Abstract
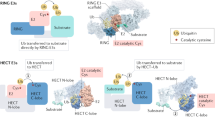
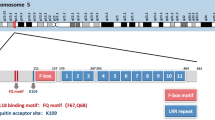
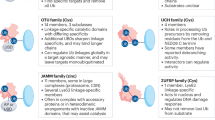
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is a multi-subunit pathway that allows for ubiquitin modification of proteins and leads to either degradation or other non-proteolytic processes such as trafficking or transcriptional activation. Given its role as a regulator of cellular homeostasis it is not surprising that members of the UPS are frequently aberrantly expressed in a number of disease states including cancer. This review will focus on one member of the UPS, the F-box protein, Fbw7 (also known as Sel-10, Ago, hCDC4) and mechanisms by which Fbw7 interacts with its substrates in the context of development and tumorigenesis will be discussed. In addition, antagonists of this pathway as well as current and future therapeutics for the UPS will be examined.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A et al. (2007). FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res 67: 9006–9012.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR . (2003). AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell 3: 51–62.
Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW et al. (1996). SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86: 263–274.
Barr AR, Gergely F . (2007). Aurora-A: the maker and breaker of spindle poles. J Cell Sci 120 (Part 17): 2987–2996.
Bassermann F, Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Busino L, Peschiaroli A, Pagano M . (2008). The Cdc14B-Cdh1-Plk1 axis controls the G2 DNA-damage-response checkpoint. Cell 134: 256–267.
Bechard M, Dalton S . (2009). Subcellular localization of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta controls embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Mol Cell Biol 29: 2092–2104.
Bhatia K, Huppi K, Spangler G, Siwarski D, Iyer R, Magrath I . (1993). Point mutations in the c-Myc transactivation domain are common in Burkitt's lymphoma and mouse plasmacytomas. Nat Genet 5: 56–61.
Cartwright P, McLean C, Sheppard A, Rivett D, Jones K, Dalton S . (2005). LIF/STAT3 controls ES cell self-renewal and pluripotency by a Myc-dependent mechanism. Development 132: 885–896.
Cohen P, Frame S . (2001). The renaissance of GSK3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 769–776.
Eischen CM, Weber JD, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Cleveland JL . (1999). Disruption of the ARF-Mdm2-p53 tumor suppressor pathway in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Genes Dev 13: 2658–2669.
Ferrando AA . (2009). The role of NOTCH1 signaling in T-ALL. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 353–361.
Finkin S, Aylon Y, Anzi S, Oren M, Shaulian E . (2008). Fbw7 regulates the activity of endoreduplication mediators and the p53 pathway to prevent drug-induced polyploidy. Oncogene 27: 4411–4421.
Fryer CJ, White JB, Jones KA . (2004). Mastermind recruits CycC:CDK8 to phosphorylate the Notch ICD and coordinate activation with turnover. Mol Cell 16: 509–520.
Ganem NJ, Godinho SA, Pellman D . (2009). A mechanism linking extra centrosomes to chromosomal instability. Nature 460: 278–282.
Gupta-Rossi N, Le Bail O, Gonen H, Brou C, Logeat F, Six E et al. (2001). Functional interaction between SEL-10, an F-box protein, and the nuclear form of activated Notch1 receptor. J Biol Chem 276: 34371–34378.
Hao B, Oehlmann S, Sowa ME, Harper JW, Pavletich NP . (2007). Structure of a Fbw7-Skp1-cyclin E complex: multisite-phosphorylated substrate recognition by SCF ubiquitin ligases. Mol Cell 26: 131–143.
Hartwell LH, Mortimer RK, Culotti J, Culotti M . (1973). Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast: V. Genetic analysis of cdc mutants. Genetics 74: 267–286.
Hemann MT, Bric A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Herbst A, Nilsson JA, Cordon-Cardo C et al. (2005). Evasion of the p53 tumour surveillance network by tumour-derived MYC mutants. Nature 436: 807–811.
Henriksson M, Bakardjiev A, Klein G, Luscher B . (1993). Phosphorylation sites mapping in the N-terminal domain of c-myc modulate its transforming potential. Oncogene 8: 3199–3209.
