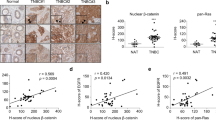
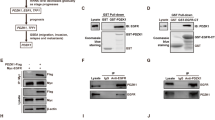
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated cell signaling is critical for mammary epithelial cell growth and survival; however, targeting EGFR has shown no or only minimal therapeutic benefit in patients with breast cancer. Here, we report a novel regulatory mechanism of EGFR signaling that may explain the low response rates. We found that breast tumor kinase (Brk)/protein-tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6), a nonreceptor protein-tyrosine kinase highly expressed in most human breast tumors, interacted with EGFR and sustained ligand-induced EGFR signaling. We demonstrate that Brk inhibits ligand-induced EGFR degradation through uncoupling activated EGFR from casitas B-lineage lymphoma-mediated EGFR ubiquitination. In addition, upon activation by EGFR, Brk directly phosphorylated Y845 in the EGFR kinase domain, thereby further potentiating EGFR kinase activity. Experimental elevation of Brk conferred resistance of breast cancer cells to cetuximab (an EGFR-blocking antibody)-induced inhibition of cell signaling and proliferation, whereas knockdown of Brk sensitized the cells to cetuximab by inducing apoptosis. Our findings reveal a previously unknown role of Brk in EGFR-targeted therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker KT, Jackson LE, Crompton MR . (1997). BRK tyrosine kinase expression in a high proportion of human breast carcinomas. Oncogene 15: 799–805.
Biscardi JS, Maa MC, Tice DA, Cox ME, Leu TH, Parsons SJ . (1999). c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J Biol Chem 274: 8335–8343.
Born M, Quintanilla-Fend L, Braselmann H, Reich U, Richter M, Hutzler P et al. (2005). Simultaneous over-expression of the Her2/neu and PTK6 tyrosine kinases in archival invasive ductal breast carcinomas. J Pathol 205: 592–596.
Chen HY, Shen CH, Tsai YT, Lin FC, Huang YP, Chen RH . (2004). Brk activates rac1 and promotes cell migration and invasion by phosphorylating paxillin. Mol Cell Biol 24: 10558–10572.
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O'Donovan N . (2009). Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 20: 862–867.
Easty DJ, Mitchell PJ, Patel K, Florenes VA, Spritz RA, Bennett DC . (1997). Loss of expression of receptor tyrosine kinase family genes PTK7 and SEK in metastatic melanoma. Int J Cancer 71: 1061–1065.
Eck SM, Cote AL, Winkelman WD, Brinckerhoff CE . (2009). CXCR4 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are elevated in breast carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and in normal mammary fibroblasts exposed to factors secreted by breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 7: 1033–1044.
Forozan F, Veldman R, Ammerman CA, Parsa NZ, Kallioniemi A, Kallioniemi OP et al. (1999). Molecular cytogenetic analysis of 11 new breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 81: 1328–1334.
Grovdal LM, Stang E, Sorkin A, Madshus IH . (2004). Direct interaction of Cbl with pTyr 1045 of the EGF receptor (EGFR) is required to sort the EGFR to lysosomes for degradation. Exp Cell Res 300: 388–395.
Harvey AJ, Crompton MR . (2003). Use of RNA interference to validate Brk as a novel therapeutic target in breast cancer: Brk promotes breast carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncogene 22: 5006–5010.
Harvey AJ, Crompton MR . (2004). The Brk protein tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic target in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Anticancer Drugs 15: 107–111.
Hoadley KA, Weigman VJ, Fan C, Sawyer LR, He X, Troester MA et al. (2007). EGFR associated expression profiles vary with breast tumor subtype. BMC Genomics 8: 258.
Huang F, Goh LK, Sorkin A . (2007). EGF receptor ubiquitination is not necessary for its internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 16904–16909.
Irie HY, Shrestha Y, Selfors LM, Frye F, Iida N, Wang Z et al. (2010). PTK6 regulates IGF-1-induced anchorage-independent survival. PLoS One 5: e11729.
Kamalati T, Jolin HE, Fry MJ, Crompton MR . (2000). Expression of the BRK tyrosine kinase in mammary epithelial cells enhances the coupling of EGF signalling to PI 3-kinase and Akt, via erbB3 phosphorylation. Oncogene 19: 5471–5476.
Kamalati T, Jolin HE, Mitchell PJ, Barker KT, Jackson LE, Dean CJ et al. (1996). Brk, a breast tumor-derived non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase, sensitizes mammary epithelial cells to epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 271: 30956–30963.
Kang SA, Lee ES, Yoon HY, Randazzo PA, Lee ST . (2010). PTK6 inhibits down-regulation of EGF receptor through phosphorylation of ARAP1. J Biol Chem 285: 26013–26021.
Lee ST, Strunk KM, Spritz RA . (1993). A survey of protein tyrosine kinase mRNAs expressed in normal human melanocytes. Oncogene 8: 3403–3410.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Zamir E, Kam Z, Oved S, Langdon WY et al. (1998). c-Cbl/Sli-1 regulates endocytic sorting and ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Genes Dev 12: 3663–3674.
Li X, Lu Y, Liang K, Pan T, Mendelsohn J, Fan Z . (2008). Requirement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha down-regulation in mediating the antitumor activity of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 1207–1217.
Liu L, Gao Y, Qiu H, Miller WT, Poli V, Reich NC . (2006). Identification of STAT3 as a specific substrate of breast tumor kinase. Oncogene 25: 4904–4912.
