Abstract
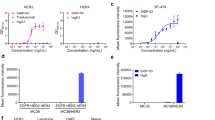
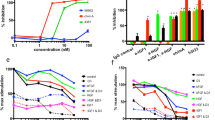
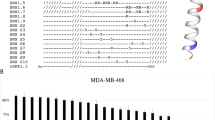
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factors control tumor progression as well as evasion from the toxic effects of chemotherapy. Accordingly, antibodies targeting the cognate receptors, such as EGFR/ErbB-1 and the co-receptor HER2/ErbB-2, are widely used to treat cancer patients, but agents that target the EGF-like growth factors are not available. To circumvent the existence of 11 distinct ErbB ligands, we constructed a soluble fusion protein (hereinafter: TRAP-Fc) comprising truncated extracellular domains of EGFR/ErbB-1 and ErbB-4. The recombinant TRAP-Fc retained high-affinity ligand binding to EGF-like growth factors and partially inhibited growth of a variety of cultured tumor cells. Consistently, TRAP-Fc displayed an inhibitory effect in xenograft models of human cancer, as well as synergy with chemotherapy. Additionally, TRAP-Fc inhibited invasive growth of mammary tumor cells and reduced their metastatic seeding in the lungs of animals. Taken together, the activities displayed by TRAP-Fc reinforce critical roles of EGF-like growth factors in tumor progression, and they warrant further tests of TRAP-Fc in preclinical models.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboud-Pirak E, Hurwitz E, Pirak ME, Bellot F, Schlessinger J, Sela M . (1988). Efficacy of antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor against KB carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 80: 1605–1611.
Adams TE, Koziolek EJ, Hoyne PH, Bentley JD, Lu L, Lovrecz G et al. (2009). A truncated soluble epidermal growth factor receptor-Fc fusion ligand trap displays anti-tumour activity in vivo. Growth Factors 27: 141–154.
Atlas E, Cardillo M, Mehmi I, Zahedkargaran H, Tang C, Lupu R . (2003). Heregulin is sufficient for the promotion of tumorigenicity and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vivo. Mol Cancer Res 1: 165–175.
Barozzi C, Ravaioli M, D'Errico A, Grazi GL, Poggioli G, Cavrini G et al. (2002). Relevance of biological markers in colorectal carcinoma: a comparative study of a broad panel. Cancer 94: 647–657.
Baselga J . (2006). Targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer: the second wave. Science 312: 1175–1178.
Bianchi S, Palli D, Falchetti M, Saieva C, Masala G, Mancini B et al. (2006). ErbB-receptors expression and survival in breast carcinoma: a 15-year follow-up study. J Cell Physiol 206: 702–708.
Bijman MN, van Berkel MP, Kok M, Janmaat ML, Boven E . (2009). Inhibition of functional HER family members increases the sensitivity to docetaxel in human ovarian cancer cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 20: 450–460.
Britten CD . (2004). Targeting ErbB receptor signaling: a pan-ErbB approach to cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 1335–1342.
Chen X, Levkowitz G, Tzahar E, Karunagaran D, Lavi S, Ben-Baruch N et al. (1996). An immunological approach reveals biological differences between the two NDF/heregulin receptors, ErbB-3 and ErbB-4. J Biol Chem 271: 7620–7629.
De Jong KP, Stellema R, Karrenbeld A, Koudstaal J, Gouw AS, Sluiter WJ et al. (1998). Clinical relevance of transforming growth factor alpha, epidermal growth factor receptor, p53, and Ki67 in colorectal liver metastases and corresponding primary tumors. Hepatology 28: 971–979.
De Luca A, Carotenuto A, Rachiglio A, Gallo M, Maiello MR, Aldinucci D et al. (2008). The role of the EGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. J Cell Physiol 214: 559–567.
Domagala T, Konstantopoulos N, Smyth F, Jorissen RN, Fabri L, Geleick D et al. (2000). Stoichiometry, kinetic and binding analysis of the interaction between epidermal growth factor (EGF) and the extracellular domain of the EGF receptor. Growth Factors 18: 11–29.
Elleman TC, Domagala T, McKern NM, Nerrie M, Lonnqvist B, Adams TE et al. (2001). Identification of a determinant of epidermal growth factor receptor ligand-binding specificity using a truncated, high-affinity form of the ectodomain. Biochemistry 40: 8930–8939.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO et al. (2007). MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316: 1039–1043.
Fitzpatrick VD, Pisacane PI, Vandlen RL, Sliwkowski MX . (1998). Formation of a high affinity heregulin binding site using the soluble extracellular domains of ErbB2 with ErbB3 or ErbB4. FEBS Lett 431: 102–106.
Freeman DJ, Bush T, Ogbagabriel S, Belmontes B, Juan T, Plewa C et al. (2009). Activity of panitumumab alone or with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines expressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cancer Ther 8: 1536–1546.
Grandis JR, Chakraborty A, Zeng Q, Melhem MF, Tweardy DJ . (1998). Downmodulation of TGF-alpha protein expression with antisense oligonucleotides inhibits proliferation of head and neck squamous carcinoma but not normal mucosal epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem 69: 55–62.
Hsieh SY, He JR, Hsu CY, Chen WJ, Bera R, Lin KY et al. (2011). Neuregulin/erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 3 autocrine loop contributes to invasion and early recurrence of human hepatoma. Hepatology 53: 504–516.
