Abstract
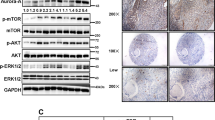
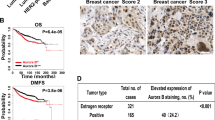
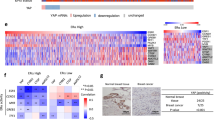
Despite the clinical success of tamoxifen, its resistance remains a major challenge in breast cancer. Here we show that Aurora-A determines tamoxifen sensitivity by regulation of oestrogen receptor (ER)α. Ectopic expression of Aurora-A decreases and depletion of Aurora-A enhances tamoxifen sensitivity in ERα-positive breast cancer. Elevated Aurora-A was significantly associated with the recurrence of ERα-positive tumours. Notably, Aurora-A inhibitor MLN8237, which is currently in clinical trial, synergizes with tamoxifen and overcomes tamoxifen resistance. Furthermore, Aurora-A interacts with and phosphorylates ERα on serine-167 and -305, leading to increase in ERα DNA-binding and transcriptional activity. Elevated levels of Aurora-A are significantly associated with disease-free survival in ERα-positive but not ERα-negative breast cancers. These data suggest that Aurora-A has a pivotal role in tamoxifen resistance and ERα is a bona fide substrate of Aurora-A. Thus, Aurora-A represents a prognostic marker in ERα-positive tumour and a critical therapeutic target in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer, and Aurora-A inhibitor could be used as either an independent or concurrent agent in tamoxifen-resistant tumour.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 February 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-02983-9
References
Warner SL, Bearss DJ, Han H, Von Hoff DD . Targeting Aurora-2 kinase in cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2003; 2: 589–595.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR . AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 51–62.
Bodvarsdottir SK, Hilmarsdottir H, Birgisdottir V, Steinarsdottir M, Jonasson JG, Eyfjord JE . Aurora-A amplification associated with BRCA2 mutation in breast tumours. Cancer Lett 2007; 248: 96–102.
Li JJ, Weroha SJ, Lingle WL, Papa D, Salisbury JL, Li SA . Estrogen mediates Aurora-A overexpression, centrosome amplification, chromosomal instability, and breast cancer in female ACI rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 18123–18128.
Wang X, Zhou YX, Qiao W, Tominaga Y, Ouchi M, Ouchi T et al. Overexpression of aurora kinase A in mouse mammary epithelium induces genetic instability preceding mammary tumor formation. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7148–7158.
D’Assoro AB, Liu T, Quatraro C, Amato A, Opyrchal M, Leontovich A et al. The mitotic kinase Aurora-A promotes distant metastases by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ERalpha(+) breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2014; 33: 599–610.
Wang LH, Xiang J, Yan M, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Yue CF et al. The mitotic kinase Aurora-A induces mammary cell migration and breast cancer metastasis by activating the Cofilin-F-actin pathway. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 9118–9128.
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC . Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1474–1481.
Osborne CK, Schiff R, Fuqua SA, Shou J . Estrogen receptor: current understanding of its activation and modulation. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 4338s–4342s discussion 411s–412s.
Klinge CM . Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 2905–2919.
Jordan VC, O’Malley BW . Selective estrogen-receptor modulators and antihormonal resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 5815–5824.
Clarke R, Liu MC, Bouker KB, Gu Z, Lee RY, Zhu Y et al. Antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer and the role of estrogen receptor signaling. Oncogene 2003; 22: 7316–7339.
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL . Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 631–643.
Ring A, Dowsett M . Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer 2004; 11: 643–658.
Johnston SR, Saccani-Jotti G, Smith IE, Salter J, Newby J, Coppen M et al. Changes in estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and pS2 expression in tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 3331–3338.
Lupien M, Meyer CA, Bailey ST, Eeckhoute J, Cook J, Westerling T et al. Growth factor stimulation induces a distinct ER(alpha) cistrome underlying breast cancer endocrine resistance. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 2219–2227.
Nagashima T, Shimodaira H, Ide K, Nakakuki T, Tani Y, Takahashi K et al. Quantitative transcriptional control of ErbB receptor signaling undergoes graded to biphasic response for cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 4045–4056.
Yang H, Ou CC, Feldman RI, Nicosia SV, Kruk PA, Cheng JQ . Aurora-A kinase regulates telomerase activity through c-Myc in human ovarian and breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 463–467.
Cutrupi S, Reineri S, Panetto A, Grosso E, Caizzi L, Ricci L et al. Targeting of the adaptor protein Tab2 as a novel approach to revert tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2012; 31: 4353–4361.
Manfredi MG, Ecsedy JA, Chakravarty A, Silverman L, Zhang M, Hoar KM et al. Characterization of Alisertib (MLN8237), an investigational small-molecule inhibitor of aurora A kinase using novel in vivo pharmacodynamic assays. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 7614–7624.
Tonetti DA, Jordan VC . Possible mechanisms in the emergence of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 1995; 6: 498–507.
Murphy LC, Seekallu SV, Watson PH . Clinical significance of estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Endocr Relat Cancer 2011; 18: R1–14.
Ferrari S, Marin O, Pagano MA, Meggio F, Hess D, El-Shemerly M et al. Aurora-A site specificity: a study with synthetic peptide substrates. Biochem J 2005; 390: 293–302.
