Abstract
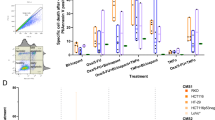
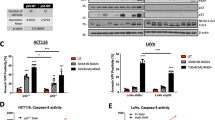
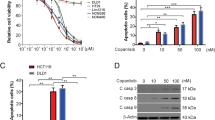
Resistance towards the drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a key challenge in the adjuvant chemotherapy of colorectal cancer (CRC), and novel targeted approaches are required to improve the therapeutic outcome. Necroptosis is a recently discovered form of programmed cell death, which depends on receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1) and particularly occurs under caspase-deficient conditions. The targeted induction of necroptosis represents a promising strategy to overcome apoptosis resistance in cancer. The aim of this study was to systematically explore the usage of pan-caspase inhibitors to sensitize resistant CRC cells for 5-FU. We found that pan-caspase inhibitors facilitated 5-FU-induced necroptosis, which was mediated by autocrine secretion of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α). TNF-α production was driven by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and required RIP1 kinase. In vivo xenograft experiments showed that the novel pan-caspase inhibitor IDN-7314 in combination with 5-FU synergistically blocked tumor growth. Ex vivo experiments with fresh human CRC tissue specimens further indicated that a subgroup of patients could benefit from combinatory treatment. Thereby, elevated levels of secreted TNF-α and expression of components of the necroptotic pathway might help to predict the sensitivity to pro-necroptotic therapies. Together, our results shed new light on the molecular regulation of necroptosis by NF-κB and RIP1. Moreover, we identify necroptotic cell death as an important effector mechanism of 5-FU-mediated anti-tumoral activity. On the basis of this study, we propose pan-caspase inhibitors as a novel approach in the adjuvant chemotherapy of CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2014; 136: E359–E386.
Hagan S, Orr MC, Doyle B . Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer-an integrative view by PPPM. EPMA J 2013; 4: 3.
Marshall JL, Haller DG, de Gramont A, Hochster HS, Lenz HJ, Ajani JA et al. Adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: Consensus Report of the International Society of Gastrointestinal Oncology. Gastrointest Cancer Res 2007; 1: 146–154.
Tournigand C, Andre T, Achille E, Lledo G, Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D et al. FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 229–237.
Douillard JY, Sobrero A, Carnaghi C, Comella P, Diaz-Rubio E, Santoro A et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: integrating irinotecan into combination and sequential chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 2003; 14: ii7–12.
Wilson PM, Ladner RD, Lenz HJ . Predictive and prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res 2007; 1: 237–246.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Cooks T, Pateras IS, Tarcic O, Solomon H, Schetter AJ, Wilder S et al. Mutant p53 prolongs NF-kappaB activation and promotes chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 634–646.
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH et al. Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ 2009 16: 3–11.
Kreuzaler P, Watson CJ . Killing a cancer: what are the alternatives? Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 411–424.
Zhou W, Yuan J . Necroptosis in health and diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 35: 14–23.
Christofferson DE, Li Y, Yuan J . Control of life-or-death decisions by RIP1 kinase. Annu Rev Physiol 2014; 76: 129–150.
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en IL, Korkina O, Teng X et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 2008; 4: 313–321.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003; 114: 181–190.
Darding M, Meier P . IAPs: guardians of RIPK1. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: 58–66.
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G . Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 700–714.
Hitomi J, Christofferson DE, Ng A, Yao J, Degterev A, Xavier RJ et al. Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell 2008; 135: 1311–1323.
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 2009; 137: 1100–1111.
Laukens B, Jennewein C, Schenk B, Vanlangenakker N, Schier A, Cristofanon S et al. Smac mimetic bypasses apoptosis resistance in FADD- or caspase-8-deficient cells by priming for tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced necroptosis. Neoplasia 2011; 13: 971–979.
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 2012; 148: 213–227.
Kaiser WJ, Sridharan H, Huang C, Mandal P, Upton JW, Gough PJ et al. Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 31268–31279.
Tenev T, Bianchi K, Darding M, Broemer M, Langlais C, Wallberg F et al. The Ripoptosome, a signaling platform that assembles in response to genotoxic stress and loss of IAPs. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 432–448.
Feoktistova M, Geserick P, Kellert B, Dimitrova DP, Langlais C, Hupe M et al. cIAPs block ripoptosome formation, a RIP1/caspase-8 containing intracellular cell death complex differentially regulated by cFLIP isoforms. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 449–463.
Biton S, Ashkenazi A . NEMO and RIP1 control cell fate in response to extensive DNA damage via TNF-alpha feedforward signaling. Cell 2011; 145: 92–103.
Christofferson DE, Li Y, Hitomi J, Zhou W, Upperman C, Zhu H et al. A novel role for RIP1 kinase in mediating TNFalpha production. Cell Death Dis 2012; 3: e320.
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Riquet F, Duprez L, Vanden Berghe T, Takahashi N, Vandenabeele P . Necroptosis, in vivo detection in experimental disease models. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 35: 2–13.
Wang W, Cassidy J, O'Brien V, Ryan KM, Collie-Duguid E . Mechanistic and predictive profiling of 5-Fluorouracil resistance in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 8167–8176.
Fulda S . Therapeutic exploitation of necroptosis for cancer therapy. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 35: 51–56.