Ishikawa N, Daigo Y, Takano A, Taniwaki M, Kato T, Hayama S et al. (2005). Increases of amphiregulin and transforming growth factor-alpha in serum as predictors of poor response to gefitinib among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res 65: 9176–9184.
Jones JT, Akita RW, Sliwkowski MX . (1999). Binding specificities and affinities of egf domains for ErbB receptors. FEBS Lett 447: 227–231.
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW . (2003). Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 284: 31–53.
Karamouzis MV, Badra FA, Papavassiliou AG . (2007). Breast cancer: the upgraded role of HER-3 and HER-4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39: 851–856.
Krane IM, Leder P . (1996). NDF/heregulin induces persistence of terminal end buds and adenocarcinomas in the mammary glands of transgenic mice. Oncogene 12: 1781–1788.
Lindzen M, Lavi S, Leitner O, Yarden Y . (2010). Tailored cancer immunotherapy using combinations of chemotherapy and a mixture of antibodies against EGF-receptor ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 12559–12563.
Mackenzie RP, McCollum AD . (2009). Novel agents for the treatment of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 9: 1473–1485.
Riese 2nd DJ, Stern DF . (1998). Specificity within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network. Bioessays 20: 41–48.
Ritter CA, Perez-Torres M, Rinehart C, Guix M, Dugger T, Engelman JA et al. (2007). Human breast cancer cells selected for resistance to trastuzumab in vivo overexpress epidermal growth factor receptor and ErbB ligands and remain dependent on the ErbB receptor network. Clin Cancer Res 13: 4909–4919.
Sanui A, Yotsumoto F, Tsujioka H, Fukami T, Horiuchi S, Shirota K et al. (2010). HB-EGF inhibition in combination with various anticancer agents enhances its antitumor effects in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 30: 3143–3149.
Sarup J, Jin P, Turin L, Bai X, Beryt M, Brdlik C et al. (2008). Human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER-1:HER-3) Fc-mediated heterodimer has broad antiproliferative activity in vitro and in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 3223–3236.
Sheng Q, Liu X, Fleming E, Yuan K, Piao H, Chen J et al. (2010). An activated ErbB3/NRG1 autocrine loop supports in vivo proliferation in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell 17: 298–310.
Sporn MB, Todaro GJ . (1980). Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med 303: 878–880.
Sun M, Behrens C, Feng L, Ozburn N, Tang X, Yin G et al. (2009). HER family receptor abnormalities in lung cancer brain metastases and corresponding primary tumors. Clin Cancer Res 15: 4829–4837.
Thogersen VB, Sorensen BS, Poulsen SS, Orntoft TF, Wolf H, Nexo E . (2001). A subclass of HER1 ligands are prognostic markers for survival in bladder cancer patients. Cancer Res 61: 6227–6233.
Tsujioka H, Yotsumoto F, Hikita S, Ueda T, Kuroki M, Miyamoto S . (2011). Targeting the heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in ovarian cancer therapy. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 23: 24–30.
Valabrega G, Montemurro F, Sarotto I, Petrelli A, Rubini P, Tacchetti C et al. (2005). TGFalpha expression impairs Trastuzumab-induced HER2 downregulation. Oncogene 24: 3002–3010.
Weiner LM, Borghaei H . (2006). Targeted therapies in solid tumors: monoclonal antibodies and small molecules. Hum Antibodies 15: 103–111.
Wheeler DL, Huang S, Kruser TJ, Nechrebecki MM, Armstrong EA, Benavente S et al. (2008). Mechanisms of acquired resistance to cetuximab: role of HER (ErbB) family members. Oncogene 27: 3944–3956.
Witsch E, Sela M, Yarden Y . (2010). Roles for growth factors in cancer progression. Physiology (Bethesda) 25: 85–101.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . (2001). Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 127–137.
Zhou BB, Peyton M, He B, Liu C, Girard L, Caudler E et al. (2006). Targeting ADAM-mediated ligand cleavage to inhibit HER3 and EGFR pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 10: 39–50.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the help of the Israel Structural Proteomics Center. Our lab is supported by the National Cancer Institute (CA072981), the Israel Cancer Research Fund and Dr Miriam and Sheldon G Adelson Medical Research Foundation. WJK received a fellowship for PhD track for specialist medical doctors from the Linda and Michael Jacobs Charitable Trust. YY is the incumbent of the Harold and Zelda Goldenberg Professorial Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindzen, M., Carvalho, S., Starr, A. et al. A recombinant decoy comprising EGFR and ErbB-4 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 31, 3505–3515 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.518
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.518
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Senescence-associated reprogramming induced by interleukin-1 impairs response to EGFR neutralization
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2022)
-
Targeting autocrine amphiregulin robustly and reproducibly inhibits ovarian cancer in a syngeneic model: roles for wildtype p53
Oncogene (2021)
-
An antibody to amphiregulin, an abundant growth factor in patients’ fluids, inhibits ovarian tumors
Oncogene (2016)
-
Targeting non-canonical autophagy overcomes erlotinib resistance in tongue cancer
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
Strategies of targeting the extracellular domain of RON tyrosine kinase receptor for cancer therapy and drug delivery
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2016)