Abstract
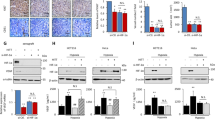
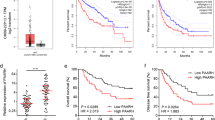
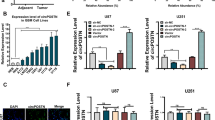
Angiogenesis is one of the critical biological elements affecting the development and progression of cancer. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are important regulators and aberrantly expressed in various types of human cancer. Our previous studies indicated that lncRNA taurine upregulated 1 (TUG1) implicated in the regulation of blood-tumor barrier permeability; however, its role in glioblastoma angiogenesis still unclear. Here we demonstrated that TUG1 was up-expressed in human glioblastoma tissues and glioblastoma cell lines. Knockdown of TUG1 remarkably suppressed tumor-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube formation as well as reducing spheroid-based angiogenesis ability in vitro, which are the critical steps for tumor angiogenesis. Besides, knockdown of TUG1 significantly increased the expression of mircroRNA-299 (miR-299), which was down-expressed in glioblastoma tissues and glioblastoma cell lines. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay revealed that TUG1 influenced tumor angiogenesis via directly binding to the miR-299 and there was a reciprocal repression between TUG1 and miR-299 in the same RNA-induced silencing complex. Moreover, knockdown of TUG1 reduced the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), which was defined as a functional downstream target of miR-299. In addition, knockdown of TUG1, shown in the in vivo studies, has effects on suppressing tumor growth, reducing tumor microvessel density and decreasing the VEGFA expression by upregulating miR-299 in xenograft glioblastoma model. Overall, the results demonstrated that TUG1 enhances tumor-induced angiogenesis and VEGF expression through inhibiting miR-299. Also, the inhibition of TUG1 could provide a novel therapeutic target for glioblastoma treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ . Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 166–193.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 2007; 114: 97–109.
Bai RY, Staedtke V, Riggins GJ . Molecular targeting of glioblastoma: drug discovery and therapies. Trends Mol Med 2011; 17: 301–312.
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT . Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007; 8: 610–622.
Folkerth RD . Descriptive analysis and quantification of angiogenesis in human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 2000; 50: 165–172.
Jouanneau E . Angiogenesis and gliomas: current issues and development of surrogate markers. Neurosurgery 2008; 62: 31–50.
Chi AS, Sorensen AG, Jain RK, Batchelor TT . Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in malignant gliomas. Oncologist 2009; 14: 621–636.
Kerbel R, Folkman J . Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 727–739.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM . The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 391–407.
Batista PJ, Chang HY . Long noncoding RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013; 152: 1298–1307.
Wang KC, Chang HY . Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 904–914.
Wang L, Shi ZM, Jiang CF, Liu X, Chen QD, Qian X et al. MiR-143 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting N-RAS and enhances temozolomide-induced apoptosis in glioma. Oncotarget 2014; 5: 5416–5427.
Shi Z, Chen Q, Li C, Wang L, Qian X, Jiang C et al. MiR-124 governs glioma growth and angiogenesis and enhances chemosensitivity by targeting R-Ras and N-Ras. Neuro Oncol 2014; 16: 1341–1353.
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M . Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 34: 9–14.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP . The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014; 505: 344–352.
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP . A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011; 146: 353–358.
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M et al. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011; 147: 358–369.
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB, Yin DD et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 92.
Rapicavoli NA, Blackshaw S . New meaning in the message: noncoding RNAs and their role in retinal development. Dev Dyn 2009; 238: 2103–2114.
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP, Yao J . Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2013; 14: 2311–2315.
Han Y, Liu Y, Gui Y, Cai Z . Long intergenic non-coding RNA TUG1 is overexpressed in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. J Surg Oncol 2013; 107: 555–559.
Xu Y, Wang J, Qiu M, Xu L, Li M, Jiang F et al. Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol 2014; 36: 1643–1651.
Cai H, Xue Y, Wang P, Wang Z, Li Z, Hu Y et al. The long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability by targeting miR-144. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 19759–19779.
Wurdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J, Grau S, Soutschek J et al. miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 382–393.
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y et al. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38: 5366–5383.
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N, Nuovo G, Costinean S et al. microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4750–4756.
Jiang X, Yan Y, Hu M, Chen X, Wang Y, Dai Y et al. Increased level of H19 long noncoding RNA promotes invasion, angiogenesis, and stemness of glioblastoma cells. J Neurosurg 2016; 124: 129–136.
Wang P, Liu YH, Yao YL, Li Z, Li ZQ, Ma J et al. Long non-coding RNA CASC2 suppresses malignancy in human gliomas by miR-21. Cell Signal 2014; 27: 275–282.