Hubbard EJ, Wu G, Kitajewski J, Greenwald I . (1997). sel-10, a negative regulator of lin-12 activity in Caenorhabditis elegans, encodes a member of the CDC4 family of proteins. Genes Dev 11: 3182–3193.
Ishikawa Y, Onoyama I, Nakayama KI, Nakayama K . (2008). Notch-dependent cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking Fbxw7. Oncogene 27: 6164–6174.
Kane RC, Bross PF, Farrell AT, Pazdur R . (2003). Velcade: U.S. FDA approval for the treatment of multiple myeloma progressing on prior therapy. Oncologist 8: 508–513.
Kane RC, Dagher R, Farrell A, Ko CW, Sridhara R, Justice R et al. (2007). Bortezomib for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 13: 5291–5294.
Kanei-Ishii C, Nomura T, Takagi T, Watanabe N, Nakayama KI, Ishii S . (2008). Fbxw7 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets c-Myb for nemo-like kinase (NLK)-induced degradation. J Biol Chem 283: 30540–30548.
Kitagawa K, Hiramatsu Y, Uchida C, Isobe T, Hattori T, Oda T et al. (2009). Fbw7 promotes ubiquitin-dependent degradation of c-Myb: involvement of GSK3-mediated phosphorylation of Thr-572 in mouse c-Myb. Oncogene 28: 2393–2405.
Koepp DM, Schaefer LK, Ye X, Keyomarsi K, Chu C, Harper JW et al. (2001). Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Science 294: 173–177.
Li J, Pauley AM, Myers RL, Shuang R, Brashler JR, Yan R et al. (2002). SEL-10 interacts with presenilin 1, facilitates its ubiquitination, and alters A-beta peptide production. J Neurochem 82: 1540–1548.
Loeb KR, Kostner H, Firpo E, Norwood T, K DT, Clurman BE et al. (2005). A mouse model for cyclin E-dependent genetic instability and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 8: 35–47.
Love KR, Catic A, Schlieker C, Ploegh HL . (2007). Mechanisms, biology and inhibitors of deubiquitinating enzymes. Nat Chem Biol 3: 697–705.
Lowe SW, Sherr CJ . (2003). Tumor suppression by Ink4a-Arf: progress and puzzles. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 77–83.
Lutterbach B, Hann SR . (1994). Hierarchical phosphorylation at N-terminal transformation-sensitive sites in c-Myc protein is regulated by mitogens and in mitosis. Mol Cell Biol 14: 5510–5522.
Mao JH, Kim IJ, Wu D, Climent J, Kang HC, DelRosario R et al. (2008). FBXW7 targets mTOR for degradation and cooperates with PTEN in tumor suppression. Science 321: 1499–1502.
Mao JH, Perez-Losada J, Wu D, Delrosario R, Tsunematsu R, Nakayama KI et al. (2004). Fbxw7/Cdc4 is a p53-dependent, haploinsufficient tumour suppressor gene. Nature 432: 775–779.
Maser RS, Choudhury B, Campbell PJ, Feng B, Wong KK, Protopopov A et al. (2007). Chromosomally unstable mouse tumours have genomic alterations similar to diverse human cancers. Nature 447: 966–971.
Masuda K, Ishikawa Y, Onoyama I, Unno M, de Alboran IM, Nakayama KI et al. (2010). Complex regulation of cell-cycle inhibitors by Fbxw7 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Oncogene 29: 1798–1809.
Matsuoka S, Oike Y, Onoyama I, Iwama A, Arai F, Takubo K et al. (2008). Fbxw7 acts as a critical fail-safe against premature loss of hematopoietic stem cells and development of T-ALL. Genes Dev 22: 986–991.
Minella AC, Swanger J, Bryant E, Welcker M, Hwang H, Clurman BE . (2002). p53 and p21 form an inducible barrier that protects cells against cyclin E-cdk2 deregulation. Curr Biol 12: 1817–1827.
Moberg KH, Bell DW, Wahrer DC, Haber DA, Hariharan IK . (2001). Archipelago regulates cyclin E levels in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Nature 413: 311–316.
Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H . (2007). Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science 315: 201–205.
