Abstract
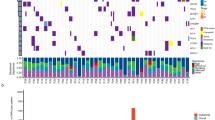
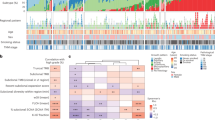
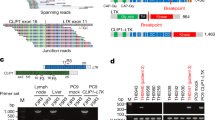
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most aggressive subtype of lung cancer in its clinical behavior, with a 5-year overall survival as low as 5%. Despite years of research in the field, molecular determinants of SCLC behavior are still poorly understood, and this deficiency has translated into an absence of specific diagnostics and targeted therapeutics. We hypothesized that tumor DNA copy number alterations would allow the identification of molecular pathways involved in SCLC progression. Array comparative genomic hybridization was performed on DNA extracted from 46 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded SCLC tissue specimens. Genomic profiling of tumor and sex-matched control DNA allowed the identification of 70 regions of copy number gain and 55 regions of copy number loss. Using molecular pathway analysis, we found a strong enrichment in these regions of copy number alterations for 11 genes associated with the focal adhesion pathway. We verified these findings at the genomic, gene expression and protein level. Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK), one of the central genes represented in this pathway, was commonly expressed in SCLC tumors and constitutively phosphorylated in SCLC cell lines. Those were poorly adherent to most substrates but not to laminin-322. Inhibition of FAK phosphorylation at Tyr397 by a small-molecule inhibitor, PF-573,228, induced a dose-dependent decrease of adhesion and an increase of spreading in SCLC cell lines on laminin-322. Cells that tended to spread also showed a decrease in focal adhesions, as demonstrated by a decreased vinculin expression. These results support the concept that pathway analysis of genes in regions of copy number alterations may uncover molecular mechanisms of disease progression and demonstrate a new role of FAK and associated adhesion pathways in SCLC. Further investigations of FAK at the functional level may lead to a better understanding of SCLC progression and may have therapeutic implications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balsara BR, Testa JR . (2002). Chromosomal imbalances in human lung cancer. Oncogene 21: 6877–6883.
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP . (2003). A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19: 185–193.
Burridge K, Turner CE, Romer LH . (1992). Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol 119: 893–903.
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L et al. (2005). Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97: 643–655.
Coe BP, Lockwood WW, Girard L, Chari R, Macaulay C, Lam S et al. (2006). Differential disruption of cell cycle pathways in small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 94: 1927–1935.
Cooper S, Spiro SG . (2006). Small cell lung cancer: treatment review. Respirology 11: 241–248.
Gabarra-Niecko V, Schaller MD, Dunty JM . (2003). FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22: 359–374.
Gallia GL, Rand V, Siu IM, Eberhart CG, James CD, Marie SK et al. (2006). PIK3CA gene mutations in pediatric and adult glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Res 4: 709–714.
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M et al. (2001). Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 13784–13789.
Greulich H, Chen TH, Feng W, Janne PA, Alvarez JV, Zappaterra M et al. (2005). Oncogenic transformation by inhibitor-sensitive and -resistant EGFR mutants. PLoS Med 2: e313.
Guan JL, Trevithick JE, Hynes RO . (1991). Fibronectin/integrin interaction induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a 120-kDa protein. Cell Regul 2: 951–964.
Hanks SK, Ryzhova L, Shin NY, Brabek J . (2003). Focal adhesion kinase signaling activities and their implications in the control of cell survival and motility. Front Biosci 8: d982–d996.
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn Jr PA, Di Maria MV, Veve R, Bremmes RM et al. (2003). Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol 21: 3798–3807.
Jackman DM, Johnson BE . (2005). Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 366: 1385–1396.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ . (2009). Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59: 225–249.
Kim YH, Girard L, Giacomini CP, Wang P, Hernandez-Boussard T, Tibshirani R et al. (2006). Combined microarray analysis of small cell lung cancer reveals altered apoptotic balance and distinct expression signatures of MYC family gene amplification. Oncogene 25: 130–138.
Kirov SA, Peng X, Baker E, Schmoyer D, Zhang B, Snoddy J . (2005). GeneKeyDB: a lightweight, gene-centric, relational database to support data mining environments. BMC Bioinformatics 6: 72.
Levin NA, Brzoska P, Gupta N, Minna JD, Gray JW, Christman MF . (1994). Identification of frequent novel genetic alterations in small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 54: 5086–5091.
Lindblad-Toh K, Tanenbaum DM, Daly MJ, Winchester E, Lui WO, Villapakkam A et al. (2000). Loss-of-heterozygosity analysis of small-cell lung carcinomas using single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Nat Biotechnol 18: 1001–1005.
Massion PP, Kuo WL, Stokoe D, Olshen AB, Treseler PA, Chin K et al. (2002). Genomic copy number analysis of non-small cell lung cancer using array comparative genomic hybridization: implications of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Cancer Res 62: 3636–3640.
Massion PP, Taflan PM, Jamshedur Rahman SM, Yildiz P, Shyr Y, Edgerton ME et al. (2003). Significance of p63 amplification and overexpression in lung cancer development and prognosis. Cancer Res 63: 7113–7121.
Massion PP, Zou Y, Chen H, Jiang A, Coulson P, Amos CI et al. (2008). Smoking-related genomic signatures in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178: 1164–1172.
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD . (2005). Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 56–68.
Miura I, Graziano SL, Cheng JQ, Doyle LA, Testa JR . (1992). Chromosome alterations in human small cell lung cancer: frequent involvement of 5q. Cancer Res 52: 1322–1328.