Ke J, Yao YL, Zheng J, Wang P, Liu YH, Ma J et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits malignant biological behaviors of human glioma cells via modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 21934–21949.
Zhou Y, Zhang X, Klibanski A . MEG3 noncoding RNA: a tumor suppressor. J Mol Endocrinol 2012; 48: R45–R53.
Young TL, Matsuda T, Cepko CL . The noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 501–512.
Isin M, Ozgur E, Cetin G, Erten N, Aktan M, Gezer U et al. Investigation of circulating lncRNAs in B-cell neoplasms. Clin Chim Acta 2014; 431: 255–259.
Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, Kong R, Liu XH, You LH et al. P53-regulated long non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7 expression. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1243.
Liu Q, Sun S, Yu W, Jiang J, Zhuo F, Qiu G et al. Altered expression of long non-coding RNAs during genotoxic stress-induced cell death in human glioma cells. J Neurooncol 2015; 122: 283–292.
Saharinen P, Eklund L, Pulkki K, Bono P, Alitalo K . VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Trends Mol Med 2011; 17: 347–362.
Azoitei N, Pusapati GV, Kleger A, Moller P, Kufer R, Genze F et al. Protein kinase D2 is a crucial regulator of tumour cell-endothelial cell communication in gastrointestinal tumours. Gut 2010; 59: 1316–1330.
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB et al. Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7843–7848.
Tate MC, Aghi MK . Biology of angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Neurotherapeutics 2009; 6: 447–457.
Jiao F, Hu H, Han T, Yuan C, Wang L, Jin Z et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 enhances stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 16: 6677–6693.
Wang K, Long B, Zhou LY, Liu F, Zhou QY, Liu CY et al. CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 3596.
Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J, Yan L et al. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell 2013; 52: 101–112.
Han X, Yang F, Cao H, Liang Z . Malat1 regulates serum response factor through miR-133 as a competing endogenous RNA in myogenesis. FASEB J 2015; 29: 3054–3064.
Kobayashi H, Tomari Y . RISC assembly: coordination between small RNAs and Argonaute proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1859: 71–81.
Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Watabe K, Zhang X, Bai C, Xu M et al. Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21. Cell Death Differ 2013; 20: 1558–1568.
Shevde LA, Metge BJ, Mitra A, Xi Y, Ju J, King JA et al. Spheroid-forming subpopulation of breast cancer cells demonstrates vasculogenic mimicry via hsa-miR-299-5p regulated de novo expression of osteopontin. J Cell Mol Med 2010; 14: 1693–1706.
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano D, Finazzi-Agro' E, Levine AJ et al. MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c, miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p, mapped to the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2014; 33: 5173–5182.
Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995; 1: 27–31.
Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG . The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol 2005; 7: 122–133.
Dunn IF, Heese O, Black PM . Growth factors in glioma angiogenesis: FGFs, PDGF, EGF, and TGFs. J Neurooncol 2000; 50: 121–137.
Ezhilarasan R, Mohanam I, Govindarajan K, Mohanam S . Glioma cells suppress hypoxia-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and promote the angiogenic process. Int J Oncol 2007; 30: 701–707.
Jafarifar F, Yao P, Eswarappa SM, Fox PL . Repression of VEGFA by CA-rich element-binding microRNAs is modulated by hnRNP L. EMBO J 2011; 30: 1324–1334.
Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, Mione M, Koyanagi M, Fischer A et al. MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science 2009; 324: 1710–1713.
Leon SP, Folkerth RD, Black PM . Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 1996; 77: 362–372.
Gaiser T, Becker MR, Meyer J, Habel A, Siegelin MD . p53-mediated inhibition of angiogenesis in diffuse low-grade astrocytomas. Neurochem Int 2009; 54: 458–463.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81172197, 81272564, 81272795, 81372484 and 81573010) and Shenyang Science and Technology Plan Projects (nos F15-199-1-30 and F15-199-1-57), and outstanding scientific fund of Shengjing hospital (no. 201304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Liu, X., Zheng, J. et al. Long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated 1 enhances tumor-induced angiogenesis through inhibiting microRNA-299 in human glioblastoma. Oncogene 36, 318–331 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.212
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.212
This article is cited by
-
The role of long noncoding RNAs in ocular angiogenesis and vascular oculopathy
Cell & Bioscience (2024)
-
Crosstalk between long noncoding RNA and microRNA in Cancer
Cellular Oncology (2023)
-
CircSCAP interacts with SF3A3 to inhibit the malignance of non-small cell lung cancer by activating p53 signaling
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
Non-coding RNAs in the regulation of blood–brain barrier functions in central nervous system disorders
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
Transcriptome-wide analysis of glioma stem cell specific m6A modifications in long-non-coding RNAs
Scientific Reports (2022)