Abstract
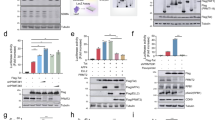
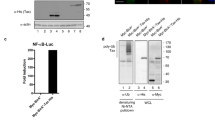
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) encodes a Tax oncoprotein that has crucial roles in both virus replication and cell transformation. Our recent studies suggest that the counterbalance between HTLV-I/Tax and PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein PDLIM2 may determine the outcome of HTLV-I infection. Although HTLV-I represses PDLIM2 epigenetically and specifically in transformed cells, PDLIM2 shuttles Tax into the nuclear matrix for ubiquitination-mediated proteasomal degradation, thereby suppressing the transforming ability of HTLV-I. Here, we have further shown that PDLIM2 binds to Tax directly, which was mediated by a putative α-helix motif of PDLIM2 at amino acids 236–254. Consistently, selective disruption of this short-helix crippled PDLIM2 in shutting Tax to the nuclear matrix for ubiquitination-mediated degradation, therefore, PDLIM2 lost the ability in tumor suppression. Although the C-terminal LIM domain of PDLIM2 was not required for Tax binding, it was important for PDLIM2 to interact with the nuclear matrix. Accordingly, the LIM domain was essential for PDLIM2-mediated Tax repression. On the contrary, the N-terminal PDZ domain of PDLIM2 was dispensable for all these events, although the PDZ domain was involved in PDLIM2 binding to cytoskeleton. These studies dissect functional sequences within PDLIM2 and their distinct roles in Tax regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Ono H, Shimotohno K . (1995). Characterization of T cells immortalized by Tax1 of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Blood 86: 4243–4249.
Bex F, McDowall A, Burny A, Gaynor R . (1997). The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 transactivator protein Tax colocalizes in unique nuclear structures with NF-κB proteins. J Virol 71: 3484–3497.
Boxus M, Twizere JC, Legros S, Dewulf JF, Kettmann R, Willems L . (2008). The HTLV-1 Tax interactome. Retrovirology 5: 76–110.
Fryrear KA, Durkin SS, Gupta SK, Tiedebohl JB, Semmes OJ . (2009). Dimerization and a novel Tax speckled structure localization signal are required for Tax nuclear localization. J Virol 83: 5339–5352.
Gallo RC . (2005). The discovery of the first human retrovirus: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Retrovirology 2: 17.
Grassmann R, Aboud M, Jeang KT . (2005). Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 Tax. Oncogene 24: 5976–5985.
Grassmann R, Berchtold S, Radant I, Alt M, Fleckenstein B, Sodroski JG et al. (1992). Role of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 X region proteins in immortalization of primary human lymphocytes in culture. J Virol 66: 4570–4575.
Grossman WJ, Kimata JT, Wong FH, Zutter M, Ley TJ, Ratner L . (1995). Development of leukemia in mice transgenic for the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1057–1061.
Hasegawa H, Sawa H, Lewis MJ, Orba Y, Sheehy N, Yamamoto Y et al. (2006). Thymus-derived leukemia-lymphoma in mice transgenic for the Tax gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nat Med 12: 466–472.
Kwon H, Ogle L, Benitez B, Bohuslav J, Montano M, Felsher DW et al. (2005). Lethal cutaneous disease in transgenic mice conditionally expressing type I human T cell leukemia virus Tax. J Biol Chem 280: 35713–35722.
Loughran G, Healy NC, Kiely PA, Huigsloot M, Kedersha NL, O'Connor R . (2005). Mystique is a new insulin-like growth factor-I-regulated PDZ-LIM domain protein that promotes cell attachment and migration and suppresses anchorage-independent growth. Mol Biol Cell 16: 1811–1822.
Nerenberg M, Hinrichs SH, Reynolds RK, Khoury G, Jay G . (1987). The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science 237: 1324–1329.
Oka T, Sonobe H, Iwata J, Kubonishi I, Satoh H, Takata M et al. (1992). Phenotypic progression of a rat lymphoid cell line immortalized by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 to induce lymphoma/leukemia-like disease in rats. J Virol 66: 6686–6694.
Peebles RS, Maliszewski CR, Sato TA, Hanley-Hyde J, Maroulakou IG, Hunziker R et al. (1995). Abnormal B-cell function in HTLV-I-tax transgenic mice. Oncogene 10: 1045–1051.
