Abstract
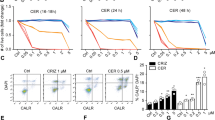
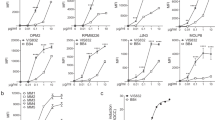
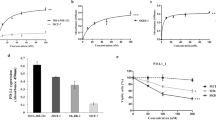
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a receptor tyrosine kinase aberrantly expressed in neuroblastoma, a devastating pediatric cancer of the sympathetic nervous system. Germline and somatically acquired ALK aberrations induce increased autophosphorylation, constitutive ALK activation and increased downstream signaling. Thus, ALK is a tractable therapeutic target in neuroblastoma, likely to be susceptible to both small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors and therapeutic antibodies—as has been shown for other receptor tyrosine kinases in malignancies such as breast and lung cancer. Small-molecule inhibitors of ALK are currently being studied in the clinic, but common ALK mutations in neuroblastoma appear to show de novo insensitivity, arguing that complementary therapeutic approaches must be developed. We therefore hypothesized that antibody targeting of ALK may be a relevant strategy for the majority of neuroblastoma patients likely to have ALK-positive tumors. We show here that an antagonistic ALK antibody inhibits cell growth and induces in vitro antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of human neuroblastoma-derived cell lines. Cytotoxicity was induced in cell lines harboring either wild type or mutated forms of ALK. Treatment of neuroblastoma cells with the dual Met/ALK inhibitor crizotinib sensitized cells to antibody-induced growth inhibition by promoting cell surface accumulation of ALK and thus increasing the accessibility of antigen for antibody binding. These data support the concept of ALK-targeted immunotherapy as a highly promising therapeutic strategy for neuroblastomas with mutated or wild-type ALK.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL et al. (1994) Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science 263: 1281–1284.
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H et al. (2007) Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 131: 1190–1203.
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S et al. (2007) Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 448: 561–566.
Jazii FR, Najafi Z, Malekzadeh R, Conrads TP, Ziaee AA, Abnet C et al. (2006) Identification of squamous cell carcinoma associated proteins by proteomics and loss of beta tropomyosin expression in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12: 7104–7112.
Griffin CA, Hawkins AL, Dvorak C, Henkle C, Ellingham T, Perlman EJ (1999) Recurrent involvement of 2p23 in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors. Cancer Res 59: 2776–2780.
Miyake I, Hakomori Y, Shinohara A, Gamou T, Saito M, Iwamatsu A et al. (2002) Activation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase is responsible for hyperphosphorylation of ShcC in neuroblastoma cell lines. Oncogene 21: 5823–5834.
Maris JM (2010) Recent advances in neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med 362: 2202–2211.
Smith MA, Seibel NL, Altekruse SF, Ries LA, Melbert DL, O’Leary M et al. (2010) Outcomes for children and adolescents with cancer: challenges for the twenty-first century. J Clin Oncol 28: 2625–2634.
George RE, Attiyeh EF, Li S, Moreau LA, Neuberg D, Li C et al. (2007) Genome-wide analysis of neuroblastomas using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. PLoS One 2: e255.
Mosse YP, Laudenslager M, Longo L, Cole KA, Wood A, Attiyeh EF et al. (2008) Identification of ALK as a major familial neuroblastoma predisposition gene. Nature 455: 930–935.
Mazot P, Cazes A, Boutterin MC, Figueiredo A, Raynal V, Combaret V et al. (2011) The constitutive activity of the ALK mutated at positions F1174 or R1275 impairs receptor trafficking. Oncogene 30: 2017–2025.
George R, Attiyeh E, Li S, Moreau L, Neuberg D, Li C et al. (2007) Genome-wide analysis of neuroblastomas using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. PLoS One 2: e255.
Osajima-Hakomori Y, Miyake I, Ohira M, Nakagawara A, Nakagawa A, Sakai R (2005) Biological role of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in neuroblastoma. Am J Pathol 167: 213–222.
De Brouwer S, De Preter K, Kumps C, Zabrocki P, Porcu M, Westerhout EM et al. (2010) Meta-analysis of neuroblastomas reveals a skewed ALK mutation spectrum in tumors with MYCN amplification. Clin Cancer Res. [Meta-Analysis Research Support, Non-US Government] 16: 4353–4362.
Passoni L, Longo L, Collini P, Coluccia AM, Bozzi F, Podda M et al. (2009) Mutation-independent anaplastic lymphoma kinase overexpression in poor prognosis neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res 69: 7338–7346.
Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS (2009) Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 9: 28–39.
Weiner LM, Surana R, Wang S (2010) Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 10: 317–327.
Hudis CA (2007) Trastuzumab—mechanism of action and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med (Review) 357: 39–51.
Kurai J, Chikumi H, Hashimoto K, Yamaguchi K, Yamasaki A, Sako T et al. (2007) Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab against lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1552–1561.
