Abstract
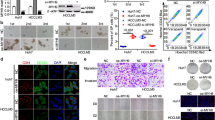
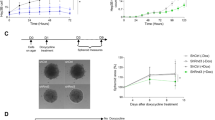
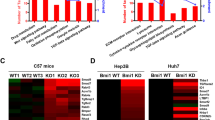
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia 1 and 2 (MKL1/2) are transcriptional coactivators of Serum Response Factor (SRF) with an essential role for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and oncogene-induced senescence. In this report, we identified myoferlin as a novel MKL/SRF target gene by gene expression profiling and verification in vivo in HCC xenografts. Myoferlin was overexpressed in human and murine HCCs triggered by conditional expression of constitutively active SRF-VP16 protein in hepatocytes. Furthermore, myoferlin was required for HCC cell invasion, proliferation and anchorage-independent cell growth. We provide evidence that myoferlin is a crucial gene target of MKL1/2 mediating its effect on oncogene-induced senescence by modulating the activation state of the EGFR and downstream MAPK and p16-/Rb pathways. Depletion of myoferlin in tumour cells from SRF-VP16-derived murine HCCs induced a senescence phenotype. These findings identify MKL1/2 and myoferlin as novel therapeutic targets to treat human HCC by a senescence-inducing strategy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015; 136: E359–E386.
Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX . The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4989–5005.
Xue W, Krasnitz A, Lucito R, Sordella R, Vanaelst L, Cordon-Cardo C et al. DLC1 is a chromosome 8p tumor suppressor whose loss promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 1439–1444.
Yuan BZ, Miller MJ, Keck CL, Zimonjic DB, Thorgeirsson SS, Popescu NC . Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a gene frequently deleted in human liver cancer (DLC-1) homologous to rat RhoGAP. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 2196–2199.
Muehlich S, Hampl V, Khalid S, Singer S, Frank N, Breuhahn K et al. The transcriptional coactivators megakaryoblastic leukemia 1/2 mediate the effects of loss of the tumor suppressor deleted in liver cancer 1. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3913–3923.
Wang DZ, Li S, Hockemeyer D, Sutherland L, Wang Z, Schratt G et al. Potentiation of serum response factor activity by a family of myocardin-related transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 14855–14860.
Cen B, Selvaraj A, Burgess RC, Hitzler JK, Ma Z, Morris SW et al. Megakaryoblastic leukemia 1, a potent transcriptional coactivator for serum response factor (SRF), is required for serum induction of SRF target genes. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 6597–6608.
Esnault C, Stewart A, Gualdrini F, East P, Horswell S, Matthews N et al. Rho-actin signaling to the MRTF coactivators dominates the immediate transcriptional response to serum in fibroblasts. Genes Dev 2014; 28: 943–958.
Johansen FE, Prywes R . Serum response factor: transcriptional regulation of genes induced by growth factors and differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995; 1242: 1–10.
Olson EN, Nordheim A . Linking actin dynamics and gene transcription to drive cellular motile functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 353–365.
Takeda S, North DL, Lakich MM, Russell SD, Whalen RG . A possible regulatory role for conserved promoter motifs in an adult-specific muscle myosin gene from mouse. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 16957–16967.
Treisman R . Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell 1986; 46: 567–574.
Miralles F, Posern G, Zaromytidou AI, Treisman R . Actin dynamics control SRF activity by regulation of its coactivator MAL. Cell 2003; 113: 329–342.
Vartiainen MK, Guettler S, Larijani B, Treisman R . Nuclear actin regulates dynamic subcellular localization and activity of the SRF cofactor MAL. Science 2007; 316: 1749–1752.
Ohrnberger S, Thavamani A, Braeuning A, Lipka DB, Kirilov M, Geffers R et al. Dysregulated serum response factor triggers formation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015; 61: 979–989.
Bai S, Nasser MW, Wang B, Hsu SH, Datta J, Kutay H et al. MicroRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 32015–32027.
Park MY, Kim KR, Park HS, Park BH, Choi HN, Jang KY et al. Expression of the serum response factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol 2007; 31: 1309–1315.
