Abstract
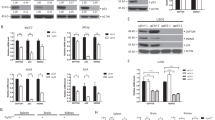
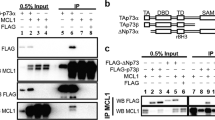
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) modulates the p53 tumor suppressor through its interaction with p53 and MDM2. We found that activated big MAP kinase 1 (BMK1) preferentially associates with PML isoform IV and disrupts PML–MDM2 interaction. Doxorubicin, a common chemotherapeutic agent, is known to promote PML-mediated p53 activation in part by promoting PML-dependent MDM2 nucleolar sequestration. We discovered that BMK1 deactivation coupled with doxorubicin synergistically enhanced MDM2 nucleolar sequestration and, consequently, promoted PML-mediated p53 upregulation leading to tumor cell apoptosis in vitro and tumor regression in vivo. Collectively, these results not only suggest that BMK1 activity has a role in suppressing p53 by blocking the interaction between PML and MDM2, but also implicate that pharmacological BMK1 inhibitor should significantly enhance the anticancer capacity of doxorubicin-based chemotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang L, Karin M . Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001; 410: 37–40.
Johnson GL, Lapadat R . Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 2002; 298: 1911–1912.
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers GT, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K et al. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 2001; 22: 153–183.
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH . Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3100–3112.
Zhou G, Bao ZQ, Dixon JE . Components of a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 12665–12669.
Lee JD, Ulevitch RJ, Han J . Primary structure of BMK1: a new mammalian map kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995; 213: 715–724.
Weldon CB, Scandurro AB, Rolfe KW, Clayton JL, Elliott S, Butler NN et al. Identification of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase as a chemoresistant pathway in MCF-7 cells by using gene expression microarray. Surgery 2002; 132: 293–301.
Esparis-Ogando A, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Montero JC, Yuste L, Crespo P, Pandiella A . Erk5 participates in neuregulin signal transduction and is constitutively active in breast cancer cells overexpressing ErbB2. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 270–285.
Mehta PB, Jenkins BL, McCarthy L, Thilak L, Robson CN, Neal DE et al. MEK5 overexpression is associated with metastatic prostate cancer, and stimulates proliferation, MMP-9 expression and invasion. Oncogene 2003; 22: 1381–1389.
Hayashi M, Fearns C, Eliceiri B, Yang Y, Lee JD . Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 signaling pathway is essential for tumor-associated angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 7699–7706.
Oren M . Regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 36031–36034.
Bernardi R, Scaglioni PP, Bergmann S, Horn HF, Vousden KH, Pandolfi PP . PML regulates p53 stability by sequestering Mdm2 to the nucleolus. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 665–672.
Yang Q, Deng X, Lu B, Cameron M, Fearns C, Patricelli MP et al. Pharmacological inhibition of BMK1 suppresses tumor growth through promyelocytic leukemia protein. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 258–267.
Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP . Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 1006–1016.
Pearson M, Carbone R, Sebastiani C, Cioce M, Fagioli M, Saito S et al. PML regulates p53 acetylation and premature senescence induced by oncogenic Ras. Nature 2000; 406: 207–210.
Guo A, Salomoni P, Luo J, Shih A, Zhong S, Gu W et al. The function of PML in p53-dependent apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 730–736.
Louria-Hayon I, Grossman T, Sionov RV, Alsheich O, Pandolfi PP, Haupt Y . The promyelocytic leukemia protein protects p53 from Mdm2-mediated inhibition and degradation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 33134–33141.
Kato Y, Kravchenko VV, Tapping RI, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Lee JD . BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C. EMBO J 1997; 16: 7054–7066.
Yan C, Luo H, Lee JD, Abe J, Berk BC . Molecular cloning of mouse ERK5/BMK1 splice variants and characterization of ERK5 functional domains. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 10870–10878.
Kondoh K, Terasawa K, Morimoto H, Nishida E . Regulation of nuclear translocation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 by active nuclear import and export mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 1679–1690.
Ferbeyre G, de Stanchina E, Querido E, Baptiste N, Prives C, Lowe SW . PML is induced by oncogenic ras and promotes premature senescence. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 2015–2027.
Zhu H, Wu L, Maki CG . MDM2 and promyelocytic leukemia antagonize each other through their direct interaction with p53. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 49286–49292.
Kurki S, Latonen L, Laiho M . Cellular stress and DNA damage invoke temporally distinct Mdm2, p53 and PML complexes and damage-specific nuclear relocalization. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 3917–3925.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM . The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990; 63: 1129–1136.
Polsky D, Bastian BC, Hazan C, Melzer K, Pack J, Houghton A et al. HDM2 protein overexpression, but not gene amplification, is related to tumorigenesis of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 7642–7646.
Haluska FG, Hodi FS . Molecular genetics of familial cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 670–682.
Bisht S, Maitra A . Dextran-doxorubicin/chitosan nanoparticles for solid tumor therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2009; 1: 415–425.
Abe J, Kusuhara M, Ulevitch RJ, Berk BC, Lee JD . Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) is a redox-sensitive kinase. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 16586–16590.
Huibregtse JM, Scheffner M, Howley PM . A cellular protein mediates association of p53 with the E6 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus types 16 or 18. EMBO J 1991; 10: 4129–4135.
Baker SJ, Markowitz S, Fearon ER, Willson JK, Vogelstein B . Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science 1990; 249: 912–915.
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Zou Y, Spohn B, Hung MC . HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2 phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 973–982.
Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T, Burkhart WA et al. Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 8902–8912.
Kato Y, Tapping RI, Huang S, Watson MH, Ulevitch RJ, Lee JD . Bmk1/Erk5 is required for cell proliferation induced by epidermal growth factor. Nature 1998; 395: 713–716.
Beech SJ, Lethbridge KJ, Killick N, McGlincy N, Leppard KN . Isoforms of the promyelocytic leukemia protein differ in their effects on ND10 organization. Exp Cell Res 2005; 307: 109–117.
Hayashi M, Kim SW, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Abel ED, Eliceiri B et al. Targeted deletion of BMK1/ERK5 in adult mice perturbs vascular integrity and leads to endothelial failure. J Clin Investig 2004; 113: 1138–1148.
Hayashi M, Tapping RI, Chao TH, Lo JF, King CC, Yang Y et al. BMK1 mediates growth factor-induced cell proliferation through direct cellular activation of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 8631–8634.
Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H et al. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr Biol 2002; 12: 1–11.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Giovanni Blandino, Dr Myung Kim and Dr Pier Paolo Pandolfi for generously providing the PML null and control cell lines. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [CA079871 and CA114059 to JDL] and by the funds from the Tobacco-Related Disease, Research Program of the University of California [19XT-0084 to JDL].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Liao, L., Deng, X. et al. BMK1 is involved in the regulation of p53 through disrupting the PML–MDM2 interaction. Oncogene 32, 3156–3164 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.332
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.332
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MAP kinase ERK5 modulates cancer cell sensitivity to extrinsic apoptosis induced by death-receptor agonists
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
The ERK5/NF-κB signaling pathway targets endometrial cancer proliferation and survival
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Targeting BMK1 Impairs the Drug Resistance to Combined Inhibition of BRAF and MEK1/2 in Melanoma
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The function, regulation and therapeutic implications of the tumor suppressor protein, PML
Cell & Bioscience (2015)
-
Nesprin-2-dependent ERK1/2 compartmentalisation regulates the DNA damage response in vascular smooth muscle cell ageing
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)