Abstract
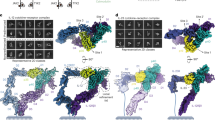
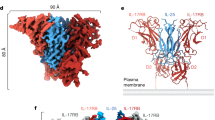
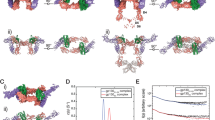
Interleukin-1 (IL-1)-family cytokines are mediators of innate and adaptive immunity. They exert proinflammatory effects by binding a primary receptor that recruits a receptor accessory protein to form a signaling-competent heterotrimeric complex. Here we present the crystal structure of IL-1β bound to its primary receptor IL-1RI and its receptor accessory protein IL-1RAcP, providing insight into how IL-1–type cytokines initiate signaling and revealing an evolutionary relationship with the fibroblast growth factor receptor family.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sims, J.E. & Smith, D.E. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10, 89–102 (2010).
Arend, W.P., Palmer, G. & Gabay, C. Immunol. Rev. 223, 20–38 (2008).
Wang, D. et al. Nat. Immunol. 11, 905–911 (2010).
Vigers, G.P., Anderson, L.J., Caffes, P. & Brandhuber, B.J. Nature 386, 190–194 (1997).
Murzin, A.G., Lesk, A.M. & Chothia, C. J. Mol. Biol. 223, 531–543 (1992).
Schreuder, H. et al. Nature 386, 194–200 (1997).
Venkataraman, G., Raman, R., Sasisekharan, V. & Sasisekharan, R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 3658–3663 (1999).
Schlessinger, J. et al. Mol. Cell 6, 743–750 (2000).
Casadio, R. et al. FEBS Lett. 499, 65–68 (2001).
Kiselyov, V.V., Kochoyan, A., Poulsen, F.M., Bock, E. & Berezin, V. Protein Sci. 15, 2318–2322 (2006).
Kalinina, J. et al. Structure 20, 77–88 (2012).
Wass, M.N., David, A. & Sternberg, M.J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 21, 382–390 (2011).
Ehrlich, M., Horbelt, D., Marom, B., Knaus, P. & Henis, Y.I. Cell. Signal. 23, 1424–1432 (2011).
Wang, X., Lupardus, P., Laporte, S.L. & Garcia, K.C. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 29–60 (2009).
Thomas, C. et al. Cell 146, 621–632 (2011).
Chen, H. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19660–19665 (2008).
Nyman, T. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 11861–11865 (2008).
Ely, L.K., Fischer, S. & Garcia, K.C. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1245–1251 (2009).
Dinarello, C. et al. Nat. Immunol. 11, 973 (2010).
Boraschi, D. & Tagliabue, A. Vitam. Horm. 74, 229–254 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at the Advanced Light Source for their assistance. K.C.G. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and is supported by NIH grant R01-AI51321. C.T. was supported by a long-term postdoctoral fellowship from the International Human Frontier Science Program Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.C.G. conceived of the project, supervised the experiments and participated in writing the manuscript; J.F.B. contributed insights into the evolutionary relationships of the IL-1R activating complex to other receptors; C.T. executed the study and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Discussion and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1000 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, C., Bazan, J. & Garcia, K. Structure of the activating IL-1 receptor signaling complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 455–457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2260
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2260
This article is cited by
-
Bio-guided isolation of potential anti-inflammatory constituents of some endophytes isolated from the leaves of ground cherry (Physalis pruinosa L.) via ex-vivo and in-silico studies
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2023)
-
Discovery of a selective and biologically active low-molecular weight antagonist of human interleukin-1β
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Optimization of IL-1RA structure to achieve a smaller protein with a higher affinity to its receptor
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Comparative Analyses of the Conformational Dynamics Between the Soluble and Membrane-Bound Cytokine Receptors
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Specific targeting of IL-1β activity to CD8+ T cells allows for safe use as a vaccine adjuvant
npj Vaccines (2020)