Han W, Li L, Qiu S, Lu Q, Pan Q, Gu Y et al. Shikonin circumvents cancer drug resistance by induction of a necroptotic death. Mol Cancer Ther 2007; 6: 1641–1649.
Grassilli E, Narloch R, Federzoni E, Ianzano L, Pisano F, Giovannoni R et al. Inhibition of GSK3B bypass drug resistance of p53-null colon carcinomas by enabling necroptosis in response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 3820–3831.
Steinhart L, Belz K, Fulda S . Smac mimetic and demethylating agents synergistically trigger cell death in acute myeloid leukemia cells and overcome apoptosis resistance by inducing necroptosis. Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e802.
Dunai ZA, Imre G, Barna G, Korcsmaros T, Petak I, Bauer PI et al. Staurosporine induces necroptotic cell death under caspase-compromised conditions in U937 cells. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e41945.
Lin Y, Devin A, Rodriguez Y, Liu ZG . Cleavage of the death domain kinase RIP by caspase prompts TNF-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 2514–2526.
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007; 131: 669–681.
Festjens N, Berghe TV, Cornelis S, Vandenabeele P . RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 400–410.
Lamkanfi M, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P . Caspases leave the beaten track: caspase-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 165–171.
Chaudhary PM, Eby MT, Jasmin A, Kumar A, Liu L, Hood L . Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by caspase 8 and its homologs. Oncogene 2000; 19: 4451–4460.
Shikama Y, Yamada M, Miyashita T . Caspase-8 and caspase-10 activate NF-kappaB through RIP, NIK and IKKalpha kinases. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 1998–2006.
Staal J, Bekaert T, Beyaert R . Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by caspases and MALT1 paracaspase. Cell Res 2011; 21: 40–54.
McComb S, Shutinoski B, Thurston S, Cessford E, Kumar K, Sad S . Cathepsins limit macrophage necroptosis through cleavage of Rip1 kinase. J Immunol 2014; 192: 5671–5678.
Zhang L, Blackwell K, Workman LM, Chen S, Pope MR, Janz S et al. RIP1 cleavage in the kinase domain regulates TRAIL-induced NF-kappaB activation and lymphoma survival. Mol Cell Biol 2015; 35: 3324–3338.
Probst BL, Liu L, Ramesh V, Li L, Sun H, Minna JD et al. Smac mimetics increase cancer cell response to chemotherapeutics in a TNF-alpha-dependent manner. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 1645–1654.
Moretti L, Kim KW, Jung DK, Willey CD, Lu B . Radiosensitization of solid tumors by Z-VAD, a pan-caspase inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 1270–1279.
Linton SD, Aja T, Armstrong RA, Bai X, Chen LS, Chen N et al. First-in-class pan caspase inhibitor developed for the treatment of liver disease. J Med Chem 2005; 48: 6779–6782.
Shiffman ML, Pockros P, McHutchison JG, Schiff ER, Morris M, Burgess G . Clinical trial: the efficacy and safety of oral PF-03491390, a pancaspase inhibitor - a randomized placebo-controlled study in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010; 31: 969–978.
Vanden Berghe T, Grootjans S, Goossens V, Dondelinger Y, Krysko DV, Takahashi N et al. Determination of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in vitro and in vivo. Methods 2013; 61: 117–129.
Fuchs D, Metzig M, Bickeboller M, Brandel C, Roth W . The Gbeta5 protein regulates sensitivity to TRAIL-induced cell death in colon carcinoma. Oncogene 2014; 34: 2753–2763.
Fassl A, Tagscherer KE, Richter J, Berriel Diaz M, Alcantara Llaguno SR, Campos B et al. Notch1 signaling promotes survival of glioblastoma cells via EGFR-mediated induction of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1. Oncogene 2012; 31: 4698–4708.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Marina Gernold, Martina Keith, Katarina Duglova and Scott Oliver for excellent technical assistance. We thank Sylvia Kaden for technical assistance during electron microscopy. We thank the tissue bank of the Center for National Tumor Disease (NCT, Heidelberg, Germany) for providing CRC tissues, and Sarah Meßnard and David Jansen for technical assistance during immunohistochemistry. This study was supported by a grant from the Manfred-Stolte-Foundation to WR, and by the Rahel Goitein-Straus Program of the Medical Faculty of Heidelberg (fellowship to MOM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver Metzig, M., Fuchs, D., Tagscherer, K. et al. Inhibition of caspases primes colon cancer cells for 5-fluorouracil-induced TNF-α-dependent necroptosis driven by RIP1 kinase and NF-κB. Oncogene 35, 3399–3409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.398
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.398
This article is cited by
-
TNFα-induced IDH1 hyperacetylation reprograms redox homeostasis and promotes the chemotherapeutic sensitivity
Oncogene (2023)
-
Pan-cancer analysis of cuproptosis-promoting gene signature from multiple perspectives
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2023)
-
Rubiarbonol B induces RIPK1-dependent necroptosis via NOX1-derived ROS production
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2023)
-
Colon tumour cell death causes mTOR dependence by paracrine P2X4 stimulation
Nature (2022)
-
Pan-cancer analysis of necroptosis-related gene signature for the identification of prognosis and immune significance
Discover Oncology (2022)