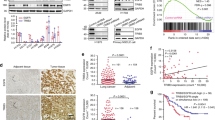
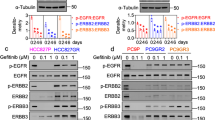
Abstract
The c-Met receptor is a potential therapeutic target for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Signaling interactions between c-Met and the mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) have been studied extensively, but signaling intermediates and biological consequences of lateral signaling to c-Met in EGFR wild-type tumors are minimally understood. Our observations indicate that delayed c-Met activation in NSCLC cell lines is initiated by wild-type EGFR, the receptor most often found in NSCLC tumors. EGFR ligands induce accumulation of activated c-Met, which begins at 8 h and continues for 48 h. This effect is accompanied by an increase in c-Met expression and phosphorylation of critical c-Met tyrosine residues without activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) or Akt. Gene transcription is required for delayed c-Met activation; however, phosphorylation of c-Met by EGFR occurs without production of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or another secreted factor, supporting a ligand-independent mechanism. Lateral signaling is blocked by two selective c-Met tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), PF2341066 and SU11274, or with gefitinib, an EGFR TKI, suggesting kinase activity of both receptors is required for this effect. Prolonged c-Src phosphorylation is observed, and c-Src pathway is essential for EGFR to c-Met communication. Pretreatment with pan-Src family kinase inhibitors, PP2 and dasatinib, abolishes delayed c-Met phosphorylation. A c-Src dominant-negative construct reduces EGF-induced c-Met phosphorylation compared with control, further confirming a c-Src requirement. Inhibition of c-Met with PF2341066 and siRNA decreases EGF-induced phenotypes of invasion by ∼86% and motility by ∼81%, suggesting that a novel form of c-Met activation is utilized by EGFR to maximize these biological effects. Combined targeting of c-Met and EGFR leads to increased xenograft antitumor activity, demonstrating that inhibition of downstream and lateral signaling from the EGFR-c-Src–c-Met axis might be effective in treatment of NSCLC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- HGF:
-
hepatocyte growth factor
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- SFK:
-
Src family kinase
- TKI:
-
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TGF-α:
-
transforming growth factor-α
References
Bergstrom JD, Westermark B, Heldin NE . (2000). Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling activates met in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 259: 293–299.
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF et al. (1991). Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 251: 802–804.
Cai T, Nishida K, Hirano T, Khavari PA . (2002). Gab1 and SHP-2 promote Ras/MAPK regulation of epidermal growth and differentiation. J Cell Biol 159: 103–112.
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Angeloni D, Skeel A, Donley S, Lerman M, Leonard EJ . (2000). Integrin-mediated RON growth factor receptor phosphorylation requires tyrosine kinase activity of both the receptor and c-Src. J Biol Chem 275: 14783–14786.
Daub H, Wallasch C, Lankenau A, Herrlich A, Ullrich A . (1997). Signal characteristics of G protein-transactivated EGF receptor. Embo J 16: 7032–7044.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO et al. (2007). MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316: 1039–1043.
Fischer OM, Giordano S, Comoglio PM, Ullrich A . (2004). Reactive oxygen species mediate Met receptor transactivation by G protein-coupled receptors and the epidermal growth factor receptor in human carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 279: 28970–28978.
Goi T, Shipitsin M, Lu Z, Foster DA, Klinz SG, Feig LA . (2000). An EGF receptor/Ral-GTPase signaling cascade regulates c-Src activity and substrate specificity. Embo J 19: 623–630.
Guo A, Villen J, Kornhauser J, Lee KA, Stokes MP, Rikova K et al. (2008). Signaling networks assembled by oncogenic EGFR and c-Met. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 692–697.
Jo M, Stolz DB, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Michalopoulos GK, Strom SC . (2000). Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Met signal pathways in transformed cells. J Biol Chem 275: 8806–8811.
Karni R, Dor Y, Keshet E, Meyuhas O, Levitzki A . (2002). Activated pp60c-Src leads to elevated hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha expression under normoxia. J Biol Chem 277: 42919–42925.
Kim LC, Song L, Haura EB . (2009). Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6: 587–595.
Klinghoffer RA, Sachsenmaier C, Cooper JA, Soriano P . (1999). Src family kinases are required for integrin but not PDGFR signal transduction. Embo J 18: 2459–2471.
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Barrow D, Gee JM, Nicholson RI . (2005). Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Endocrinology 146: 4609–4618.
Liu X, Carlisle DL, Swick MC, Gaither-Davis A, Grandis JR, Siegfried JM . (2007). Gastrin-releasing peptide activates Akt through the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway and abrogates the effect of gefitinib. Exp Cell Res 313: 1361–1372.
Ma PC, Jagadeeswaran R, Jagadeesh S, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Fox EA et al. (2005). Functional expression and mutations of c-Met and its therapeutic inhibition with SU11274 and small interfering RNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 65: 1479–1488.
Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J, Salgia R . (2003). Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22: 309–325.
Molina JR, Adjei AA, Jett JR . (2006). Advances in chemotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 130: 1211–1219.
Moro L, Dolce L, Cabodi S, Bergatto E, Boeri Erba E, Smeriglio M et al. (2002). Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J Biol Chem 277: 9405–9414.
Nakajima M, Sawada H, Yamada Y, Watanabe A, Tatsumi M, Yamashita J et al. (1999). The prognostic significance of amplification and overexpression of c-met and c-erb B-2 in human gastric carcinomas. Cancer 85: 1894–1902.
