Abstract
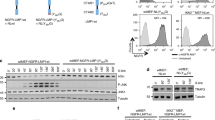
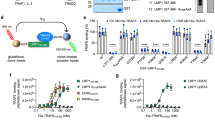
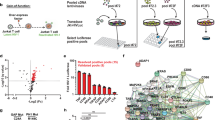
Interferon (IFN) regulatory factors (IRFs) have crucial roles in immune regulation and oncogenesis. We have recently shown that IRF4 is activated through c-Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation in virus-transformed cells. However, the intracellular signaling pathway triggering Src activation of IRF4 remains unknown. In this study, we provide evidence that Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) promotes IRF4 phosphorylation and markedly stimulates IRF4 transcriptional activity, and that Src mediates LMP1 activation of IRF4. As to more precise mechanism, we show that LMP1 physically interacts with c-Src, and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) subunit P85 mediates their interaction. Depletion of P85 by P85-specific short hairpin RNAs disrupts their interaction and diminishes IRF4 phosphorylation in EBV-transformed cells. Furthermore, we show that Src is upstream of PI3K for activation of both IRF4 and Akt. In turn, inhibition of PI3K kinase activity by the PI3K-speicfic inhibitor LY294002 impairs Src activity. Our results show that LMP1 signaling is responsible for IRF4 activation, and further characterize the IRF4 regulatory network that is a promising therapeutic target for specific hematological malignancies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boshoff C, Weiss R . Aids-related malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 373–382.
Carbone A, Gloghini A, Dotti G . EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: classification and treatment. Oncologist 2008; 13: 577–585.
Pagano JS, Blaser M, Buendia MA, Damania B, Khalili K, Raab-Traub N et al. Infectious agents and cancer: criteria for a causal relation. Semin Cancer Biol 2004; 14: 453–471.
Saddawi-Konefka R, Crawford JR . Chronic viral infection and primary central nervous system malignancy. J Neuroimmun Pharmacol 2010; 5: 387–403.
Ning S, Pagano J, Barber G . IRF7: activation, regulation, modification, and function. Genes Immun 2011; 12: 399–414.
Wang L, Toomey NL, Diaz LA, Walker G, Ramos JC, Barber GN et al. Oncogenic IRFs provide a survival advantage for EBV- or HTLV1-transformed cells through induction of BIC expression. J Virol 2011; 85: 8328–8337.
Thornburg NJ, Kulwichit W, Edwards RH, Shair KHY, Bendt KM, Raab-Traub N . LMP1 signaling and activation of NF-kappaB in LMP1 transgenic mice. Oncogene 2006; 25: 288–297.
Kieser A . Signal transduction by the Epstein-Barr virus oncogene latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). Signal Transduction 2007; 7: 20–33.
Li HP, Chang YS . Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1: structure and functions. J Biomed Sci 2003; 10: 490–504.
Middeldorp JM, Pegtel DM . Multiple roles of LMP1 in Epstein-Barr virus induced immune escape. Semin Cancer Biol 2008; 18: 388–396.
Soni V, Cahir-McFarland E, Kieff E . LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways. In: Wu H (ed). Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology vol. 597. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007, pp 173–187.
Huye LE, Ning S, Kelliher M, Pagano JS . IRF7 is activated by a viral oncoprotein through RIP-dependent ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 2910–2918.
Ning S, Campos AD, Darnay B, Bentz G, Pagano JS . TRAF6 and the three C-terminal lysine sites on IRF7 are required for its ubiquitination-mediated activation by the tumor necrosis factor receptor family member latent membrane protein 1. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 6536–6546.
Zhang L, Zhang J, Lambert Q, Der CJ, Del Valle L, Miklossy J et al. Interferon regulatory factor 7 is associated with Epstein-Barr virus-transformed central nervous system lymphoma and has oncogenic properties. J Virol 2004; 78: 12987–12995.
Cahir-McFarland ED, Carter K, Rosenwald A, Giltnane JM, Henrickson SE, Staudt LM et al. Role of NF- k B in cell survival and transcription of latent membrane protein 1-expressing or Epstein-Barr Virus latency III-infected cells. J Virol 2004; 78: 4108–4119.