Pozzatti R, Vogel J, Jay G . (1990). The human T-lymphotropic virus type I tax gene can cooperate with the ras oncogene to induce neoplastic transformation of cells. Mol Cell Biol 10: 413–417.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . (2005). Regulation of NF-κB2 p100 processing by its cis-activating domain. J Biol Chem 280: 18–27.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . (2007). Proteasome-mediated endoproteolytic processing of the NF-κB2 precursor at the κB promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 5324–5329.
Qu Z, Fu J, Yan P, Hu J, Cheng S, Xiao G . (2010a). Epigenetic repression of PDLIM2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer. J Biol Chem 285: 11786–11792.
Qu Z, Qing G, Rabson R, Xiao G . (2004). Tax deregulation of NF-κB2 p100 processing involves both β-TrCP-dependent and independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 279: 44563–44572.
Qu Z, Yan P, Fu J, Jiang J, Grusby MJ, Smithgall TE et al. (2010b). DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDZ-LIM-containing protein 2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Res 70: 1766–1772.
Radivojac P, Iakoucheva LM, Oldfield CJ, Obradovic Z, Uversky VN, Dunker AK . (2007). Intrinsic disorder and functional proteomics. Biophys J 92: 1439–1456.
Rousset R, Fabre S, Desbois C, Bantignies F, Jalinot P . (1998). The C-terminus of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein mediates interaction with the PDZ domain of cellular proteins. Oncogene 16: 643–654.
Semmes OJ, Jeang KT . (1996). Localization of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax to subnuclear compartments that overlap with interchromatin speckles. J Virol 70: 6347–6357.
Sun SC, Yamaoka S . (2005). Activation of NF-κB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation. Oncogene 24: 5952–5964.
Takatsuki K . (2005). Discovery of adult T-cell leukemia. Retrovirology 2: 16.
Tanaka A, Takahashi C, Yamaoka S, Nosaka T, Maki M, Hatanaka M . (1990). Oncogenic transformation by the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1071–1075.
Tanaka T, Grusby MJ, Kaisho T . (2007). PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-κB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nat Immunol 8: 584–591.
Tanaka T, Soriano MA, Grusby MJ . (2005). SLIM is a nuclear ubiquitin E3 ligase that negatively regulates STAT signaling. Immunity 22: 729–736.
Torrado M, Senatorov VV, Trivedi R, Fariss RN, Tomarev SI . (2004). Pdlim2, a novel PDZ-LIM domain protein, interacts with alpha-actinins and filamin A. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45: 3955–3963.
Xiao G, Harhaj EW, Sun SC . (2000). Domain-specific interaction with IKKγ is an essential step in Tax-mediated activation of IKK. J Biol Chem 275: 34060–34067.
Xiao G, Rabson A, Young W, Qing G, Qu Z . (2006). Alternative pathways of NF-κB activation: a double-edged sword in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 281–293.
Yamaoka S, Tobe T, Hatanaka M . (1992). Tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Oncogene 7: 43–47.
Yan P, Fu J, Qu Z, Li S, Tanaka T, Grusby MJ et al. (2009a). PDLIM2 suppresses HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis by targeting Tax into the nuclear matrix for proteasomal degradation. Blood 113: 4370–4380.
Yan P, Qu Z, Ishikawa C, Mori N, Xiao G . (2009b). HTLV-I-mediated repression of PDLIM2 involves DNA methylation but independent of the viral oncoprotein Tax. Neoplasia 11: 1036–1041.
Yoshida M . (2005). Discovery of HTLV-1, the first human retrovirus, its unique regulatory mechanisms, and insights into pathogenesis. Oncogene 24: 5931–5937.
Acknowledgements
We thank N Raab-Traub for Rat-1 cells, OJ Semmes for Tax-GFP mutants, and NIH AIDS Research & Reference Reagent Program for various reagents. This study was supported by NIH/NCI Grant R01 CA116616 and ACS Grant RSG-06-066-01-MGO to G Xiao.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., Yan, P., Li, S. et al. Molecular determinants of PDLIM2 in suppressing HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 29, 6499–6507 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.374
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.374
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Causative role of PDLIM2 epigenetic repression in lung cancer and therapeutic resistance
Nature Communications (2019)
-
NF-κB1 p105 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through the Tpl2 kinase but independently of its NF-κB function
Oncogene (2016)
-
Differential roles of STAT3 in the initiation and growth of lung cancer
Oncogene (2015)
-
PDLIM2 restricts Th1 and Th17 differentiation and prevents autoimmune disease
Cell & Bioscience (2012)