O'Neil J, Grim J, Strack P, Rao S, Tibbitts D, Winter C et al. (2007). FBW7 mutations in leukemic cells mediate NOTCH pathway activation and resistance to gamma-secretase inhibitors. J Exp Med 204: 1813–1824.
Oberg C, Li J, Pauley A, Wolf E, Gurney M, Lendahl U . (2001). The Notch intracellular domain is ubiquitinated and negatively regulated by the mammalian Sel-10 homolog. J Biol Chem 276: 35847–35853.
Oh IH, Reddy EP . (1999). The myb gene family in cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Oncogene 18: 3017–3033.
Onoyama I, Tsunematsu R, Matsumoto A, Kimura T, de Alboran IM, Nakayama K et al. (2007). Conditional inactivation of Fbxw7 impairs cell-cycle exit during T cell differentiation and results in lymphomatogenesis. J Exp Med 204: 2875–2888.
Palomero T, Odom DT, O'Neil J, Ferrando AA, Margolin A, Neuberg DS et al. (2006). Transcriptional regulatory networks downstream of TAL1/SCL in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 108: 986–992.
Petroski MD . (2008). The ubiquitin system, disease, and drug discovery. BMC Biochem 9 (Suppl 1): S7.
Pickart CM, Eddins MJ . (2004). Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695: 55–72.
Popov N, Herold S, Llamazares M, Schulein C, Eilers M . (2007a). Fbw7 and Usp28 regulate myc protein stability in response to DNA damage. Cell Cycle 6: 2327–2331.
Popov N, Wanzel M, Madiredjo M, Zhang D, Beijersbergen R, Bernards R et al. (2007b). The ubiquitin-specific protease USP28 is required for MYC stability. Nat Cell Biol 9: 765–774.
Pui JC, Allman D, Xu L, DeRocco S, Karnell FG, Bakkour S et al. (1999). Notch1 expression in early lymphopoiesis influences B versus T lineage determination. Immunity 11: 299–308.
Rajagopalan H, Jallepalli PV, Rago C, Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B et al. (2004). Inactivation of hCDC4 can cause chromosomal instability. Nature 428: 77–81.
Reavie L, Gatta GD, Crusio K, Aranda-Orgilles B, Buckley SM, Thompson B et al. (2010). Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation by a single ubiquitin ligase-substrate complex. Nat Immunol 11: 207–215.
Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A . (2009). Targeting proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49: 73–96.
Schwickart M, Huang X, Lill JR, Liu J, Ferrando R, French DM et al. (2010). Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 463: 103–107.
Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, Nevins JR . (2000). Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev 14: 2501–2514.
Siegert W, Beutler C, Langmach K, Keitel C, Schmidt CA . (1990). Differential expression of the oncoproteins c-myc and c-myb in human lymphoproliferative disorders. Eur J Cancer 26: 733–737.
Skaar JR, Pagano M . (2009). Control of cell growth by the SCF and APC/C ubiquitin ligases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 816–824.
Slamon DJ, Boone TC, Murdock DC, Keith DE, Press MF, Larson RA et al. (1986). Studies of the human c-myb gene and its product in human acute leukemias. Science 233: 347–351.
Smith AP, Henze M, Lee JA, Osborn KG, Keck JM, Tedesco D et al. (2006). Deregulated cyclin E promotes p53 loss of heterozygosity and tumorigenesis in the mouse mammary gland. Oncogene 25: 7245–7259.
Song L, Rape M . (2008). Reverse the curse—the role of deubiquitination in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20: 156–163.
Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Berger AJ, Gavin JM, Adhikari S et al. (2009). An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature 458: 732–736.
Spruck CH, Strohmaier H, Sangfelt O, Muller HM, Hubalek M, Muller-Holzner E et al. (2002). hCDC4 gene mutations in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res 62: 4535–4539.
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI . (1999). Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature 401: 297–300.
Strohmaier H, Spruck CH, Kaiser P, Won KA, Sangfelt O, Reed SI . (2001). Human F-box protein hCdc4 targets cyclin E for proteolysis and is mutated in a breast cancer cell line. Nature 413: 316–322.