Martin HJ, Lee JM, Walls D, Hayward SD . Manipulation of the Toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 2007; 81: 9748–9758.
Spender LC, Lucchesi W, Bodelon G, Bilancio A, Karstegl CE, Asano T et al. Cell target genes of Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor EBNA-2: induction of the p55á regulatory subunit of PI3-kinase and its role in survival of EREB2.5 cells. J Gen Virol 2006; 87: 2859–2867.
Xu D, Zhao L, Del Valle L, Miklossy J, Zhang L . Interferon regulatory factors 4 is involved in Epstein-Barr virus-mediated transformation of human B lymphocytes. J Virol 2008; 82: 6251–6258.
Iida S, Rao PH, Butler M, Corradini P, Boccadoro M, Klein B et al. Deregulation of MUM1/IRF4 by chromosomal translocation in multiple myeloma. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 226–230.
Shaffer AL, Emre NCT, Lamy L, Ngo VN, Wright G, Xiao W et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature 2008; 454: 226–231.
Grandvaux N, Servant MJ, tenOever BR, Sen GC, Balachandran S, Barber GN et al. Transcriptional profiling of interferon regulatory factor 3 target genes: direct involvement in the regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. J Virol 2002; 76: 5532–5539.
Mamane Y, Sharma S, Grandvaux N, Hernandez E, Hiscott J . IRF-4 activities in HTLV-I-induced T cell leukemogenesis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2002; 22: 135–143.
Ramos JC, Ruiz Jr P, Ratner L, Reis IM, Brites C, Pedroso C et al. IRF4 and c-Rel expression in antiviral-resistant adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2007; 109: 3060–3068.
Sharma S, Grandvaux N, Mamane Y, Genin P, Azimi N, Waldmann T et al. Regulation of IFN regulatory factor 4 expression in human T cell leukemia virus-I-transformed T cells. J Immunol 2002; 169: 3120–3130.
Banerjee S, Lu J, Cai Q, Saha A, Jha HC, Dzeng RK et al. The EBV latent antigen 3C inhibits apoptosis through targeted regulation of interferon regulatory factors 4 and 8. PLoS Pathog 2013; 9: e1003314.
Rui L, Schmitz R, Ceribelli M, Staudt LM . Malignant pirates of the immune system. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 933–940.
Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Romesser PB, Staudt LM . IRF4: immunity. malignancy! therapy? Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2954–2961.
Feldman AL, Law M, Remstein ED, Macon WR, Erickson LA, Grogg KL et al. Recurrent translocations involving the IRF4 oncogene locus in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2009; 23: 574–580.
Havelange V, Pekarsky Y, Nakamura T, Palamarchuk A, Alder H, Rassenti L et al. IRF4 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011; 118: 2827–2829.
Zhang B, Kracker S, Yasuda T, Casola S, Vanneman M, Homig-Holzel C et al. Immune surveillance and therapy of lymphomas driven by Epstein-Barr Virus protein LMP1 in a mouse model. Cell 2012; 148: 739–751.
Chang CC, Lorek J, Sabath DE, Li Y, Chitambar CR, Logan B et al. Expression of MUM1/IRF4 correlates with clinical outcome in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 4671–4675.
Ning S . IRF4 as an oncogenic biomarker for hematological malignancies. J Oncobiomarkers 2013; 1: 6.
Sundram U, Harvell JD, Rouse RV, Natkunam Y . Expression of the B-cell proliferation marker MUM1 by melanocytic lesions and comparison with S100, gp100 (HMB45), and MelanA. Mod Pathol 2003; 16: 802–810.
Biswas PS, Bhagat G, Pernis AB . IRF4 and its regulators: evolving insights into the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis? Immunol Rev 2010; 233: 79–96.
Wang L, Yao ZQ, Moorman JP, Xu Y, Ning S . Gene expression profiling identifies IRF4-associated molecular signatures in hematological malignancies. PLoS One 2014; 9: e106788.
Wang L, Ning S . IRF4 is activated through c-Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation in virus-transformed cells. J Virol 2013; 87: 9672–9679.
Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE . The role of Src in solid and hematologic malignancies. Cancer 2006; 107: 1918–1929.
