Abstract
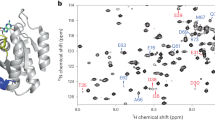
The reliable prediction of the precise three-dimensional structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence is a major, still unresolved problem in biochemistry. Pressure is a parameter that controls folding/unfolding transitions of proteins through the volume change ΔV of the protein-solvent system. By varying the pressure from 30 to 2,000 bar we detected using 15N/1H 2D NMR spectroscopy a unique equilibrium unfolding intermediate I in the Ras binding domain of the Ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator (Ral GDS). It is characterized by a local melting of specific structural elements near hydrophobic cavities while the overall folded structure is maintained.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morishima, I. In Current perspectives in high pressure biology. (ed. Jannasch, H.W.) 315–332 (Academic Press, San Diego, Calfornia; 1987).
Samarasinghe, S.D., Campbell, D.M., Jonas, A. & Jonas, J. Biochemistry 31, 7773–7778 (1992).
Vidugiris, G.J.A., Truckses, D.M., Markley J.L. & Royer, C.A. Biochemistry 35, 3857–3864 (1996).
Jonas, J., Ballard, L. & Nash, D. Biophys. J. 75, 445– 452 (1998).
Yamada, H. NMR Basic Principles Progress 24, 232– 263 (1990).
Akasaka, K. Tezuka, T. & Yamada, H. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 671– 678 (1997).
Li, H., Yamada, H. & Akasaka, K. Biochemistry 5, 1167– 1173 (1998).
Inoue, K., Yamada, H., Imoto, T. & Akasaka, K. J. Biomol. NMR 12, 535–541 ( 1998).
Akasaka, K. et al. Protein Sci. 8, 1946– 1953 (1999).
Li, H., Yamada, H. & Akasaka, K. Biophys. J. 77, 2801– 2812 (1999).
Herrmann, C., Horn, G., Spaargaren, M. & Wittinghofer, A. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6794–6800 ( 1996).
Geyer, M., Herrmann, C., Wohlgemuth, S., Wittinghofer, A. & Kalbitzer, H.R. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 694–699 (1997).
Huang, L., Weng, X., Hofer, F., Martin, G.S. & Kim, S.-H. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 609– 615 (1997).
Schleucher, J. et al. J. Biomol. NMR 4, 301– 306 (1994).
Wishart, D.S., Bigam, C.G., Holm, A., Hodges, R.S. & Sykes, B.D. J. Biomol. NMR 5, 67– 81 (1995).
Zhang, O., Kay, L.E., Olivier, J.P. & Forman Kay, J.D. J. Biomol. NMR 4, 845–858 ( 1994).
IAPWS Release on the Skeleton Tables 1985 for the Thermodynamic Properties of Ordinary Water Substance (The International Association for the Prperties of Water and Steam, Palo Alto; 1985)
Fuentes, E.J. and Wand, A.J. Biochemistry 37, 9877–9883 (1998).
Makhatadze, G.I. & Privalov, P.L. Biophys. Chem. 51, 291–425 ( 1995).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Proteins 11, 281– 296 (1991).
Kauzmann, W. Adv. Protein Chem. 14, 1–63 (1959).
Weber, G. & Drickamer, H.G. Q. Rev. Biophys. 16, 89–112 (1983).
Frye, K.J. & Royer, C.A. Protein Sci. 7, 2217–2222 (1998).
Hummer, G., Garde, S., Garcia, A.E., Paulaitis, M.E. & Pratt, L.R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 1552–1555 (1998).
States, D.J., Haberkorn, R.A. & Ruben, D.J. J. Magn. Reson. 48, 286– 292 (1982).
Piotto, M., Saudek, V. & Sklenar, V. J. Biomol. NMR 2, 661– 666 (1992).
Sklenar, V. Piotto, M., Leppik, R. & Saudek, V. J. Magn. Reson. A 102, 241–245 ( 1993).
Wishart, D.S. et al. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 135– 140 (1995).
Farrow, N.A. et al. Biochemistry 33, 5948 ( 1994).
Delaglio, F. et al. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 277– 293 (1995).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the European Union, the Humboldt foundation and the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. We thank R. Jaenicke and A. Wittinghofer for helpful discussions, and M. Geyer for aid with the sample preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, K., Yamada, H., Akasaka, K. et al. Pressure-induced local unfolding of the Ras binding domain of RalGDS . Nat Struct Mol Biol 7, 547–550 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/76764
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/76764
This article is cited by
-
Monitoring protein unfolding transitions by NMR-spectroscopy
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2022)
-
Pressure accelerates the circadian clock of cyanobacteria
Scientific Reports (2019)