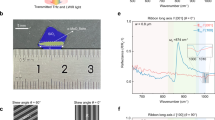
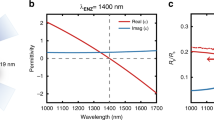
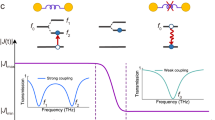
Abstract
Over the past two decades, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy1 and quantum-cascade lasers2 have been two of the most important developments in terahertz science and technology. These technologies may contribute to a multitude of terahertz applications that are currently under investigation globally3. However, the devices and components necessary to effectively manipulate terahertz radiation require substantial development beyond what has been accomplished to date. Here we demonstrate an electrically controlled planar hybrid metamaterial device that linearly controls the phase of terahertz radiation with constant insertion loss over a narrow frequency band. Alternatively, our device may operate as a broadband terahertz modulator because of the causal relation between the amplitude modulation and phase shifting. We perform terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, in which our hybrid metamaterial modulator replaces a commercial mechanical optical chopper, demonstrating comparable broadband performance and superior high-speed operation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grischkowsky, D., Keiding, S., van Exter, M. & Fattinger, Ch. Far-infrared time-domain spectroscopy with terahertz beams of dielectrics and semiconductors. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 7, 2006–2015 (1990).
Köhler, R. et al. Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure lasers. Nature 417, 156–159 (2002).
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
Smith, D. R., Pendry, J. B. & Wiltshire, M. C. K. Metamaterials and negative refractive index. Science 305, 788–792 (2004).
Veselago, V. G. The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of ɛ and μ. Sov. Phys. Usp. 10, 509–514 (1968).
Shelby, R. A., Smith, D. R. & Schultz, S. Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction. Science 292, 77–79 (2001).
Pendry, J. B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3966–3969 (2000).
Fang, N., Lee, H., Sun, C. & Zhang, X. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308, 534–537 (2005).
Schurig, D. et al. Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 314, 977–980 (2006).
Yen, T. J. et al. Terahertz magnetic response from artificial materials. Science 303, 1494–1496 (2004).
Azad, A. K., Dai, J. & Zhang, W. Transmission properties of terahertz pulses through subwavelength double split-ring resonators. Opt. Lett. 31, 634–636 (2006).
Chen, H.-T. et al. Complementary planar terahertz metamaterials. Opt. Express 15, 1084–1095 (2007).
Chen, H.-T. et al. Experimental demonstration of frequency-agile terahertz metamaterials. Nature Photon. 2, 295–298 (2008).
Padilla, W. J., Taylor, A. J., Highstrete, C., Lee, M. & Averitt, R. D. Dynamical electric and magnetic metamaterial response at terahertz frequencies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 107401 (2006).
Chen, H.-T. et al. Ultrafast optical switching of terahertz metamaterials fabricated on ErAs/GaAs nanoisland superlattices. Opt. Lett. 32, 1620–1622 (2007).
Landy, N. I., Sajuyigbe, S., Mock, J. J., Smith, D. R. & Padilla, W. J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402 (2008).
Tao, H. et al. A metamaterial absorber for the terahertz regime: Design, fabrication and characterization. Opt. Express 16, 7181–7188 (2008).
Chen, H.-T. et al. Active terahertz metamaterial devices. Nature 444, 597–600 (2006).
Chen, H.-T. et al. Hybrid metamaterials enable fast electrical modulation of freely propagating terahertz waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 091117 (2008).
Libon, I. H. et al. An optically controllable terahertz filter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2821–2823 (2000).
Kersting, R., Strasser, G. & Unterrainer, K. Terahertz phase modulator. Electron. Lett. 36, 1156–1158 (2000).
Hsieh, C.-F., Pan, R.-P., Tang, T.-T., Chen, H.-L. & Pan, C.-L. Voltage-controlled liquid-crystal terahertz phase shifter and quarter-wave plate. Opt. Lett. 31, 1112–1114 (2006).
Padilla, W. J. et al. Electrically resonant terahertz metamaterials: Theoretical and experimental investigations. Phys. Rev. B 75, 041102(R) (2007).
O'Hara, J. F., Zide, J. M. O., Gossard, A. C., Taylor, A. J. & Averitt, R. D. Enhanced terahertz detection via ErAs:GaAs nanoisland superlattices, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 251119 (2006).
Acuna, G. et al. Surface plasmons in terahertz metamaterials. Opt. Express 16, 18745–18751 (2008).
Lee, J. W. et al. Invisible plasmonic meta-materials through impedance matching to vacuum. Opt. Express 13, 10681–10687 (2005).
Zhao, G., Schouten, R. N., van der Valk, N., Wenckebach, W. Th. & Planken, P. C. M. Design and performance of a THz emission and detection setup based on a semi-insulating GaAs emitter. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 1715–1719 (2002).
Cai, Y. et al. Coherent terahertz radiation detection: Direct comparison between free-space electro-optic sampling and antenna detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 444–446 (1998).
Jackson, J. D. Classical Electrodynamics 3rd edn (John Wiley & Sons, 1998).
Azad, A. K., Taylor, A. J., Smirnova, E. & O'Hara, J. F. Characterization and analysis of terahertz metamaterials based on rectangular split-ring resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 011119 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Brener for coordinating the sample fabrication, J.F. O'Hara for discussions and the use of the terahertz system, and D. Lippens for useful discussions. We acknowledge support from the Los Alamos National Laboratory LDRD Program. This work was performed, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences Nanoscale Science Research Center operated jointly by Los Alamos and Sandia National Laboratories. Los Alamos National Laboratory, an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, for the National Nuclear Security Administration of the US Department of Energy under contract DE-AC52-06NA25396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HT., Padilla, W., Cich, M. et al. A metamaterial solid-state terahertz phase modulator. Nature Photon 3, 148–151 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.3
This article is cited by
-
Active terahertz beam steering based on mechanical deformation of liquid crystal elastomer metasurface
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
A wide angle polarization insensitive multi-band metamaterial absorber for L, C, S and X band applications
Multimedia Tools and Applications (2023)
-
Terahertz wavefront engineering using a hard-coded metasurface
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Superimposed multilayer randomly distributed graphene quantum dots and broadband terahertz perfect absorber
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Terahertz Beam Steering: from Fundamentals to Applications
Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (2023)