Abstract
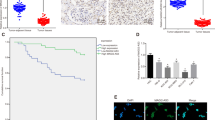
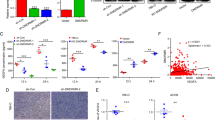
Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) are crucial regulators of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. The autocrine VEGF signaling is required for maintaining the homeostasis of vasculature. Dysregulation of angiogenesis is implicated in the development of many human cancers, especially in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a highly vascularized tumor. Meanwhile, antiangiogenesis has become a mainstay in the treatment of human cancers. In this study, we analyzed the functional roles of RKTG (Raf Kinase Trapping to Golgi), a negative regulator of mitogen-activated protein kinase (Raf/MEK/ERK) signaling, by sequestration of Raf kinase to the Golgi apparatus, in angiogenesis and ccRCC. Through a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments, we found that RKTG has a negative effect on cell proliferation, migration, sprouting and angiogenesis of endothelial cells. RKTG, by suppressing mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, negatively regulates the transactivation activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) by inhibiting formation of HIF-1α/p300 complex and suppressing VEGF transcription, thereby reducing hypoxia-induced VEGF production. The expression level of RKTG is significantly downregulated in clinical ccRCC tumor samples, with an inverse correlation with VEGF expression level. These results highlight the functional roles of RKTG and its regulated Raf/ERK/MEK signaling cascade in angiogenesis and autocrine VEGF signaling. In addition, this study indicates that RKTG is likely implicated in the development of ccRCC through its regulation on angiogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi A, Hood JD, Frausto R, Stupack DG, Cheresh DA . (2003). Role of Raf in vascular protection from distinct apoptotic stimuli. Science 301: 94–96.
Arany Z, Huang LE, Eckner R, Bhattacharya S, Jiang C, Goldberg MA et al. (1996). An essential role for p300/CBP in the cellular response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 12969–12973.
Dougher M, Terman BI . (1999). Autophosphorylation of KDR in the kinase domain is required for maximal VEGF-stimulated kinase activity and receptor internalization. Oncogene 18: 1619–1627.
Ema M, Hirota K, Mimura J, Abe H, Yodoi J, Sogawa K et al. (1999). Molecular mechanisms of transcription activation by HLF and HIF1alpha in response to hypoxia: their stabilization and redox signal-induced interaction with CBP/p300. EMBO J 18: 1905–1914.
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M et al.. (2007). Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356: 125–134.
Fan F, Feng L, He J, Wang X, Jiang X, Zhang Y et al. (2008). RKTG sequesters B-Raf to the Golgi apparatus and inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenicity of human malignant melanoma cells. Carcinogenesis 29: 1157–1163.
Feng L, Xie X, Ding Q, Luo X, He J, Fan F et al. (2007). Spatial regulation of Raf kinase signaling by RKTG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 14348–14353.
Ferrara N . (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25: 581–611.
Grugel S, Finkenzeller G, Weindel K, Barleon B, Marme D . (1995). Both v-Ha-Ras and v-Raf stimulate expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor in NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 270: 25915–25919.
Guo D, Jia Q, Song HY, Warren RS, Donner DB . (1995). Vascular endothelial cell growth factor promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of mediators of signal transduction that contain SH2 domains. Association with endothelial cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 270: 6729–6733.
Haas CS, Amin MA, Allen BB, Ruth JH, Haines III GK, Woods JM et al. (2006). Inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin-4 gene therapy in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54: 2402–2414.
Hur E, Chang KY, Lee E, Lee SK, Park H . (2001). Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor PD98059 blocks the trans-activation but not the stabilization or DNA binding ability of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol Pharmacol 59: 1216–1224.
Iliopoulos O, Kibel A, Gray S, Kaelin Jr WG . (1995). Tumour suppression by the human von Hippel–Lindau gene product. Nat Med 1: 822–826.
Iwai K, Yamanaka K, Kamura T, Minato N, Conaway RC, Conaway JW et al. (1999). Identification of the von Hippel–lindau tumor-suppressor protein as part of an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 12436–12441.
Kallio PJ, Okamoto K, O'Brien S, Carrero P, Makino Y, Tanaka H et al. (1998). Signal transduction in hypoxic cells: inducible nuclear translocation and recruitment of the CBP/p300 coactivator by the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. EMBO J 17: 6573–6586.
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC, Murdock J, Desai S et al. (2007). Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell 130: 691–703.
Levy AP, Levy NS, Wegner S, Goldberg MA . (1995). Transcriptional regulation of the rat vascular endothelial growth factor gene by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 270: 13333–13340.
Lisztwan J, Imbert G, Wirbelauer C, Gstaiger M, Krek W . (1999). The von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor protein is a component of an E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase activity. Genes Dev 13: 1822–1833.
Liu Y, Cox SR, Morita T, Kourembanas S . (1995). Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in endothelial cells. Identification of a 5′ enhancer. Circ Res 77: 638–643.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF et al. (2008). Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359: 378–390.
Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K . (2009). VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 154–165.
Luo X, Feng L, Jiang X, Xiao F, Wang Z, Feng GS et al. (2008). Characterization of the topology and functional domains of RKTG. Biochem J 414: 399–406.
Mack FA, Rathmell WK, Arsham AM, Gnarra J, Keith B, Simon MC . (2003). Loss of pVHL is sufficient to cause HIF dysregulation in primary cells but does not promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell 3: 75–88.
Matsumoto T, Bohman S, Dixelius J, Berge T, Dimberg A, Magnusson P et al. (2005). VEGF receptor-2 Y951 signaling and a role for the adapter molecule TSAd in tumor angiogenesis. EMBO J 24: 2342–2353.
Matsumoto T, Mugishima H . (2006). Signal transduction via vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors and their roles in atherogenesis. J Atheroscler Thromb 13: 130–135.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. (1999). The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399: 271–275.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O et al. (2007). Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356: 115–124.
Mukhopadhyay D, Tsiokas L, Zhou XM, Foster D, Brugge JS, Sukhatme VP . (1995). Hypoxic induction of human vascular endothelial growth factor expression through c-Src activation. Nature 375: 577–581.
Mylonis I, Chachami G, Samiotaki M, Panayotou G, Paraskeva E, Kalousi A et al. (2006). Identification of MAPK phosphorylation sites and their role in the localization and activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem 281: 33095–33106.
Sang N, Stiehl DP, Bohensky J, Leshchinsky I, Srinivas V, Caro J . (2003). MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300. J Biol Chem 278: 14013–14019.
Srivastava RK, Unterman TG, Shankar S . (2009). FOXO transcription factors and VEGF neutralizing antibody enhance antiangiogenic effects of resveratrol. Mol Cell Biochem 337: 201–212.
Tang N, Wang L, Esko J, Giordano FJ, Huang Y, Gerber HP et al. (2004). Loss of HIF-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 6: 485–495.
Wakioka T, Sasaki A, Kato R, Shouda T, Matsumoto A, Miyoshi K et al. (2001). Spred is a Sprouty-related suppressor of Ras signalling. Nature 412: 647–651.
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, Qi X, McAnally J, Hill JA et al. (2008). The endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesis. Dev Cell 15: 261–271.
Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T, Dumas J, Smith RA et al. (2006). Discovery and development of sorafenib: a multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 835–844.
Wu LW, Mayo LD, Dunbar JD, Kessler KM, Baerwald MR, Jaffe EA et al. (2000). Utilization of distinct signaling pathways by receptors for vascular endothelial cell growth factor and other mitogens in the induction of endothelial cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 275: 5096–5103.
Xia P, Aiello LP, Ishii H, Jiang ZY, Park DJ, Robinson GS et al. (1996). Characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor's effect on the activation of protein kinase C, its isoforms, and endothelial cell growth. J Clin Invest 98: 2018–2026.
Xie X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Liu W, Ma H, Wang Z et al. (2008). Suppressive function of RKTG on chemical carcinogen-induced skin carcinogenesis in mouse. Carcinogenesis 29: 1632–1638.
Yi T, Yi Z, Cho SG, Luo J, Pandey MK, Aggarwal BB et al. (2008). Gambogic acid inhibits angiogenesis and prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res 68: 1843–1850.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr George Simons and Dr Ilias Mylonis (University of Thessaly, Greece) for providing the plasmid of full-length HIF-1α fused to GST; Dr William E Carson III and Dr Gregory B Lesinski (Ohio State University, USA) for discussion about the CD31 immunohistochemistry experiment; Dr Young-Guen Kwon and Yong-Sun Maeng (Yonsei University, Korea) and Dr Morag Park and Caroline Saucier (McGill University Health Centre, Quebec, Canada) for discussion about the Matrigel plug assay experiment; Dr Luisa Iruela-Arispe and Dr Tom Chen (University of California, Los Angeles, USA) for providing the experimental protocols; and Dr Jurgen Seppen (Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, Netherlands) for discussion about the experiment with lentivirus. This work was supported by research grants from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Knowledge Innovation Program KSCX1-YW-02), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30830037) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2007CB947100 and 2006CB943900) to YC. This work was also supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2010CB529506) to ZW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., Qin, X. et al. RKTG inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing MAPK-mediated autocrine VEGF signaling and is downregulated in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 29, 5404–5415 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.270
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.270
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A protein with broad functions: damage-specific DNA-binding protein 2
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
-
C-terminal binding protein 2 promotes high-glucose-triggered cell proliferation, angiogenesis and cellular adhesion of human retinal endothelial cell line
International Ophthalmology (2022)
-
Myc-associated zinc-finger protein promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression through transcriptional activation of the MAP2K2-dependent ERK pathway
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Role of the Golgi Apparatus in the Blood-Brain Barrier: Golgi Protection May Be a Targeted Therapy for Neurological Diseases
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
PAQR3 plays a suppressive role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Tumor Biology (2016)