Hampl V, Martin C, Aigner A, Hoebel S, Singer S, Frank N et al. Depletion of the transcriptional coactivators megakaryoblastic leukaemia 1 and 2 abolishes hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft growth by inducing oncogene-induced senescence. EMBO Mol Med 2013; 5: 1367–1382.
Hobel S, Koburger I, John M, Czubayko F, Hadwiger P, Vornlocher HP et al. Polyethylenimine/small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of vascular endothelial growth factor in vivo exerts anti-tumor effects synergistically with Bevacizumab. J Gene Med 2010; 12: 287–300.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 2013; 6: pl1.
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 401–404.
Muehlich S, Cicha I, Garlichs CD, Krueger B, Posern G, Goppelt-Struebe M . Actin-dependent regulation of connective tissue growth factor. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292: C1732–C1738.
Kircher P, Hermanns C, Nossek M, Drexler MK, Grosse R, Fischer M et al. Filamin A interacts with the coactivator MKL1 to promote the activity of the transcription factor SRF and cell migration. Sci Signal 2015; 8: ra112.
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 10202–10212.
Turtoi A, Blomme A, Bellahcene A, Gilles C, Hennequiere V, Peixoto P et al. Myoferlin is a key regulator of EGFR activity in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 5438–5448.
Bae JS, Noh SJ, Kim KM, Jang KY, Chung MJ, Kim DG et al. Serum response factor induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition with resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2014; 44: 129–136.
Kwon CY, Kim KR, Choi HN, Chung MJ, Noh SJ, Kim DG et al. The role of serum response factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for disease progression. Int J Oncol 2010; 37: 837–844.
Medjkane S, Perez-Sanchez C, Gaggioli C, Sahai E, Treisman R . Myocardin-related transcription factors and SRF are required for cytoskeletal dynamics and experimental metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 257–268.
Sun C, Wang L, Huang S, Heynen GJ, Prahallad A, Robert C et al. Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition in melanoma. Nature 2014; 508: 118–122.
Descot A, Hoffmann R, Shaposhnikov D, Reschke M, Ullrich A, Posern G . Negative regulation of the EGFR-MAPK cascade by actin-MAL-mediated Mig6/Errfi-1 induction. Mol Cell 2009; 35: 291–304.
Reschke M, Ferby I, Stepniak E, Seitzer N, Horst D, Wagner EF et al. Mitogen-inducible gene-6 is a negative regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in hepatocytes and human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010; 51: 1383–1390.
Giehl K, Keller C, Muehlich S, Goppelt-Struebe M . Actin-mediated gene expression depends on RhoA and Rac1 signaling in proximal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0121589.
Winkler J, Ori A, Holzer K, Sticht C, Dauch D, Eiteneuer EM et al. Prosurvival function of the cellular apoptosis susceptibility/importin-alpha1 transport cycle is repressed by p53 in liver cancer. Hepatology 2014; 60: 884–895.
Acknowledgements
We thank Elizabeth McNally and Alexis Demonbreun for the myoferlin promoter construct, and Veronika Geissler and Esther Herpel from the NCT tissue bank in Heidelberg for their support. Funded by grant MU 2737/2-2 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Alfred Nordheim was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe (grant 109886) and DKTK (German Cancer Consortium). Stephan Singer was supported by DFG (grant Si 1487/3-1), and by an HRCMM (Heidelberg Research Center for Molecular Medicine) Career Development Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermanns, C., Hampl, V., Holzer, K. et al. The novel MKL target gene myoferlin modulates expansion and senescence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 36, 3464–3476 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.496
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.496
This article is cited by
-
LPA receptor 1 (LPAR1) is a novel interaction partner of Filamin A that promotes Filamin A phosphorylation, MRTF-A transcriptional activity and oncogene-induced senescence
Oncogenesis (2022)
-
MKL1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis via the COMPASS complex and NF-κB signaling
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
SLC38A4 functions as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulating Wnt/β-catenin/MYC/HMGCS2 axis
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
Epigenetic activation of the small GTPase TCL contributes to colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
Inhibition of TRPM7 blocks MRTF/SRF-dependent transcriptional and tumorigenic activity
Oncogene (2020)