Abstract
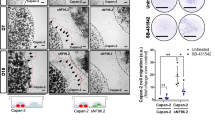
Merlin is a tumour suppressor involved in the development of a variety of tumours including mesotheliomas. Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a dominantly inherited tumour disease, is also caused by loss of merlin. NF2 patients suffer from multiple genetically well-defined tumours, schwannomas are most frequent among those. Using our in vitro model for human schwannoma, we found that schwannoma cells display enhanced proliferation because of the overexpression/activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor and ErbB2/3, increased cell–matrix adhesion because of the overexpression of integrins, and decreased apoptosis. Mechanisms underlying schwannomas basal proliferation and cell–matrix adhesion are not understood. Here, we investigated insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), which is expressed and released from central nervous system tumours and strongly overexpressed in schwannoma at the mRNA level. IGFBP-1 acts via β1-integrin and focal-adhesion-kinase (FAK), which are strongly overexpressed and basally activated in schwannoma. Using short hairpin RNA knockdown, small inhibitors and recombinant IGFBP-1, we demonstrate that schwannoma cells, in contrast to Schwann cells, release IGFBP-1 that activates the Src/FAK pathway, via integrin β1, potentiating schwannoma's proliferation and cell–matrix adhesion. We show that FAK localizes to the nucleus and Src triggers IGFBP-1 production. Further, we observed downregulation of the tumour-suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog in schwannoma cells leading to increased activity of anti-apoptotic AKT. Thus, IGFBP-1/integrin β1/Src/FAK pathway has a crucial role in merlin-related tumourigenesis and therefore represents an important therapeutic target in the treatment of merlin-deficient tumours.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammoun S, Cunliffe CH, Allen JC, Chiriboga L, Giancotti FG, Zagzag D et al. (2010a). ErbB/HER receptor activation and preclinical efficacy of lapatinib in vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol 12: 834–843.
Ammoun S, Flaiz C, Ristic N, Schuldt J, Hanemann CO . (2008). Dissecting and targeting the growth factor-dependent and growth factor-independent extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in human schwannoma. Cancer Res 68: 5236–5245.
Ammoun S, Ristic N, Matthies C, Hilton DA, Hanemann CO . (2010b). Targeting ERK1/2 activation and proliferation in human primary schwannoma cells with MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244. Neurobiol Dis 37: 141–146.
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A . (2007). PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis 28: 1379–1386.
Bretscher A, Edwards K, Fehon RG . (2002). ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 586–599.
Chaves J, Saif . (2011). MW IGF system in cancer: from bench to clinic. Anticancer Drugs 22: 206–212.
Feron M, Guevel L, Rouger K, Dubreil L, Arnaud MC, Ledevin M et al. (2009). PTEN contributes to profound PI3K/Akt signaling pathway deregulation in dystrophin-deficient dog muscle. Am J Pathol 174: 1459–1470.
Flaiz C, Kaempchen K, Matthies C, Hanemann CO . (2007). Actin-rich protrusions and nonlocalized GTPase activation in merlin-deficient schwannomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66: 608–616.
Fraenzer JT, Pan H, Minimo Jr L, Smith GM, Knauer D, Hung G . (2003). Overexpression of the NF2 gene inhibits schwannoma cell proliferation through promoting PDGFR degradation. Int J Oncol 23: 1493–1500.
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E . (1999). Integrin signaling. Science 285: 1028–1032.
Hanemann CO, Bartelt-Kirbach B, Diebold R, Kampchen K, Langmesser S, Utermark T . (2006). Differential gene expression between human schwannoma and control Schwann cells. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32: 605–614.
Hilton DA, Ristic N, Hanemann CO . (2009). Activation of ERK, AKT and JNK signalling pathways in human schwannomas in situ. Histopathology 55: 744–749.
Hiromura M, Okada F, Obata T, Auguin D, Shibata T, Roumestand C et al. (2004). Inhibition of Akt kinase activity by a peptide spanning the betaA strand of the proto-oncogene TCL1. J Biol Chem 279: 53407–53418.
Houshmandi SS, Emnett RJ, Giovannini M, Gutmann DH . (2009). The neurofibromatosis 2 protein, merlin, regulates glial cell growth in an ErbB2- and Src-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol 29: 1472–1486.
Jones JI, Busby Jr WH, Wright G, Smith CE, Kimack NM, Clemmons DR . (1993a). Identification of the sites of phosphorylation in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1. Regulation of its affinity by phosphorylation of serine 101. J Biol Chem 268: 1125–1131.
Jones JI, D'Ercole AJ, Camacho-Hubner C, Clemmons DR . (1991). Phosphorylation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein 1 in cell culture and in vivo: effects on affinity for IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 7481–7485.
Jones JI, Gockerman A, Busby Jr WH, Wright G, Clemmons DR . (1993b). Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 stimulates cell migration and binds to the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin by means of its Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 10553–10557.
Kaempchen K, Mielke K, Utermark T, Langmesser S, Hanemann CO . (2003). Upregulation of the Rac1/JNK signaling pathway in primary human schwannoma cells. Hum Mol Genet 12: 1211–1221.
Leu TH, Maa MC . (2002). Tyr-863 phosphorylation enhances focal adhesion kinase autophosphorylation at Tyr-397. Oncogene 21: 6992–7000.
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI et al. (1997). PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 275: 1943–1947.
