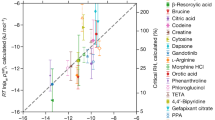
Abstract
Recognition of the limitations of high-throughput screening approaches in the discovery of candidate drugs has reawakened interest in structure-based and other rational design methods. Here, we describe how isothermal titration calorimetry can be used to obtain thermodynamic data on the binding of compounds to protein targets. We propose that these data — particularly the change in enthalpy — could provide a valuable, complementary addition to established tools for selecting compounds in lead discovery and for aiding lead optimization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ladbury, J. E. Counting the calories to stay in the groove. Structure 3, 635–639 (1995).
Ladbury, J. E. & Chowdhry, B. Z. Sensing the heat: the application of isothermal titration calorimetry to thermodynamic studies of biomolecular interactions. Chem. Biol. 3, 791–801 (1996).
Ladbury, J. E. Isothermal titration calorimetry: application to structure-based drug design. Thermochim. Acta 380, 209–215 (2001).
Velazquez-Campoy, A. & Freire, E. ITC in the post-genomic era...? Priceless. Biophys. Chem. 115, 115–124 (2005).
Freire, E. in Proteomics and Protein–Protein Interactions: Biology, Chemistry, Bioinformatics, and Drug Design. Vol. 3 (ed. Waksman, G.) 291–307 (Springer, New York, 2005).
Ohtaka, H. & Freire, E. Adaptive inhibitors of the HIV-1 protease. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 88, 193–208 (2005).
Spolar, R. & Record, M. T. Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science 263, 777–784 (1994).
Robertson, A. D. & Murphy, K. P. Protein structure and the energetics of protein stability. Chem. Rev. 97, 1251–1267 (1997).
Luque, I. & Freire, E. Structural parameterization of the binding enthalpy of small ligands. Proteins 49, 181–190 (2002).
Hilser, V. J., Gomez, J. & Freire, E. The enthalpy change in protein folding and binding. Refinement of parameters for structure based calculations. Proteins 26, 123–133 (1996).
Olsson, T. S. G., Williams, M. A., Pitt, W. R. & Ladbury, J. E. The thermodynamics of protein-ligand interaction and solvation: insights for ligand design. J. Mol. Biol. 384, 1002–1017 (2008).
Freire, E. Do enthalpy and entropy distinguish first in class from best in class? Drug Discov. Today 13, 869–874 (2008).
Davies, A. M., Teague, S. J. & Kleywegt, G. J. Application and limitations of X-ray crystallographic data in structure-based ligand and drug design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 2718–2736 (2003).
Lafont, V. et al. Compensating enthalpic and entropic changes hinder binding affinity optimization. Chem. Biol. Drug. Design 69, 413–422 (2007).
Ruben, A. J., Kiso, Y. & Freire, E. Overcoming roadblocks in lead optimization: a thermodynamic perspective. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 67, 2–4 (2006).
Hopkins, A. L., Groom, C. R. & Alex, A. Ligand efficiency: a useful metric for lead selection. Drug Discov. Today 9, 430–431 (2004).
Rees, D. C. Congreve, M., Murray, C. W. & Carr, R. Fragment-based lead discovery. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 660–672 (2004).
Abad-Zapatero, C. & Metz, J. T. Ligand efficiency indices as guideposts for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 10, 464–469 (2005).
Lipinski, C. A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 44, 235–249 (2000).
Ladbury, J. E. Enthalpic efficiency and the role of thermodynamic data in drug development: possibility or a pipeline dream. Euro. Pharmaceut. Rev. 12, 59–62 (2007).
Hahn, M. M., Leach, A. R. & Harper, G. Molecular complexity and its impact on the probability of finding leads for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 41, 856–864 (2001).
Rees, D. C., Congreve, M., Murray, C. W. & Carr, R. Fragment-based lead discovery. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 660–672 (2004).
Shuker, S. B., Hajduk, P. J., Meadows, R. P. & Fesik, S. W. Discovering high-affinity ligands for proteins: SAR by NMR. Science 274, 1531–1534 (1996).
Hartshorn, M. J. et al. Fragment-based lead discovery using X-ray crystallography. J. Med. Chem. 48, 403–413 (2005).
Taylor, J. D., Gilbert, P. J., Williams, M. A., Pitt, W. R. & Ladbury, J. E. Identification of novel fragment compounds targeted against the pY pocket of v-Src SH2 by computational and NMR screening and thermodynamic evaluation. Proteins 67, 981–990 (2007).
Ladbury, J. E. Just add water: the effect of water on the specificity of protein-ligand binding sites with applications to drug design. Chem. Biol. 3, 973–980 (1996).
Steuber, H., Heine, A. & Klebe, G. Structural and thermodynamic study on aldose reductase: nitro-substituted inhibitors with strong enthalpic binding contribution. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 618–638 (2007).
Baker, B. & Murphy, K. P. Evaluation of linked protonation effects in protein binding reactions using isothermal titration calorimetry. Biophys. J. 71, 2049–2055 (1996).
Czodrowski, P., Sotriffer, C. A. & Klebe, G. Protonation changes upon ligand binding to trypsin and thrombin: structural interpretation based on pKa calculations and ITC experiments. J. Mol. Biol. 367, 1347–1356 (2007).
Dullweber, F., Stubbs, M. T., Stürzebecher, J., Musil, D. & Klebe, G. Factorising ligand affinity: a combined thermodynamic and crystallographic study of trypsin and thrombin inhibition. J. Mol. Biol. 313, 593–614 (2001).
Gerlach, C. et al. Thermodynamic inhibition profile of a cyclopentyl- and a cyclohexyl derivative towards thrombin: the same, but for deviating reasons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 8511–8514 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladbury, J., Klebe, G. & Freire, E. Adding calorimetric data to decision making in lead discovery: a hot tip. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9, 23–27 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3054
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3054
This article is cited by
-
A miniaturized mode-of-action profiling platform enables high throughput characterization of the molecular and cellular dynamics of EZH2 inhibition
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Isothermal titration calorimetry
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2023)
-
Physical–chemical and antimicrobial activity of sulfadiazine sodium salt with β-cyclodextrin supramolecular systems
Chemical Papers (2021)
-
Uncertainty in protein–ligand binding constants: asymmetric confidence intervals versus standard errors
European Biophysics Journal (2021)
-
Theory and applications of differential scanning fluorimetry in early-stage drug discovery
Biophysical Reviews (2020)