Abstract
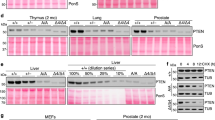
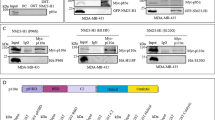
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), which negatively regulates tumorigenic phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) signaling, is a commonly mutated tumor suppressor. The majority of cancer-associated PTEN mutations block its essential PIP3 phosphatase activity. However, there is a group of clinically identified PTEN mutations that maintain enzymatic activity, and it is unknown how these mutations contribute to tumor pathogenesis. Here, we show that these enzymatically competent PTEN mutants fail to translocate to the plasma membrane where PTEN converts PIP3 to PI(4,5)P2. Artificial membrane tethering of the PTEN mutants effectively restores tumor suppressor activity and represses excess PIP3 signaling in cells. Thus, our findings reveal a novel mechanism of tumorigenic PTEN deficiency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chalhoub N, Baker SJ . PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2009; 4: 127–150.
Ali IU, Schriml LM, Dean M . Mutational spectra of PTEN/MMAC1 gene: a tumor suppressor with lipid phosphatase activity. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999; 91: 1922–1932.
Tan MH, Mester JL, Ngeow J, Rybicki LA, Orloff MS, Eng C . Lifetime cancer risks in individuals with germline PTEN mutations. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 400–407.
Hollander MC, Blumenthal GM, Dennis PA . PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 289–301.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP . The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 283–296.
Leslie NR, Batty IH, Maccario H, Davidson L, Downes CP . Understanding PTEN regulation: PIP2, polarity and protein stability. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5464–5476.
Denning G, Jean-Joseph B, Prince C, Durden DL, Vogt PK . A short N-terminal sequence of PTEN controls cytoplasmic localization and is required for suppression of cell growth. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3930–3940.
Han SY, Kato H, Kato S, Suzuki T, Shibata H, Ishii S et al. Functional evaluation of PTEN missense mutations using in vitro phosphoinositide phosphatase assay. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 3147–3151.
Rodriguez-Escudero I, Oliver MD, Andres-Pons A, Molina M, Cid VJ, Pulido R . A comprehensive functional analysis of PTEN mutations: implications in tumor- and autism-related syndromes. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: 4132–4142.
Nguyen HN, Afkari Y, Senoo H, Sesaki H, Devreotes PN, Iijima M . Mechanism of human PTEN localization revealed by heterologous expression in Dictyostelium. Oncogene (e-pub ahead of print 2 December 2013; doi:10.1038/onc.2013.507).
Rahdar M, Inoue T, Meyer T, Zhang J, Vazquez F, Devreotes PN . A phosphorylation-dependent intramolecular interaction regulates the membrane association and activity of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 480–485.
Gericke A, Leslie NR, Losche M, Ross AH . PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated cell signaling: emerging principles and PTEN as a paradigm for regulatory mechanism. Adv Exp Med Biol 2013; 991: 85–104.
Das S, Dixon JE, Cho W . Membrane-binding and activation mechanism of PTEN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7491–7496.
Keniry M, Parsons R . The role of PTEN signaling perturbations in cancer and in targeted therapy. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5477–5485.
Vazquez F, Matsuoka S, Sellers WR, Yanagida T, Ueda M, Devreotes PN . Tumor suppressor PTEN acts through dynamic interaction with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3633–3638.
Nguyen HN, Yang JM, Afkari Y, Park BH, Sesaki H, Devreotes PN et al. Engineering ePTEN, an enhanced PTEN with increased tumor suppressor activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: E2684–E2693.
Vazquez F, Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N, Sellers WR . Phosphorylation of the PTEN tail regulates protein stability and function. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 5010–5018.
Freeman DJ, Li AG, Wei G, Li HH, Kertesz N, Lesche R et al. PTEN tumor suppressor regulates p53 protein levels and activity through phosphatase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 117–130.