Sundqvist A, Bengoechea-Alonso MT, Ye X, Lukiyanchuk V, Jin J, Harper JW et al. (2005). Control of lipid metabolism by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the SREBP family of transcription factors by SCF(Fbw7). Cell Metab 1: 379–391.
Tan Y, Sangfelt O, Spruck C . (2008). The Fbxw7/hCdc4 tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Lett 271: 1–12.
Tetzlaff MT, Yu W, Li M, Zhang P, Finegold M, Mahon K et al. (2004). Defective cardiovascular development and elevated cyclin E and Notch proteins in mice lacking the Fbw7 F-box protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 3338–3345.
Thompson BJ, Buonamici S, Sulis ML, Palomero T, Vilimas T, Basso G et al. (2007). The SCFFBW7 ubiquitin ligase complex as a tumor suppressor in T cell leukemia. J Exp Med 204: 1825–1835.
Thompson BJ, Jankovic V, Gao J, Buonamici S, Vest A, Lee JM et al. (2008). Control of hematopoietic stem cell quiescence by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Fbw7. J Exp Med 205: 1395–1408.
Tsunematsu R, Nakayama K, Oike Y, Nishiyama M, Ishida N, Hatakeyama S et al. (2004). Mouse Fbw7/Sel-10/Cdc4 is required for notch degradation during vascular development. J Biol Chem 279: 9417–9423.
Wei W, Jin J, Schlisio S, Harper JW, Kaelin Jr WG . (2005). The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Cancer Cell 8: 25–33.
Weissman AM . (2001). Themes and variations on ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 169–178.
Welcker M, Clurman BE . (2007). Fbw7/hCDC4 dimerization regulates its substrate interactions. Cell Div 2: 7.
Welcker M, Clurman BE . (2008). FBW7 ubiquitin ligase: a tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division, growth and differentiation. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 83–93.
Welcker M, Orian A, Grim JE, Eisenman RN, Clurman BE . (2004a). A nucleolar isoform of the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase regulates c-Myc and cell size. Curr Biol 14: 1852–1857.
Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper JW, Eisenman RN et al. (2004b). The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9085–9090.
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris IV JP, Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C et al. (2004). Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science 306: 269–271.
Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H et al. (2004). Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. Embo J 23: 2116–2125.
Yano T, Sander CA, Clark HM, Dolezal MV, Jaffe ES, Raffeld M . (1993). Clustered mutations in the second exon of the MYC gene in sporadic Burkitt′s lymphoma. Oncogene 8: 2741–2748.
Zhang D, Zaugg K, Mak TW, Elledge SJ . (2006). A role for the deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in control of the DNA-damage response. Cell 126: 529–542.
Zhou H, Kuang J, Zhong L, Kuo WL, Gray JW, Sahin A et al. (1998). Tumour amplified kinase STK15/BTAK induces centrosome amplification, aneuploidy and transformation. Nat Genet 20: 189–193.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Aifantis Lab for advice and illuminating discussions. Supported by the National Institutes of Health (RO1CA133379, RO1CA105129, R21CA141399, RO1CA149655 and P30CA016087), the American Cancer Society (RSG0806801), the Edward Mallinckrodt Jr Foundation, the Irma T Hirschl Trust, the Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation (all to IA), NYU Molecular Oncology and Immunology/Ruth L Kirchstein Institutional Training Grant (5T32CA009161 to KC), NYU Cell and Molecular Biology/Ruth L Kirchstein Institutional Traning Grant (BK). IA is a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar and an Early Career Scientist at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crusio, K., King, B., Reavie, L. et al. The ubiquitous nature of cancer: the role of the SCFFbw7 complex in development and transformation. Oncogene 29, 4865–4873 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.222
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.222
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The tumor suppressor archipelago E3 ligase is required for spermatid differentiation in Drosophila testis
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Downregulation of specific FBXW7 isoforms with differential effects in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma
Oncogene (2019)
-
FBXL14 abolishes breast cancer progression by targeting CDCP1 for proteasomal degradation
Oncogene (2018)
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen induces genome instability by E3 ubiquitin ligase targeting
Oncogene (2017)
-
The role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in cerebellar development and medulloblastoma
Molecular Brain (2015)