Lim ST, Chen XL, Lim Y, Hanson DA, Vo TT, Howerton K et al. (2008a). Nuclear FAK promotes cell proliferation and survival through FERM-enhanced p53 degradation. Mol Cell 29: 9–22.
Lim ST, Mikolon D, Stupack DG, Schlaepfer DD . (2008b). FERM control of FAK function: implications for cancer therapy. Cell Cycle 7: 2306–2314.
Lin CH, Yeh SH, Leu TH, Chang WC, Wang ST, Gean PW . (2003). Identification of calcineurin as a key signal in the extinction of fear memory. J Neurosci 23: 1574–1579.
Liu W, Zhou Y, Reske SN, Shen C . (2008). PTEN mutation: many birds with one stone in tumorigenesis. Anticancer Res 28: 3613–3619.
McClatchey AI, Fehon RG . (2009). Merlin and the ERM proteins—regulators of receptor distribution and signaling at the cell cortex. Trends Cell Biol 19: 198–206.
Milner R, Wilby M, Nishimura S, Boylen K, Edwards G, Fawcett J et al. (1997). Division of labor of Schwann cell integrins during migration on peripheral nerve extracellular matrix ligands. Dev Biol 185: 215–228.
Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD . (2006). Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 516–523.
Morrison H, Sperka T, Manent J, Giovannini M, Ponta H, Herrlich P . (2007). Merlin/neurofibromatosis type 2 suppresses growth by inhibiting the activation of Ras and Rac. Cancer Res 67: 520–527.
Nagashima T, Maruyama T, Uchida H, Kajitani T, Arase T, Ono M et al. (2008). Activation of SRC kinase and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 are required for decidual transformation of human endometrial stromal cells. Endocrinology 149: 1227–1234.
Okada T, You L, Giancotti FG . (2007). Shedding light on Merlin's wizardry. Trends Cell Biol 17: 222–229.
Park CH, Kim YS, Kim YH, Choi MY, Yoo JM, Kang SS et al. (2008). Calcineurin mediates AKT dephosphorylation in the ischemic rat retina. Brain Res 1234: 148–157.
Perks CM, Vernon EG, Rosendahl AH, Tonge D, Holly JM . (2007). IGF-II and IGFBP-2 differentially regulate PTEN in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26: 5966–5972.
Rong R, Tang X, Gutmann DH, Ye K . (2004). Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) tumor suppressor merlin inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase through binding to PIKE-L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 18200–18205.
Rosenbaum C, Kamleiter M, Grafe P, Kluwe L, Mautner V, Muller HW et al. (2000). Enhanced proliferation and potassium conductance of Schwann cells isolated from NF2 schwannomas can be reduced by quinidine. Neurobiol Dis 7: 483–491.
Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, Sanson M, Zucman J, Marineau C et al. (1993). Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2 (see comments). Nature 363: 515–521.
Schlaepfer DD, Hanks SK, Hunter T, van der GP . (1994). Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 372: 786–791.
Schlaepfer DD, Mitra SK, Ilic D . (2004). Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1692: 77–102.
Schutt BS, Langkamp M, Rauschnabel U, Ranke MB, Elmlinger MW . (2004). Integrin-mediated action of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 in tumor cells. J Mole Endocrinol 32: 859–868.
Trotman LC, Wang X, Alimonti A, Chen Z, Teruya-Feldstein J, Yang H et al. (2007). Ubiquitination regulates PTEN nuclear import and tumor suppression. Cell 128: 141–156.
Utermark T, Kaempchen K, Antoniadis G, Hanemann CO . (2005). Reduced apoptosis rates in human schwannomas. Brain Pathol 15: 17–22.
Utermark T, Kaempchen K, Hanemann CO . (2003). Pathological adhesion of primary human schwannoma cells is dependent on altered expression of integrins. Brain Pathol 13: 352–363.
Wheatcroft SB, Kearney MT . (2009). IGF-dependent and IGF-independent actions of IGF-binding protein-1 and -2: implications for metabolic homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20: 153–162.
Xiao GH, Gallagher R, Shetler J, Skele K, Altomare DA, Pestell RG et al. (2005). The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by repressing cyclin D1 expression. Mol Cell Biol 25: 2384–2394.
Yee D . (2002). The insulin-like growth factor system as a treatment target in breast cancer. Semin Oncol 29: 86–95.
Zhang H, Yee D . (2006). Is the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer? Clin Cancer Res 12: 6323–6325.
Zumkeller W, Westphal M . (2001). The IGF/IGFBP system in CNS malignancy. Mol Pathol 54: 227–229.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CTF, Northcott Devon Medical Foundation and by Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth, UK. Pfizer supplied inhibitor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ammoun, S., Schmid, M., Zhou, L. et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) regulates human schwannoma proliferation, adhesion and survival. Oncogene 31, 1710–1722 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.357
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.357
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serum IGFBP-1 as a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 regulates HIF-1α degradation to inhibit apoptosis in hypoxic cardiomyocytes
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
IGFBP-1 expression is reduced in human type 2 diabetic glomeruli and modulates β1-integrin/FAK signalling in human podocytes
Diabetologia (2021)
-
Inactivation of Stat3 and crosstalk of miRNA155-5p and FOXO3a contribute to the induction of IGFBP1 expression by beta-elemene in human lung cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
Identification of candidate genes for devil facial tumour disease tumourigenesis
Scientific Reports (2017)