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, Lin Y, Snow B, Jang Y et al. Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol Cell 2001; 8: 317–325.
Iijima M, Devreotes P . Tumor suppressor PTEN mediates sensing of chemoattractant gradients. Cell 2002; 109: 599–610.
Iijima M, Huang YE, Devreotes P . Temporal and spatial regulation of chemotaxis. Dev Cell 2002; 3: 469–478.
Hawkins PT, Anderson KE, Davidson K, Stephens LR . Signalling through Class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans 2006; 34 (Pt 5): 647–662.
Gustin JP, Karakas B, Weiss MB, Abukhdeir AM, Lauring J, Garay JP et al. Knockin of mutant PIK3CA activates multiple oncogenic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2835–2840.
Wang GM, Wong HY, Konishi H, Blair BG, Abukhdeir AM, Gustin JP et al. Single copies of mutant KRAS and mutant PIK3CA cooperate in immortalized human epithelial cells to induce tumor formation. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3248–3261.
Kamimura Y, Xiong Y, Iglesias PA, Hoeller O, Bolourani P, Devreotes PN . PIP3-independent activation of TorC2 and PKB at the cell’s leading edge mediates chemotaxis. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 1034–1043.
Chen CL, Wang Y, Sesaki H, Iijima M . Myosin I links PIP3 signaling to remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton in chemotaxis. Sci Signal 2012; 5: ra10.
Bamford S, Dawson E, Forbes S, Clements J, Pettett R, Dogan A et al. The COSMIC (Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer) database and website. Br J Cancer 2004; 91: 355–358.
Lee JO, Yang H, Georgescu MM, Di Cristofano A, Maehama T, Shi Y et al. Crystal structure of the PTEN tumor suppressor: implications for its phosphoinositide phosphatase activity and membrane association. Cell 1999; 99: 323–334.
Wang Y, Senoo H, Sesaki H, Iijima M . Rho GTPases orient directional sensing in chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E4723–E4732.
Zhang P, Wang Y, Sesaki H, Iijima M . Proteomic identification of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) triphosphate-binding proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 11829–11834.
Kim JS, Xu X, Li H, Solomon D, Lane WS, Jin T et al. Mechanistic analysis of a DNA damage-induced, PTEN-dependent size checkpoint in human cells. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 2756–2771.
Cai H, Huang CH, Devreotes PN, Iijima M . Analysis of chemotaxis in Dictyostelium. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 757: 451–468.
Wang Y, Steimle PA, Ren Y, Ross CA, Robinson DN, Egelhoff TT et al. Dictyostelium huntingtin controls chemotaxis and cytokinesis through the regulation of myosin II phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 2011; 22: 2270–2281.
Iijima M, Huang YE, Luo HR, Vazquez F, Devreotes PN . Novel mechanism of PTEN regulation by its phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding motif is critical for chemotaxis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 16606–16613.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Todd Waldman (Georgetown University School of Medicine) for lentiviral constructs. The mutation data was obtained from the Sanger Institute Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer (COSMIC) web site (http://www.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic).27 This work was supported by NIH grants to MI (GM084015), PND (GM28007 and GM34933), HS (GM089853 and NS084154) and to RP (CA082783 and CA155117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, HN., Yang Jr, JM., Rahdar, M. et al. A new class of cancer-associated PTEN mutations defined by membrane translocation defects. Oncogene 34, 3737–3743 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.293
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.293
This article is cited by
-
Integrating thousands of PTEN variant activity and abundance measurements reveals variant subgroups and new dominant negatives in cancers
Genome Medicine (2021)
-
Multiplex assessment of protein variant abundance by massively parallel sequencing
Nature Genetics (2018)
-
Characterization of PTEN mutations in brain cancer reveals that pten mono-ubiquitination promotes protein stability and nuclear localization
Oncogene (2017)
-
Opening the conformation is a master switch for the dual localization and phosphatase activity of PTEN
Scientific Reports (2015)