Llor X, Serfas MS, Bie W, Vasioukhin V, Polonskaia M, Derry J et al. (1999). BRK/Sik expression in the gastrointestinal tract and in colon tumors. Clin Cancer Res 5: 1767–1777.
Lu Y, Li X, Lu H, Fan Z . (2010). 1, 9-Pyrazoloanthrones downregulate HIF-1alpha and sensitize cancer cells to cetuximab-mediated anti-EGFR therapy. PLoS One 5: e15823.
Marmor MD, Yarden Y . (2004). Role of protein ubiquitylation in regulating endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncogene 23: 2057–2070.
Mitchell PJ, Barker KT, Martindale JE, Kamalati T, Lowe PN, Page MJ et al. (1994). Cloning and characterisation of cDNAs encoding a novel non-receptor tyrosine kinase, brk, expressed in human breast tumours. Oncogene 9: 2383–2390.
Normanno N, De Luca A, Maiello MR, Mancino M, D'Antonio A, Macaluso M et al. (2005). Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: current status and future development. Front Biosci 10: 2611–2617.
Ostrander JH, Daniel AR, Lofgren K, Kleer CG, Lange CA . (2007). Breast tumor kinase (protein tyrosine kinase 6) regulates heregulin-induced activation of ERK5 and p38 MAP kinases in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67: 4199–4209.
Polo S, Pece S, Di Fiore PP . (2004). Endocytosis and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16: 156–161.
Qiu H, Miller WT . (2002). Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition. J Biol Chem 277: 34634–34641.
Qiu H, Miller WT . (2004). Role of the Brk SH3 domain in substrate recognition. Oncogene 23: 2216–2223.
Qiu H, Zappacosta F, Su W, Annan RS, Miller WT . (2005). Interaction between Brk kinase and insulin receptor substrate-4. Oncogene 24: 5656–5664.
Rimawi MF, Shetty PB, Weiss HL, Schiff R, Osborne CK, Chamness GC et al. (2010). Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in breast cancer association with biologic phenotype and clinical outcomes. Cancer 116: 1234–1242.
Sainsbury JR, Farndon JR, Sherbet GV, Harris AL . (1985). Epidermal-growth-factor receptors and oestrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Lancet 1: 364–366.
Sartor CI, Dziubinski ML, Yu CL, Jove R, Ethier SP . (1997). Role of epidermal growth factor receptor and STAT-3 activation in autonomous proliferation of SUM-102PT human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 57: 978–987.
Serfas MS, Tyner AL . (2003). Brk, Srm, Frk, and Src42A form a distinct family of intracellular Src-like tyrosine kinases. Oncol Res 13: 409–419.
Shen CH, Chen HY, Lin MS, Li FY, Chang CC, Kuo ML et al. (2008). Breast tumor kinase phosphorylates p190RhoGAP to regulate rho and ras and promote breast carcinoma growth, migration, and invasion. Cancer Res 68: 7779–7787.
Sorkin A, Von Zastrow M . (2009). Endocytosis and signalling: intertwining molecular networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 609–622.
Taketani Y, Oka T . (1983). Biological action of epidermal growth factor and its functional receptors in normal mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 2647–2650.
Tice DA, Biscardi JS, Nickles AL, Parsons SJ . (1999). Mechanism of biological synergy between cellular Src and epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1415–1420.
Waterman H, Katz M, Rubin C, Shtiegman K, Lavi S, Elson A et al. (2002). A mutant EGF-receptor defective in ubiquitylation and endocytosis unveils a role for Grb2 in negative signaling. EMBO J 21: 303–313.
Weaver AM, Silva CM . (2007). Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b: a new target of breast tumor kinase/protein tyrosine kinase 6. Breast Cancer Res 9: R79.
Xiang B, Chatti K, Qiu H, Lakshmi B, Krasnitz A, Hicks J et al. (2008). Brk is coamplified with ErbB2 to promote proliferation in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 12463–12468.
Yamaoka T, Frey MR, Dise RS, Bernard JK, Polk DB . (2011). Specific epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation sites promote mouse colon epithelial cell chemotaxis and restitution. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301: G368–G376.
Zhang P, Ostrander JH, Faivre EJ, Olsen A, Fitzsimmons D, Lange CA . (2005). Regulated association of protein kinase B/Akt with breast tumor kinase. J Biol Chem 280: 1982–1991.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mark R Crompton (University of London) for providing the Brk DNA constructs, Dr Steven P Ethier (Karmanos Cancer Institute) for the SUM series of cell lines and Stephanie Deming (Department of Scientific Publications, MD Anderson Cancer Center) for editing the manuscript. This work was supported in part by grants from the US Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs of the Department of Defense (W81XWH-06-1-0544 and W81XWH-07-1-0526), the Breast Cancer Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (5R01CA129036) and MD Anderson's NIH Cancer Center Support Grant (CA016672).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lu, Y., Liang, K. et al. Brk/PTK6 sustains activated EGFR signaling through inhibiting EGFR degradation and transactivating EGFR. Oncogene 31, 4372–4383 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.608
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.608
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PTK6 inhibits autophagy to promote uveal melanoma tumorigenesis by binding to SOCS3 and regulating mTOR phosphorylation
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Understanding the cellular roles of Fyn-related kinase (FRK): implications in cancer biology
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2016)
-
The Rak/Frk tyrosine kinase associates with and internalizes the epidermal growth factor receptor
Oncogene (2014)
-
Downregulated expression of PTK6 is correlated with poor survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Medical Oncology (2014)
-
Protein tyrosine kinase 6 protects cells from anoikis by directly phosphorylating focal adhesion kinase and activating AKT
Oncogene (2013)