Bostner J, Ahnstrom Waltersson M, Fornander T, Skoog L, Nordenskjold B, Stal O . Amplification of CCND1 and PAK1 as predictors of recurrence and tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6997–7005.
Lundgren K, Brown M, Pineda S, Cuzick J, Salter J, Zabaglo L et al. Effects of cyclin D1 gene amplification and protein expression on time to recurrence in postmenopausal breast cancer patients treated with anastrozole or tamoxifen: a TransATAC study. Breast Cancer Res 2012; 14: R57.
Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q et al. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010; 123: 725–731.
Guo JP, Shu SK, Esposito NN, Coppola D, Koomen JM, Cheng JQ . IKKepsilon phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha Ser-167 and contribution to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 3676–3684.
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 9817–9824.
Holz MK . The role of S6K1 in ER-positive breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 3159–3165.
Joel PB, Smith J, Sturgill TW, Fisher TL, Blenis J, Lannigan DA . pp90rsk1 regulates estrogen receptor-mediated transcription through phosphorylation of Ser-167. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 1978–1984.
Barkhem T, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA . Molecular mechanisms, physiological consequences and pharmacological implications of estrogen receptor action. Am J Pharmacogenomics 2004; 4: 19–28.
Le Romancer M, Poulard C, Cohen P, Sentis S, Renoir JM, Corbo L . Cracking the estrogen receptor’s posttranslational code in breast tumors. Endocr Rev 2011; 32: 597–622.
Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R . P21-activated kinase-1 phosphorylates and transactivates estrogen receptor-alpha and promotes hyperplasia in mammary epithelium. EMBO J 2002; 21: 5437–5447.
Michalides R, Griekspoor A, Balkenende A, Verwoerd D, Janssen L, Jalink K et al. Tamoxifen resistance by a conformational arrest of the estrogen receptor alpha after PKA activation in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 597–605.
Holm C, Kok M, Michalides R, Fles R, Koornstra RH, Wesseling J et al. Phosphorylation of the oestrogen receptor alpha at serine 305 and prediction of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Pathol 2009; 217: 372–379.
Kok M, Zwart W, Holm C, Fles R, Hauptmann M, Van’t Veer LJ et al. PKA-induced phosphorylation of ERalpha at serine 305 and high PAK1 levels is associated with sensitivity to tamoxifen in ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 125: 1–12.
Bostner J, Skoog L, Fornander T, Nordenskjöld B, Stål O . Estrogen receptor-alpha phosphorylation at serine 305, nuclear p21-activated kinase 1 expression, and response to tamoxifen in postmenopausal breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 1624–1633.
Ohishi T, Hirota T, Tsuruo T, Seimiya H . TRF1 mediates mitotic abnormalities induced by Aurora-A overexpression. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2041–2052.
Lim KH, Brady DC, Kashatus DF, Ancrile BB, Der CJ, Cox AD et al. Aurora-A phosphorylates, activates, and relocalizes the small GTPase RalA. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 508–523.
Liu Q, Kaneko S, Yang L, Feldman RI, Nicosia SV, Chen J et al. Aurora-A abrogation of p53 DNA binding and transactivation activity by phosphorylation of serine 215. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52175–52182.
Pugacheva EN, Jablonski SA, Hartman TR, Henske EP, Golemis EA . HEF1-dependent Aurora A activation induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell 2007; 129: 1351–1363.
Qi W, Cooke LS, Liu X, Rimsza L, Roe DJ, Manziolli A et al. Aurora inhibitor MLN8237 in combination with docetaxel enhances apoptosis and anti-tumor activity in mantle cell lymphoma. Biochem Pharmacol 2011; 81: 881–890.
Sehdev V, Peng D, Soutto M, Washington MK, Revetta F, Ecsedy J et al. The aurora kinase A inhibitor MLN8237 enhances cisplatin-induced cell death in esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 763–774.
Lykkesfeldt AE, Madsen MW, Briand P . Altered expression of estrogen-regulated genes in a tamoxifen-resistant and ICI 164,384 and ICI 182,780 sensitive human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7/TAMR-1. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 1587–1595.
Chou TC . Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 440–446.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Dr Kenji Fukasawa for his scientific input. We are grateful for Tissue Procurement, DNA Sequence, Proteomics and Image Core Facilities at H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center for providing cancer specimens, sequencing and cell apoptosis analysis. This work was partially supported by grants from NIH grant CA160455 (JQC) and Florida James and Esther King Biomedical Research Program 1KG02 (JQC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Guo, J., Yang, H. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Aurora-A is a determinant of tamoxifen sensitivity through phosphorylation of ERα in breast cancer. Oncogene 33, 4985–4996 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.444
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.444
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting Aurora-A inhibits tumor progression and sensitizes thyroid carcinoma to Sorafenib by decreasing PFKFB3-mediated glycolysis
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Monopolar spindle 1 contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer through phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2023)
-
Targeting AURKA in Cancer: molecular mechanisms and opportunities for Cancer therapy
Molecular Cancer (2021)
-
Aurora-A-mediated phosphorylation of LKB1 compromises LKB1/AMPK signaling axis to facilitate NSCLC growth and migration
Oncogene (2018)
-
Aurora kinase B is important for antiestrogen resistant cell growth and a potential biomarker for tamoxifen resistant breast cancer
BMC Cancer (2015)