Bloss T, Kaykas A, Sugden B . Dissociation of patching by latent membrane protein-1 of Epstein-Barr virus from its stimulation of NF-kappaB activity. J Gen Virol 1999; 80: 3227–3232.
Dawson CW, Tramountanis G, Eliopolous AG, Young LS . Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to promote cell survival and induce actin filament remodeling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 3694–3704.
Pleiman C, Hertz W, Cambier J . Activation of phosphatidylinositol-3' kinase by Src-family kinase SH3 binding to the p85 subunit. Science 1994; 263: 1609–1612.
Arron JR, Vologodskaia M, Wong BR, Naramura M, Kim N, Gu H et al. A positive regulatory role for Cbl family proteins in tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE) and CD40L-mediated Akt activation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 30011–30017.
Wong BR, Besser D, Kim N, Arron JR, Vologodskaia M, Hanafusa H et al. TRANCE, a TNF family member, activates Akt/PKB through a signaling complex involving TRAF6 and c-Src. Mol Cell 1999; 4: 1041–1049.
Hatton O, Lambert SL, Krams SM, Martinez OM . Src kinase and Syk activation initiate PI3K signaling by a chimeric latent membrane protein 1 in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+ B cell lymphomas. PLoS One 2012; 7: e42610.
Davies CC, Mak TW, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG . TRAF6 is required for TRAF2-dependent CD40 signal transduction in nonhemopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 9806–9819.
Deregibus MC, Buttiglieri S, Russo S, Bussolati B, Camussi G . CD40-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway mediates endothelial cell survival and in vitro angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 18008–18014.
So T, Choi H, Croft M . OX40 complexes with phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase B (PKB) to augment TCR-dependent PKB signaling. J Immunol 2011; 186: 3547–3555.
Dawson CW, Port RJ, Young LS . The role of the EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins LMP1 and LMP2 in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Semin Cancer Biol 2012; 22: 144–153.
Kieser A, Sterz KR The latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). In: Münz C (ed). Epstein Barr Virus Volume 2: One Herpes Virus: Many Diseases. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015, pp 119–149.
Stunz LL, Bishop GA . Latent membrane protein 1 and the B lymphocyte-A complex relationship. Crit Rev Immunol 2014; 34: 177–198.
Gu TL, Cherry J, Tucker M, Wu J, Reeves C, Polakiewicz RD . Identification of activated Tnk1 kinase in Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leukemia 2010; 24: 861–865.
St-Germain JR, Taylor P, Tong J, Jin LL, Nikolic A, Stewart II et al. Multiple myeloma phosphotyrosine proteomic profile associated with FGFR3 expression, ligand activation, and drug inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 20127–20132.
Fukuda M, Longnecker R . Latent membrane protein 2 A inhibits transforming growth factor-á1-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Virol 2004; 78: 1697–1705.
Portis T, Longnecker R . Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP2 A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras//PI3K//Akt pathway. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8619–8628.
Scholle F, Bendt KM, Raab-Traub N . Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A transforms epithelial cells, inhibits cell differentiation, and activates Akt. J Virol 2000; 74: 10681–10689.
Swart R, Ruf IK, Sample J, Longnecker R . Latent membrane protein 2A-mediated effects on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Virol 2000; 74: 10838–10845.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an NIH NIDDK grant to ZQY/JPM (R01DK093526), an NIH NIAID grant to ZQY/JPM (R01AI114748), the American Society of Hematology Scholar Award to SN, and in part by the NIH grant C06RR0306551. We thank Dr Bill Sugden for providing pSV2-LMP1 and its deletion mutant pSV2-LMP1Δ(12-20). This publication is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the James H Quillen Veterans Affairs Medical Center. The contents in this publication do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Ren, J., Li, G. et al. LMP1 signaling pathway activates IRF4 in latent EBV infection and a positive circuit between PI3K and Src is required. Oncogene 36, 2265–2274 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.380
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.380
This article is cited by
-
Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Dasatinib exacerbates splenomegaly of mice inoculated with Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphoblastoid cell lines
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The regulatory role of protein phosphorylation in human gammaherpesvirus associated cancers
Virologica Sinica (2017)