Regales L, Gong Y, Shen R, de Stanchina E, Vivanco I, Goel A et al. (2009) Dual targeting of EGFR can overcome a major drug resistance mutation in mouse models of EGFR mutant lung cancer. J Clin Invest. [Research Support, NIH, Extramural Research Support, Non-US Government]. 119: 3000–3010.
Scaltriti M, Verma C, Guzman M, Jimenez J, Parra JL, Pedersen K et al. (2009) Lapatinib, a HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces stabilization and accumulation of HER2 and potentiates trastuzumab-dependent cell cytotoxicity. Oncogene. [Research Support, Non-US Government]. 28: 803–814.
Xia W, Gerard CM, Liu L, Baudson NM, Ory TL, Spector NL (2005) Combining lapatinib (GW572016), a small molecule inhibitor of ErbB1 and ErbB2 tyrosine kinases, with therapeutic anti-ErbB2 antibodies enhances apoptosis of ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 6213–6221.
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG et al. (2010) Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med [Clinical Trial, Phase I Multicenter Study Research Support, NIH, Extramural Research Support, Non-US Government]. 363: 1693–1703.
Bresler SC, Wood AC, Haglund EA, Courtright J, Belcastro LT, Plegaria JS et al. (2011) Differential inhibitor sensitivity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase variants found in neuroblastoma. Sci Transl Med 3: 108ra14.
George RE, Sanda T, Hanna M, Frohling S, Luther 2nd W, Zhang J et al. (2008) Activating mutations in ALK provide a therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. Nature 455: 975–978.
Sasaki T, Okuda K, Zheng W, Butrynski J, Capelletti M, Wang L et al. (2010) The neuroblastoma-associated F1174L ALK mutation causes resistance to an ALK kinase inhibitor in ALK-translocated cancers. Cancer Res. [Research Support, NIH, Extramural]. 70: 10038–10043.
Engelman JA, Settleman J (2008) Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer therapy. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18: 73–79.
Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, Ueno T, Takashima J, Nakajima T et al. (2010) EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med 363: 1734–1739.
Sasaki T, Okuda K, Zheng W, Butrynski J, Capelletti M, Wang L et al. (2010) The neuroblastoma associated F1174L ALK mutation causes resistance to an ALK kinase inhibitor in ALK translocated cancers. Cancer Res 70: 10038–10043.
Haupt R, Garaventa A, Gambini C, Parodi S, Cangemi G, Casale F et al. (2010) Improved survival of children with neuroblastoma between 1979 and 2005: a report of the Italian Neuroblastoma Registry. J Clin Oncol 28: 2331–2338.
Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, London WB, Kreissman SG, Chen HX et al. (2010) Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. [Multicenter Study Randomized Controlled Trial Research Support, NIH, Extramural Research Support, US Government, PHS]. 363: 1324–1334.
Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T et al. (1997) Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene 14: 439–449.
Wang Q, Diskin S, Rappaport E, Attiyeh E, Mosse Y, Shue D et al. (2006) Integrative genomics identifies distinct molecular classes of neuroblastoma and shows that multiple genes are targeted by regional alterations in DNA copy number. Cancer Res 66: 6050–6062.
Moog-Lutz C, Degoutin J, Gouzi JY, Frobert Y, Brunet-de Carvalho N, Bureau J et al. (2005) Activation and inhibition of anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor tyrosine kinase by monoclonal antibodies and absence of agonist activity of pleiotrophin. J Biol Chem 280: 26039–26048.
Hank JA, Robinson RR, Surfus J, Mueller BM, Reisfeld RA, Cheung NK et al. (1990) Augmentation of antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity following in vivo therapy with recombinant interleukin 2. Cancer Res. [Research Support, Non-US Government Research Support, US Government, PHS]. 50: 5234–5239.
Bougherara H, Subra F, Crepin R, Tauc P, Auclair C, Poul MA (2009) The aberrant localization of oncogenic kit tyrosine kinase receptor mutants is reversed on specific inhibitory treatment. Mol Cancer Res 7: 1525–1533.
Tabone-Eglinger S, Subra F, El Sayadi H, Alberti L, Tabone E, Michot JP et al. (2008) KIT mutations induce intracellular retention and activation of an immature form of the KIT protein in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14: 2285–2294.
Bougherara H, Subra F, Crepin R, Tauc P, Auclair C, Poul MA (2009) The aberrant localization of oncogenic kit tyrosine kinase receptor mutants is reversed on specific inhibitory treatment. Mol Cancer Res 7: 1525–1533.
Tabone-Eglinger S, Subra F, El Sayadi H, Alberti L, Tabone E, Michot JP et al. (2008) KIT mutations induce intracellular retention and activation of an immature form of the KIT protein in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14: 2285–2294.
Hobbie WL, Moshang T, Carlson CA, Goldmuntz E, Sacks N, Goldfarb SB et al. (2008) Late effects in survivors of tandem peripheral blood stem cell transplant for high-risk neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 51: 679–683.
Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, Kawashima T, Hudson MM, Meadows AT et al. (2006) Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. N Engl J Med 355: 1572–1582.
Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, London WB, Kreissman SG, Chen HX et al. (2010) Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med 363: 1324–1334.
Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, Baughman S, Benz CC, Dantis L et al. (1996) Phase II study of weekly intravenous recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2 monoclonal antibody in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 14: 737–744.
Baselga J, Pfister D, Cooper MR, Cohen R, Burtness B, Bos M et al. (2000) Phase I studies of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor chimeric antibody C225 alone and in combination with cisplatin. J Clin Oncol 18: 904–914.
Robert F, Ezekiel MP, Spencer SA, Meredith RF, Bonner JA, Khazaeli MB et al. (2001) Phase I study of anti—epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab in combination with radiation therapy in patients with advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 19: 3234–3243.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 127–137.
Chen Y, Takita J, Choi YL, Kato M, Ohira M, Sanada M et al. (2008) Oncogenic mutations of ALK kinase in neuroblastoma. Nature 455: 971–974.
Janoueix-Lerosey I, Lequin D, Brugieres L, Ribeiro A, de Pontual L, Combaret V et al. (2008) Somatic and germline activating mutations of the ALK kinase receptor in neuroblastoma. Nature 455: 967–970.
De Brouwer S, De Preter K, Kumps C, Zabrocki P, Porcu M, Westerhout EM et al. (2010) Meta-analysis of neuroblastomas reveals a skewed ALK mutation spectrum in tumors with MYCN amplification. Clin Cancer Res 16: 4353–4362.
Johns TG, Luwor RB, Murone C, Walker F, Weinstock J, Vitali AA et al. (2003) Antitumor efficacy of cytotoxic drugs and the monoclonal antibody 806 is enhanced by the EGF receptor inhibitor AG1478. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15871–15876.
Konecny GE, Pegram MD, Venkatesan N, Finn R, Yang G, Rahmeh M et al. (2006) Activity of the dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib (GW572016) against HER-2-overexpressing and trastuzumab-treated breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66: 1630–1639.
Matar P, Rojo F, Cassia R, Moreno-Bueno G, Di Cosimo S, Tabernero J et al. (2004) Combined epidermal growth factor receptor targeting with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839) and the monoclonal antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225): superiority over single-agent receptor targeting. Clin Cancer Res 10: 6487–6501.
Regales L, Gong Y, Shen R, de Stanchina E, Vivanco I, Goel A et al. (2009) Dual targeting of EGFR can overcome a major drug resistance mutation in mouse models of EGFR mutant lung cancer. J Clin Invest 119: 3000–3010.
Jones PT, Dear PH, Foote J, Neuberger MS, Winter G (1986) Replacing the complementarity-determining regions in a human antibody with those from a mouse. Nature 321: 522–525.
Niwa R, Sakurada M, Kobayashi Y, Uehara A, Matsushima K, Ueda R et al. (2005) Enhanced natural killer cell binding and activation by low-fucose IgG1 antibody results in potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity induction at lower antigen density. Clin Cancer Res 11: 2327–2336.
Hughes B (2010) Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer: poised to deliver? Nat Rev Drug Discov 9: 665–667.
Moog-Lutz C, Degoutin J, Gouzi JY, Frobert Y, Brunet-de Carvalho N, Bureau J et al. (2005) Activation and inhibition of anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor tyrosine kinase by monoclonal antibodies and absence of agonist activity of pleiotrophin. J Biol Chem. [Research Support, Non-US Government]. 280: 26039–26048.
Acknowledgements
We thank Pfizer for their gift of crizotinib, and Dr Marc Vigny for his gift of the ALK monoclonal antibodies 30, 49, 46 and 14. This work was supported in part by NIH Grants R01-CA140198 (YPM), 2R01 CA60104-16 (RCS), 2R01 CA60104-16S1 (RCS), the Children's Oncology Group, the Carly Hillman Fund (YPM), NIH Training Grant in Structural Biology T32-GM008275 (SCB), a fellowship grant from the St Baldrick's Foundation (ACW) and the US Army Peer-Reviewed Medical Research Program (W81XWH-10-1-0212/3 to MAL/YPM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carpenter, E., Haglund, E., Mace, E. et al. Antibody targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase induces cytotoxicity of human neuroblastoma. Oncogene 31, 4859–4867 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.647
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.647
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
New perspectives for targeting therapy in ALK-positive human cancers
Oncogene (2023)
-
Promising Molecular Targets and Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Neuroblastoma
Current Pharmacology Reports (2022)
-
Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Nature (2021)
-
Inhibiting Phosphorylation of Tau (τ) Proteins at Ser262 Using Peptide-Based R1 Domain Mimetics
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2019)
-
The Presence of ALK Alterations and Clinical Relevance of Crizotinib Treatment in Pediatric Solid Tumors
Pathology & Oncology Research (2019)