Olejniczak ET, Van Sant C, Anderson MG, Wang G, Tahir SK, Sauter G et al. (2007). Integrative genomic analysis of small-cell lung carcinoma reveals correlates of sensitivity to bcl-2 antagonists and uncovers novel chromosomal gains. Mol Cancer Res 5: 331–339.
Osada H, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Tatematsu Y, Takeuchi T, Murakami H et al. (2008). Roles of achaete-scute homologue 1 in DKK1 and E-cadherin repression and neuroendocrine differentiation in lung cancer. Cancer Res 68: 1647–1655.
Owens LV, Xu L, Craven RJ, Dent GA, Weiner TM, Kornberg L et al. (1995). Overexpression of the focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in invasive human tumors. Cancer Res 55: 2752–2755.
Parsons JT . (2003). Focal adhesion kinase: the first ten years. J Cell Sci 116: 1409–1416.
Peng WX, Shibata T, Katoh H, Kokubu A, Matsuno Y, Asamura H et al. (2005). Array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis of high-grade neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Cancer Sci 96: 661–667.
Pinkel D, Segraves R, Sudar D, Clark S, Poole I, Kowbel D et al. (1998). High resolution analysis of DNA copy number variation using comparative genomic hybridization to microarrays. Nat Genet 20: 207–211.
Qian J, Zou Y, Rahman JS, Lu B, Massion PP . (2009). Synergy between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and Bcl-xL in the control of apoptosis in adenocarcinoma cells of the lung. Mol Cancer Ther 8: 101–109.
Ried T, Petersen I, Holtgreve-Grez H, Speicher MR, Schrock E, du Manoir S et al. (1994). Mapping of multiple DNA gains and losses in primary small cell lung carcinomas by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Res 54: 1801–1806.
Roberts WG, Ung E, Whalen P, Cooper B, Hulford C, Autry C et al. (2008). Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res 68: 1935–1944.
Rozengurt E . (2007). Mitogenic signaling pathways induced by G protein-coupled receptors. J Cell Physiol 213: 589–602.
Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH . (1995). Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 11: 549–599.
Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Keir ST, Song L, Wickman S, Jackson D et al. (2007). A novel low-molecular weight inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, TAE226, inhibits glioma growth. Mol Carcinog 46: 488–496.
Sidhu GS . (1979). The endodermal origin of digestive and respiratory tract APUD cells. Histopathologic evidence and a review of the literature. Am J Pathol 96: 5–20.
Siesser PM, Hanks SK . (2006). The signaling and biological implications of FAK overexpression in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12: 3233–3237.
Slack-Davis JK, Martin KH, Tilghman RW, Iwanicki M, Ung EJ, Autry C et al. (2007). Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 282: 14845–14852.
Sozzi G, Bertoglio MG, Borrello MG, Giani S, Pilotti S, Pierotti M et al. (1987). Chromosomal abnormalities in a primary small cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 27: 45–50.
Taniwaki M, Daigo Y, Ishikawa N, Takano A, Tsunoda T, Yasui W et al. (2006). Gene expression profiles of small-cell lung cancers: molecular signatures of lung cancer. Int J Oncol 29: 567–575.
Tanno S, Ohsaki Y, Nakanishi K, Toyoshima E, Kikuchi K . (2004). Human small cell lung cancer cells express functional VEGF receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3. Lung Cancer 46: 11–19.
Ullmann R, Schwendel A, Klemen H, Wolf G, Petersen I, Popper HH . (1998). Unbalanced chromosomal aberrations in neuroendocrine lung tumors as detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Hum Pathol 29: 1145–1149.
Webb DJ, Donais K, Whitmore LA, Thomas SM, Turner CE, Parsons JT et al. (2004). FAK-Src signalling through paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly. Nat Cell Biol 6: 154–161.
Zhang B, Kirov S, Snoddy J . (2005). WebGestalt: an integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res 33: W741–W748.
Zhao X, Weir BA, LaFramboise T, Lin M, Beroukhim R, Garraway L et al. (2005). Homozygous deletions and chromosome amplifications in human lung carcinomas revealed by single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis. Cancer Res 65: 5561–5570.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kathy Taylor, Director of the Research Institute at St Thomas Health Services, Nashville, TN, for sharing archived SCLC tissue blocks; Dr Coe for providing array CGH data (Coe et al., 2006); and Vanderbilt's Immunohistochemistry Core (supported by a Cancer Center Support Grant 5P30 CA068485) for their contribution. We also thank Steven K Hanks, Alissa M Weaver and Donna J Webb for their useful input in the interpretation of the paper. This work was supported by a Merit Review grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr Ocak was supported by an IASLC Young Investigator Fellowship Award and by a grant from Université Catholique de Louvain (Bourse Clinicien-Chercheur), Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocak, S., Yamashita, H., Udyavar, A. et al. DNA copy number aberrations in small-cell lung cancer reveal activation of the focal adhesion pathway. Oncogene 29, 6331–6342 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.362
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.362
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cellular Heterogeneity–Adjusted cLonal Methylation (CHALM) improves prediction of gene expression
Nature Communications (2021)
-
ENVE: a novel computational framework characterizes copy-number mutational landscapes in colorectal cancers from African American patients
Genome Medicine (2015)
-
Integrated analyses of copy number variations and gene differential expression in lung squamous-cell carcinoma
Biological Research (2015)
-
Co-expression network analysis identifies Spleen Tyrosine Kinase (SYK) as a candidate oncogenic driver in a subset of small-cell lung cancer
BMC Systems Biology (2013)
-
Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase correlates with increased lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)