Nakamura T, Teramoto H, Ichihara A . (1986). Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 6489–6493.
Naldini L, Vigna E, Ferracini R, Longati P, Gandino L, Prat M et al. (1991a). The tyrosine kinase encoded by the MET proto-oncogene is activated by autophosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1793–1803.
Naldini L, Vigna E, Narsimhan RP, Gaudino G, Zarnegar R, Michalopoulos GK et al. (1991b). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene 6: 501–504.
Naldini L, Weidner KM, Vigna E, Gaudino G, Bardelli A, Ponzetto C et al. (1991c). Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable ligands for the MET receptor. Embo J 10: 2867–2878.
Pawson T, Scott JD . (1997). Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science 278: 2075–2080.
Peschard P, Fournier TM, Lamorte L, Naujokas MA, Band H, Langdon WY et al. (2001). Mutation of the c-Cbl TKB domain binding site on the Met receptor tyrosine kinase converts it into a transforming protein. Mol Cell 8: 995–1004.
Ponzetto C, Bardelli A, Zhen Z, Maina F, dalla Zonca P, Giordano S et al. (1994). A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell 77: 261–271.
Ponzetto C, Giordano S, Peverali F, Della Valle G, Abate ML, Vaula G et al. (1991). c-met is amplified but not mutated in a cell line with an activated met tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 6: 553–559.
Popsueva A, Poteryaev D, Arighi E, Meng X, Angers-Loustau A, Kaplan D et al. (2003). GDNF promotes tubulogenesis of GFRalpha1-expressing MDCK cells by Src-mediated phosphorylation of Met receptor tyrosine kinase. J Cell Biol 161: 119–129.
Presnell SC, Stolz DB, Mars WM, Jo M, Michalopoulos GK, Strom SC . (1997). Modifications of the hepatocyte growth factor/c-met pathway by constitutive expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in rat liver epithelial cells. Mol Carcinog 18: 244–255.
Ritter CA, Arteaga CL . (2003). The epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase: a promising therapeutic target in solid tumors. Semin Oncol 30: 3–11.
Shattuck DL, Miller JK, Carraway III KL, Sweeney C . (2008). Met receptor contributes to trastuzumab resistance of Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 68: 1471–1477.
Siegfried JM, Gubish CT, Rothstein ME, Queiroz de Oliveira PE, Stabile LP . (2007). Signaling pathways involved in cyclooxygenase-2 induction by hepatocyte growth factor in non small-cell lung cancer. Mol Pharmacol 72: 769–779.
Siegfried JM, Krishnamachary N, Gaither Davis A, Gubish C, Hunt JD, Shriver SP . (1999). Evidence for autocrine actions of neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide in non-small cell lung cancer. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 12: 291–302.
Stabile LP, Lyker JS, Huang L, Siegfried JM . (2004). Inhibition of human non-small cell lung tumors by a c-Met antisense/U6 expression plasmid strategy. Gene Ther 11: 325–335.
Stabile LP, Rothstein ME, Keohavong P, Jin J, Yin J, Land SR et al. (2008). Therapeutic targeting of human hepatocyte growth factor with a single neutralizing monoclonal antibody reduces lung tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 1913–1922.
Stoker M, Gherardi E, Perryman M, Gray J . (1987). Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature 327: 239–242.
Tang Z, Du R, Jiang S, Wu C, Barkauskas DS, Richey J et al. (2008). Dual MET-EGFR combinatorial inhibition against T790M-EGFR-mediated erlotinib-resistant lung cancer. Br J Cancer 99: 911–922.
Thomas SM, Bhola NE, Zhang Q, Contrucci SC, Wentzel AL, Freilino ML et al. (2006). Cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways contributes to growth and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 66: 11831–11839.
Trusolino L, Comoglio PM . (2002). Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 289–300.
Wang R, Kobayashi R, Bishop JM . (1996). Cellular adherence elicits ligand-independent activation of the Met cell-surface receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8425–8430.
Wu CC, Hsu HY, Liu HP, Chang JW, Chen YT, Hsieh WY et al. (2008). Reversed mutation rates of KRAS and EGFR genes in adenocarcinoma of the lung in Taiwan and their implications. Cancer 113: 3199–3208.
Xu L, Nilsson MB, Saintigny P, Cascone T, Herynk MH, Du Z et al. (2010). Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates MET levels and invasiveness through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 29: 2616–2627.
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, Matsumoto K, Sakurama H, Nakamura T et al. (2008). Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Res 68: 9479–9487.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant R01 CA79882 to JMS from the National Cancer Institute and by a Predoctoral Fellowship in Pharmacology by Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America Foundation awarded to Austin M Dulak. We would like to thank Pfizer for kindly providing PF2341066.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dulak, A., Gubish, C., Stabile, L. et al. HGF-independent potentiation of EGFR action by c-Met. Oncogene 30, 3625–3635 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MET-Targeted Therapies and Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Literature Review
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2022)
-
Targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway in advanced pancreatic cancer: a key element of treatment that limits primary tumour growth and eliminates metastasis
British Journal of Cancer (2020)
-
EGFL9 promotes breast cancer metastasis by inducing cMET activation and metabolic reprogramming
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Targeting the COX2/MET/TOPK signaling axis induces apoptosis in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Histone demethylase JARID1B/KDM5B promotes aggressiveness of non-small cell lung cancer and serves as a good prognostic predictor
Clinical Epigenetics (2018)