17: 743–753.
Meili R, Cron P, Hemmings BA, Ballmer-Hofer K . Protein kinase B/Akt is activated by polyomavirus middle-T antigen via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 1998; 16: 903–907.
Lin X, Bohle AS, Dohrmann P, Leuschner I, Schulz A, Kremer B et al. Overexpression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in human lung cancer. Langenbeck Arch Surg 2001; 386: 293–301.
Massion PP, Taflan PM, Shyr Y, Rahman SM, Yildiz P, Shakthour B et al. Early involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in lung cancer progression. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004; 170: 1088–1094.
Daly RJ, Binder MD, Sutherland RL . Overexpression of the Grb2 gene in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 1994; 9: 2723–2727.
Liu AX, Testa JR, Hamilton TC, Jove R, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ . AKT2, a member of the protein kinase B family, is activated by growth factors, v-Ha-ras, and v-src through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in human ovarian epithelial cancer cells. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 2973–2977.
Wislez M, Spencer ML, Izzo JG, Juroske DM, Balhara K, Cody DD et al. Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin reverses alveolar epithelial neoplasia induced by oncogenic K-ras. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3226–3235.
Job B, Bernheim A, Beau-Faller M, Camilleri-Broet S, Girard P, Hofman P et al. Genomic aberrations in lung adenocarcinoma in never smokers. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15145.
Perez-Llamas C, Lopez-Bigas N . Gitools: analysis and visualisation of genomic data using interactive heat-maps. PLoS One 2011; 6: e19541.
Kamburov A, Stelzl U, Lehrach H, Herwig R . The ConsensusPathDB interaction database: 2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: D793–D800.
Fingar DC, Salama S, Tsou C, Harlow E, Blenis J . Mammalian cell size is controlled by mTOR and its downstream targets S6K1 and 4EBP1/eIF4E. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 1472–1487.
Yang X, Xu T . Molecular mechanism of size control in development and human diseases. Cell Res 2011; 21: 715–729.
Castellano E, Downward J . Role of RAS in the regulation of PI 3-kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2010; 346: 143–169.
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y, Dennis PA . Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3986–3997.
Chardin P, Camonis JH, Gale NW, van Aelst L, Schlessinger J, Wigler MH et al. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science 1993; 260: 1338–1343.
Li N, Batzer A, Daly R, Yajnik V, Skolnik E, Chardin P et al. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature 1993; 363: 85–88.
Shen X, Xi G, Radhakrishnan Y, Clemmons DR . PDK1 recruitment to the SHPS-1 signaling complex enhances insulin-like growth factor-i-stimulated AKT activation and vascular smooth muscle cell survival. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 29416–29424.
Maignan S, Guilloteau JP, Fromage N, Arnoux B, Becquart J, Ducruix A . Crystal structure of the mammalian Grb2 adaptor. Science 1995; 268: 291–293.
Ball LJ, Kuhne R, Schneider-Mergener J, Oschkinat H . Recognition of proline-rich motifs by protein-protein-interaction domains. Angew Chem 2005; 44: 2852–2869.
Kay BK, Williamson MP, Sudol M . The importance of being proline: the interaction of proline-rich motifs in signaling proteins with their cognate domains. FASEB J 2000; 14: 231–241.
Sparks AB, Rider JE, Hoffman NG, Fowlkes DM, Quillam LA, Kay BK . Distinct ligand preferences of Src homology 3 domains from Src, Yes, Abl, Cortactin, p53bp2, PLCgamma, Crk, and Grb2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 1540–1544.
Yu H, Chen JK, Feng S, Dalgarno DC, Brauer AW, Schreiber SL . Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell 1994; 76: 933–945.
Wissmueller S, Font J, Liew CW, Cram E, Schroeder T, Turner J et al. Protein-protein interactions: analysis of a false positive GST pulldown result. Proteins 2011; 79: 2365–2371.
Spoerke JM, O'Brien C, Huw L, Koeppen H, Fridlyand J, Brachmann RK et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway alterations are associated with histologic subtypes and are predictive of sensitivity to PI3K inhibitors in lung cancer preclinical models. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 6771–6783.
Poleshko A, Mansfield KM, Burlingame CC, Andrake MD, Shah NR, Katz RA . The human protein PRR14 tethers heterochromatin to the nuclear lamina during interphase and mitotic exit. Cell Rep 2013; 5: 292–301.
Booker GW, Gout I, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Boyd J, Waterfield MD et al. Solution structure and ligand-binding site of the SH3 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell 1993; 73: 813–822.
Yang YS, Garbay C, Duchesne M, Cornille F, Jullian N, Fromage N et al. Solution structure of GAP SH3 domain by 1H NMR and spatial arrangement of essential Ras signaling-involved sequence. EMBO J 1994; 13: 1270–1279.
Roskoski R Jr . Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 324: 1155–1164.
Guruprasad L, Dhanaraj V, Timm D, Blundell TL, Gout I, Waterfield MD . The crystal structure of the N-terminal SH3 domain of Grb2. J Mol Biol 1995; 248: 856–866.
Lysek DA, Wuthrich K . Prion protein interaction with the C-terminal SH3 domain of Grb2 studied using NMR and optical spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2004; 43: 10393–10399.
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lanczky A . Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 2013; 8: e82241.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to current and former members of the Yuan laboratory for support, advice and helpful discussions. We thank Dr Brendan Manning for reagents. This work was supported in part by the Morningside Foundation, the Zhu Fund and grants from the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (R01CA085679, RO1CA167814 and RO1CA125144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Lewinska, M., Fan, X. et al. PRR14 is a novel activator of the PI3K pathway promoting lung carcinogenesis. Oncogene 35, 5527–5538 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.93
This article is cited by
-
Targeted inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway by (+)-anthrabenzoxocinone induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2024)
-
Preliminary Findings on Proline-Rich Protein 14 as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Parkinson’s Disease
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2021)
-
PRR14L mutations are associated with chromosome 22 acquired uniparental disomy, age-related clonal hematopoiesis and myeloid neoplasia
Leukemia (2019)
-
Identification of multiple risk loci and regulatory mechanisms influencing susceptibility to multiple myeloma
Nature Communications (2018)